Alien Enemies Act: Trump's Legal Challenge Fails In Appeals Court

Table of Contents
The Alien Enemies Act: A Historical Overview and its Modern Application
The Alien Enemies Act, enacted in 1798 as part of the Alien and Sedition Acts, grants the President broad powers during wartime to apprehend and detain enemy aliens. Its original purpose was to address concerns about potential threats during periods of international conflict. However, its application has been extremely infrequent throughout US history, highlighting its controversial and potentially expansive nature.
The Act's relevance in the context of modern national security concerns is highly debated. While proponents argue it provides necessary tools to protect the nation from internal threats, critics emphasize the potential for abuse and its incompatibility with fundamental rights guaranteed by the Constitution. The Trump administration's attempt to utilize the Act underscores this ongoing tension.
Key sections of the Act relevant to the Trump administration's legal challenge include:
- Section 1: Authorizes the President to apprehend and detain enemy aliens during a declared war or other national emergency.
- Section 2: Outlines the procedures for the detention and potential deportation of enemy aliens.
- Section 3: Addresses the treatment and rights of apprehended individuals.
Legal precedents and previous interpretations of the Act are scarce, further complicating its application in contemporary circumstances. The lack of extensive case law surrounding the Act makes each invocation a significant legal event.
Trump Administration's Legal Argument and its Basis
The Trump administration's justification for invoking the Alien Enemies Act rested on claims of national security threats posed by individuals from specific countries. The administration argued that these threats necessitated restrictive immigration policies, exceeding the scope of standard immigration laws.
Their legal arguments centered on:
- The broad interpretation of "enemy alien" to encompass individuals from countries deemed to pose a national security risk.
- The assertion of inherent presidential authority to act decisively during times of perceived national emergency.
- The claim that existing immigration laws were insufficient to address the perceived threat.
The administration's key arguments repeatedly emphasized the urgency of protecting national security, framing restrictive immigration measures as a necessary response.
The Appeals Court Ruling and its Reasoning
The appeals court decisively rejected the Trump administration's challenge, finding the invocation of the Alien Enemies Act in this context to be legally unsound. The court meticulously examined the administration's arguments, highlighting several critical flaws.
The court's interpretation of the Alien Enemies Act emphasized its limited scope and historical context. The judges underscored that the Act is intended for use during actual wartime, not as a tool for broad immigration restrictions based on generalized security concerns.
Key findings and rationale of the court included:
- Rejection of the administration's broad interpretation of "enemy alien."
- Emphasis on the necessity for a direct link between an individual's actions and an actual threat to national security.
- Affirmation of the importance of due process and legal protections for individuals facing deportation.
The court's decision relied on established legal precedents concerning executive power and the rights of non-citizens, effectively limiting the president's ability to bypass established immigration procedures.
Implications of the Ruling on Immigration Policy and Presidential Power
This ruling has significant implications for both US immigration law and the balance of power between the executive and judicial branches regarding national security. The court's decision strengthens the constraints on executive power when applying legislation with broad implications for individual liberties.
The long-term consequences of this decision include:
- A re-evaluation of the Trump administration's immigration policies.
- Increased scrutiny of future attempts to use the Alien Enemies Act for immigration restrictions.
- Potential for future legal challenges testing the boundaries of presidential power in national security matters.
This ruling reinforces the role of judicial review in safeguarding individual rights even during times of perceived national emergency.
Conclusion
The appeals court's rejection of the Trump administration's use of the Alien Enemies Act marks a crucial victory for those who advocate for due process and the limitations of executive power. The ruling underscores the judiciary's role in interpreting and applying laws, including those related to national security and immigration. The court's careful consideration of historical context and legal precedent provides clarity regarding the proper application of this powerful, yet rarely used, Act.
Call to Action: Understanding the intricacies of the Alien Enemies Act and its implications for US immigration policy is paramount. We encourage further research into the legal precedents and ongoing debates surrounding this legislation and its potential impact on national security and immigration policy. Stay informed about future developments regarding the Alien Enemies Act and its potential applications.

Featured Posts
-
 The Impending Mueller Departure Reactions From Bayern Munich Fans And Media
May 11, 2025
The Impending Mueller Departure Reactions From Bayern Munich Fans And Media
May 11, 2025 -
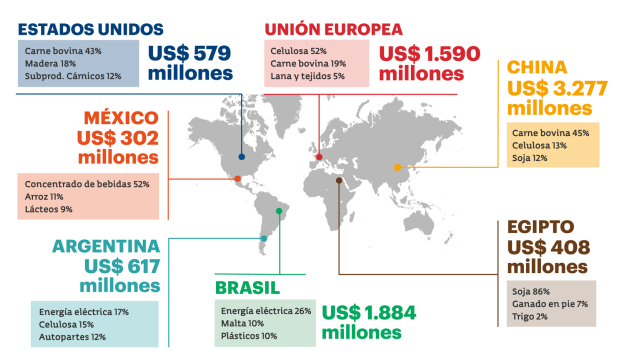 Las Exportaciones Ganaderas Uruguayas Y El Regalo Que Cambio La Relacion Con China
May 11, 2025
Las Exportaciones Ganaderas Uruguayas Y El Regalo Que Cambio La Relacion Con China
May 11, 2025 -
 Discover Montego Bay Beaches Culture And Beyond
May 11, 2025
Discover Montego Bay Beaches Culture And Beyond
May 11, 2025 -
 The Intertwined Fate Of Apple And Google
May 11, 2025
The Intertwined Fate Of Apple And Google
May 11, 2025 -
 Was Marvel Right To Drop The Henry Cavill Show Exploring The Fallout
May 11, 2025
Was Marvel Right To Drop The Henry Cavill Show Exploring The Fallout
May 11, 2025
