Addressing The Rising Number Of Wolf Incidents In The North State
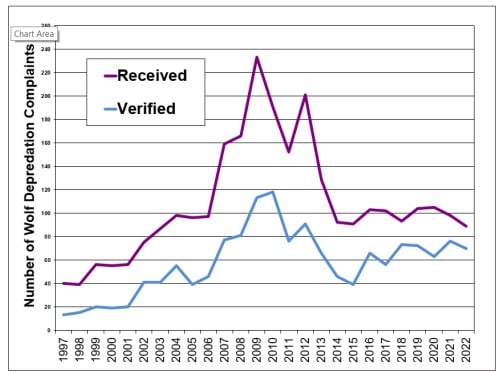
Table of Contents
Understanding the Increase in Wolf Sightings and Conflicts
The rise in reported wolf incidents North State stems from a confluence of factors, demanding a multifaceted approach to conflict resolution.
Population Growth and Expansion
Wolf populations are naturally expanding, reclaiming historical territories. This range expansion includes the North State, bringing wolves into closer proximity with human settlements and livestock.
- Successful Breeding: Higher breeding success rates contribute significantly to population growth.
- Prey Availability: Abundant prey species in the North State provide ample food sources for expanding wolf packs.
- Habitat Encroachment: As human development encroaches upon wolf habitats, encounters between wolves and humans become more frequent.
Studies from the California Department of Fish and Wildlife (CDFW) indicate a steady increase in wolf sightings and confirmed packs within the North State region over the past decade. These findings underscore the need for proactive management strategies.
Human-Wildlife Conflict
Increased wolf sightings translate to heightened human-wildlife conflict, characterized by:
- Livestock Depredation: Wolves preying on livestock, such as sheep and cattle, results in significant economic losses for ranchers. Statistics from the CDFW reveal a concerning trend of increasing livestock depredation linked to wolf activity.
- Encounters near Residential Areas: Wolves venturing closer to residential areas lead to increased human-wolf interactions, often fueled by fear and misunderstanding.
- Misconceptions about Wolf Behavior: Public misconceptions about wolf behavior and aggression exacerbate fear and contribute to calls for drastic, sometimes inappropriate, management actions.
Mitigation Strategies and Prevention Measures
Addressing the rising number of wolf incidents North State requires a balanced approach incorporating both non-lethal and, as a last resort, lethal control methods.
Non-Lethal Deterrents
Non-lethal strategies are crucial for minimizing conflict and promoting coexistence. These include:
- Fencing: Strengthening livestock enclosures with predator-resistant fencing is a primary preventative measure. Properly installed, electric fencing can be highly effective in deterring wolves.
- Livestock Guardian Dogs: Utilizing livestock guardian dogs, specifically breeds trained to protect livestock, has proven successful in numerous locations. These dogs act as a deterrent and provide a protective presence.
- Noise Deterrents: Employing noise deterrents, such as noisemakers or flashing lights, can help to temporarily scare wolves away from livestock or residential areas. However, these methods are often most effective in combination with other strategies.
- Aversive Conditioning: Pairing unpleasant stimuli with livestock to condition wolves to avoid them is another method with varying levels of success. The effectiveness depends on consistent application and careful implementation.
Lethal Control and its Implications
Lethal control of wolves should be considered only as a last resort, following exhaustive attempts at non-lethal mitigation. Ethical considerations and potential impacts on wolf populations must be carefully weighed.
- Regulatory Frameworks: Lethal control is subject to strict regulatory frameworks established by state and federal wildlife agencies. Permits are required, and strict guidelines must be followed.
- Impacts on Wolf Populations: Removing wolves through lethal control can have cascading impacts on pack dynamics and overall population health, potentially destabilizing the ecosystem.
- Public Opinion: Public opinion on lethal control is often highly divided, with conservation groups generally opposing it while ranchers may advocate for it in extreme circumstances. Transparent and open communication is vital in navigating this complex issue.
Community Engagement and Education
Successful management of wolf incidents North State demands strong community engagement and proactive education.
Public Awareness Campaigns
Proactive public education initiatives are essential for fostering understanding and responsible behavior around wolves.
- Educational Workshops: Organizing workshops and seminars to educate the public about wolf behavior, ecology, and conflict mitigation techniques.
- Public Forums: Facilitating public forums to address community concerns, share information, and foster open dialogue.
- Informational Materials: Disseminating brochures, fact sheets, and online resources to increase awareness among residents.
- Media Outreach: Utilizing media outlets (newspapers, radio, television, social media) to disseminate accurate information and counter misinformation.
Collaboration Between Stakeholders
Effective wolf management hinges on collaboration between diverse stakeholders.
- Shared Responsibility: Encouraging a sense of shared responsibility between government agencies, ranchers, conservation groups, and the general public.
- Cooperative Management Plans: Developing comprehensive management plans through collaborative efforts, ensuring a balanced approach that addresses the needs of all stakeholders.
- Fostering Communication and Trust: Building strong communication channels and fostering mutual trust between ranchers and wildlife agencies to ensure effective conflict resolution.
Conclusion
Addressing the rising number of wolf incidents North State requires a comprehensive approach encompassing non-lethal deterrents, responsible lethal control (as a last resort), and robust community engagement. Understanding wolf behavior, implementing effective mitigation strategies, and fostering collaboration between all stakeholders are crucial for reducing conflict and achieving coexistence between humans and wolves. We need to move beyond simply addressing individual wolf incidents North State and towards proactively managing the complex interplay between human activities and wolf populations. Learn more about wolf conservation and management in your region by contacting your local CDFW office and reporting any wolf sightings or conflicts immediately. Together, we can work towards responsible and effective management of wolf incidents in the North State, promoting coexistence between humans and this magnificent species.

Featured Posts
-
 Jasprit Bumrah Holds Top Position In Latest Icc Test Bowling Rankings
May 23, 2025
Jasprit Bumrah Holds Top Position In Latest Icc Test Bowling Rankings
May 23, 2025 -
 Understanding Briefs A Comprehensive Overview For Professionals
May 23, 2025
Understanding Briefs A Comprehensive Overview For Professionals
May 23, 2025 -
 Piastri Takes Pole In Bahrain F1 Qualifying Highlights
May 23, 2025
Piastri Takes Pole In Bahrain F1 Qualifying Highlights
May 23, 2025 -
 Mtabet Asear Aldhhb Fy Qtr Alithnyn 24 Mars
May 23, 2025
Mtabet Asear Aldhhb Fy Qtr Alithnyn 24 Mars
May 23, 2025 -
 Tqryr Asear Aldhhb Fy Qtr Lhdha Alywm Alithnyn 24 Mars
May 23, 2025
Tqryr Asear Aldhhb Fy Qtr Lhdha Alywm Alithnyn 24 Mars
May 23, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Ten Hags High Praise For Arsenal Star Following Real Madrid Win
May 23, 2025
Ten Hags High Praise For Arsenal Star Following Real Madrid Win
May 23, 2025 -
 Luis Castros Outburst Ten Hags Management Of Ronaldo Questioned
May 23, 2025
Luis Castros Outburst Ten Hags Management Of Ronaldo Questioned
May 23, 2025 -
 Ten Hag Under Fire Luis Castro Defends Cristiano Ronaldo
May 23, 2025
Ten Hag Under Fire Luis Castro Defends Cristiano Ronaldo
May 23, 2025 -
 Castro Condemns Ten Hags Treatment Of Ronaldo
May 23, 2025
Castro Condemns Ten Hags Treatment Of Ronaldo
May 23, 2025 -
 Luis Castro Criticizes Erik Ten Hags Handling Of Cristiano Ronaldo
May 23, 2025
Luis Castro Criticizes Erik Ten Hags Handling Of Cristiano Ronaldo
May 23, 2025
