Access To Birth Control: Examining The Post-Roe OTC Landscape
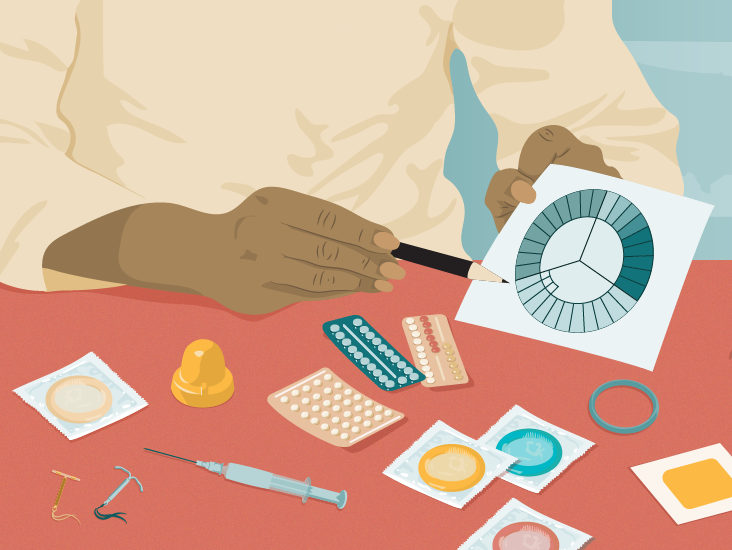

Table of Contents
The Current State of OTC Birth Control
The legal landscape surrounding OTC birth control access in the US remains complex and varies significantly by state. While the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates the approval and safety of all birth control methods, the availability of specific types without a prescription differs considerably. This patchwork of regulations creates significant challenges in guaranteeing consistent access to essential reproductive healthcare.
-
Currently Available OTC: Currently, the most readily available OTC birth control is emergency contraception, such as Plan B. Some states also allow for the sale of certain lower-dose birth control pills over the counter, depending on age and state-specific regulations. However, access to other forms of birth control, such as IUDs or hormonal implants, still generally requires a prescription from a healthcare provider.
-
Legislative Efforts: Several states are actively working on legislation to expand access to OTC birth control, aiming to remove prescription requirements for a wider range of contraceptive options. However, these efforts face considerable political opposition, highlighting the ongoing battle over reproductive rights.
-
Barriers to Access: Even with OTC options available, significant barriers to access persist. Cost remains a major impediment for many, particularly those lacking health insurance or facing financial hardship. Geographical location also plays a role, as access to pharmacies offering OTC birth control can be limited in rural areas or underserved communities. Furthermore, lack of awareness regarding available options and their correct usage contributes to low uptake.
The Role of the FDA in Regulating OTC Birth Control
The FDA plays a crucial role in determining which birth control methods can be sold OTC. The process for drug manufacturers seeking OTC status for their products involves rigorous scientific review, ensuring both safety and efficacy. This review includes extensive clinical trials to assess the risks and benefits of over-the-counter use.
The FDA considers several factors, including:
- The safety profile of the drug: Is it safe for individuals to self-administer without direct medical supervision?
- The potential for misuse or abuse: Could easy access lead to harmful self-medication practices?
- The effectiveness of the drug when used without a prescription: Can individuals correctly follow instructions and achieve the desired outcome?
Potential challenges and concerns surrounding broader OTC access include ensuring appropriate patient education materials accompany OTC products and addressing potential increases in unintended pregnancies if usage instructions are not properly followed.
Impact on Women's Health and Reproductive Rights
Access to birth control has a profound impact on women's health and reproductive rights. Increased access to various forms of birth control leads to:
- Reduced unintended pregnancies: Providing easier access to effective contraception significantly decreases unintended pregnancies, thereby reducing the need for abortions and improving maternal health outcomes.
- Lower abortion rates: Studies have shown a clear correlation between increased contraceptive access and decreased abortion rates.
- Improved maternal mortality rates: Reducing unintended pregnancies through improved birth control access contributes to lower maternal mortality rates, as many pregnancy-related deaths are linked to unintended or high-risk pregnancies.
- Exacerbated health disparities: Existing socioeconomic, racial, and geographic disparities significantly impact access to birth control, creating unequal outcomes for different population groups. Women in underserved communities often face significantly greater barriers to access.
Restricting access to birth control undermines women's reproductive autonomy and limits their ability to make informed choices about their bodies and their futures.
Addressing Barriers to Access: Cost, Education, and Equity
Addressing the significant barriers to birth control access requires a multifaceted approach:
-
Cost: Implementing affordable insurance coverage, government subsidies, or manufacturer discounts can make birth control more accessible to low-income individuals. Negotiating lower prices with pharmaceutical companies could also have a significant impact.
-
Education: Comprehensive sex education in schools and communities is crucial to promote informed decision-making and responsible birth control use. Education should include information about the various methods available, their effectiveness, and potential side effects.
-
Equity: Targeted programs and initiatives should address the disproportionate impact of limited access on marginalized communities. This includes addressing systemic inequalities and ensuring equitable distribution of resources to underserved areas.
Strategies to improve equity and accessibility include community-based outreach programs, mobile health clinics providing access to contraception, and partnerships between healthcare providers and community organizations.
Looking Ahead: Future Trends and Policy Implications
The future of birth control access will be shaped by ongoing policy changes, technological advancements, and public health priorities.
-
Future Legislative Actions: Further legislative battles regarding OTC birth control are expected, with potential for both expansion and restriction depending on political landscapes in different states.
-
Telehealth's Impact: The growing use of telehealth holds promise for expanding access to birth control, particularly for individuals in rural or underserved areas. Online consultations and virtual prescriptions could significantly improve access.
-
Research and Development: Ongoing research and development in birth control technologies aim to create more effective, long-acting, and user-friendly methods.
-
Long-Term Effects: Continued research is needed to fully understand the long-term public health effects of improved or diminished access to birth control.
The debate surrounding access to birth control will undoubtedly continue. The post-Roe landscape demands a renewed focus on ensuring equitable access to safe and effective contraception for all women.
Conclusion
Access to birth control is a critical component of women's health and reproductive freedom. The post-Roe landscape underscores the urgent need to address the significant barriers hindering equitable access, including cost, lack of education, and systemic inequities. We must advocate for policies that promote informed choices and guarantee access to a full range of contraceptive options for all individuals, regardless of their socioeconomic status, race, or geographic location. Continue the conversation about expanding access to over-the-counter birth control and the vital role it plays in ensuring women's health and reproductive freedom. Learn more about how you can support initiatives aimed at improving access to birth control in your community and advocate for policies that prioritize reproductive healthcare for all.

Featured Posts
-
 Washington Dc Power List 2025 Top 500 Influencers
May 12, 2025
Washington Dc Power List 2025 Top 500 Influencers
May 12, 2025 -
 Jose Aldo Un Modele D Adaptation Et De Determination
May 12, 2025
Jose Aldo Un Modele D Adaptation Et De Determination
May 12, 2025 -
 Stricter Border Controls Result In Fewer Arrests And Increased Turnbacks
May 12, 2025
Stricter Border Controls Result In Fewer Arrests And Increased Turnbacks
May 12, 2025 -
 Celtics Game 1 Win How Payton Pritchard Made A Difference
May 12, 2025
Celtics Game 1 Win How Payton Pritchard Made A Difference
May 12, 2025 -
 The Truth About Henry Cavills Superman Departure James Gunns Account Of Past Dc Decisions
May 12, 2025
The Truth About Henry Cavills Superman Departure James Gunns Account Of Past Dc Decisions
May 12, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 The Kyle Tucker Report And Its Impact On Cubs Fans
May 13, 2025
The Kyle Tucker Report And Its Impact On Cubs Fans
May 13, 2025 -
 Cubs Game 25 2025 Heroes And Goats Of The Match
May 13, 2025
Cubs Game 25 2025 Heroes And Goats Of The Match
May 13, 2025 -
 2025 Cubs Heroes And Goats Game 25 Recap
May 13, 2025
2025 Cubs Heroes And Goats Game 25 Recap
May 13, 2025 -
 Negative Cubs Fan Reaction To Kyle Tucker Report
May 13, 2025
Negative Cubs Fan Reaction To Kyle Tucker Report
May 13, 2025 -
 Dissecting The 2025 Cubs Game 16 A Performance Breakdown
May 13, 2025
Dissecting The 2025 Cubs Game 16 A Performance Breakdown
May 13, 2025
