Analyzing The GOP Tax Plan: The Reality Of Deficit Reduction
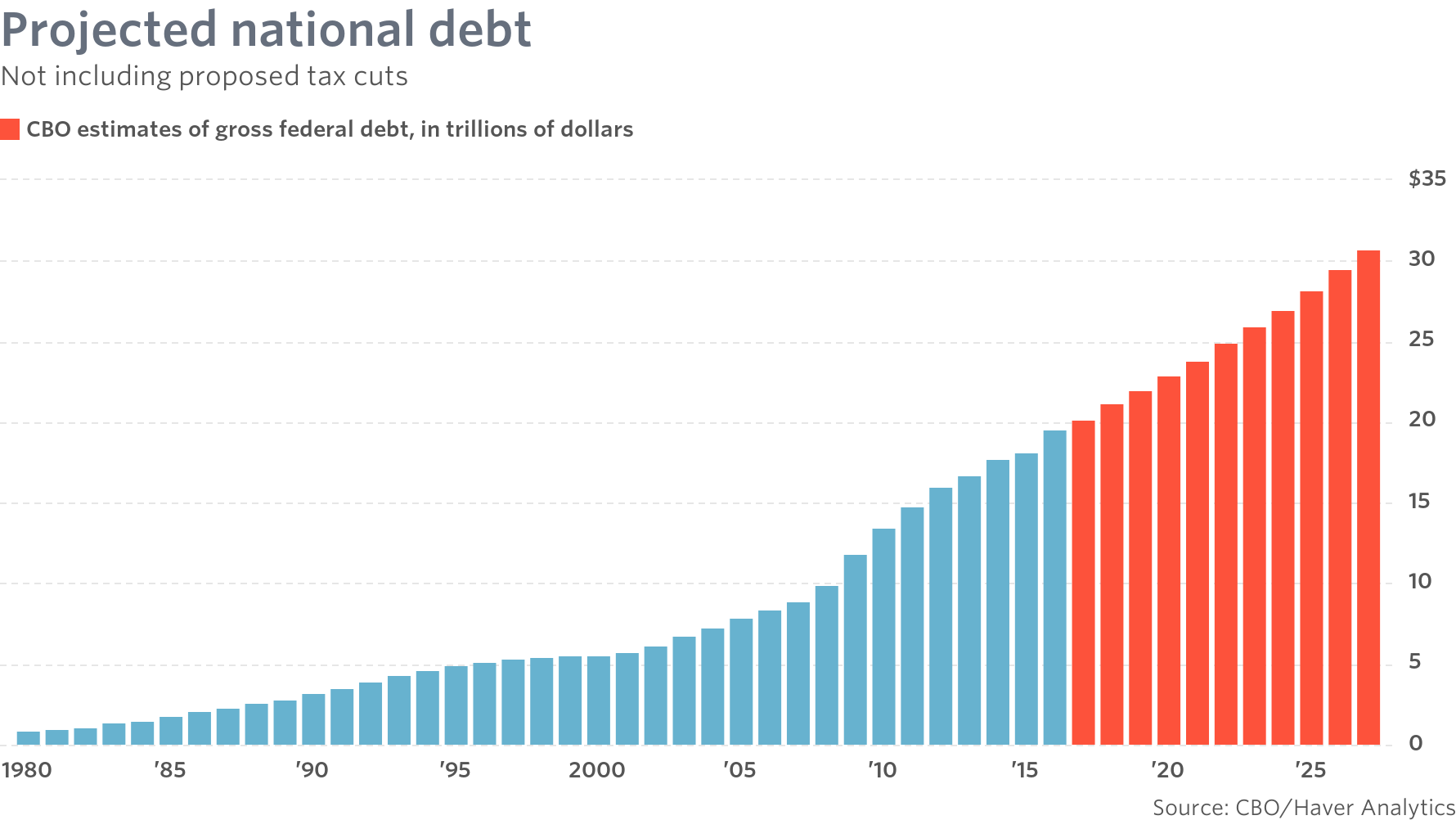
Table of Contents
Projected Revenue Impacts of the GOP Tax Plan
The GOP tax plan's core involved substantial tax cuts, aiming to boost economic growth and, consequently, tax revenue. However, the actual revenue impacts differed significantly from initial projections.
Corporate Tax Rate Cuts and Their Effect on Revenue
The plan lowered the corporate tax rate from 35% to 21%, a dramatic reduction intended to incentivize business investment and job creation.
- Initial Projections: The administration projected this cut would lead to minimal revenue loss, offset by increased economic activity.
- Actual Results: The Tax Policy Center found that the corporate tax cuts resulted in a substantial loss of revenue, far exceeding initial projections. While some increased investment occurred, it didn't compensate for the reduced tax rate.
- Increased Investment Argument: Proponents argued that the lower rate would spur significant investment, leading to higher overall tax revenue through increased economic activity. This is a cornerstone of supply-side economics.
- Counterarguments: Critics point to limited evidence of a significant surge in investment directly attributable to the tax cuts. Many corporations used the additional revenue for stock buybacks and executive compensation rather than expanding operations or hiring.
- Data Sources: Data from the Congressional Budget Office (CBO) and the Tax Policy Center consistently show a net loss in revenue due to corporate tax cuts.
Individual Income Tax Changes and Their Revenue Implications
The plan also included changes to individual income tax brackets, standard deductions, and other provisions.
- Tax Bracket Changes: Several tax brackets were altered, resulting in lower tax rates for many individuals.
- Impact on Income Groups: The tax cuts disproportionately benefited higher-income individuals, with lower-income individuals receiving less significant reductions.
- Distribution of Tax Cuts:
- Top 1% received the largest percentage of the tax cuts.
- Middle-income earners received smaller cuts.
- Lower-income individuals saw minimal changes.
- Dynamic Scoring: The administration used dynamic scoring, which assumes economic growth spurred by tax cuts would offset revenue losses. Critics argue this methodology is overly optimistic and unreliable.
- Economic Activity and Revenue: While some economic growth occurred, it did not generate enough additional revenue to offset the substantial tax cuts.
Spending Impacts and the Growing National Debt
The tax cuts, combined with increased government spending in other areas, significantly impacted the national debt.
Increased Spending Due to Economic Growth (Claimed)
A central argument of the GOP tax plan was that the tax cuts would stimulate sufficient economic growth to offset revenue losses.
- Stimulus Argument: The theory hinges on the "Laffer Curve," which suggests that tax cuts can increase revenue by stimulating economic activity.
- Actual Economic Growth: While some economic growth followed the tax cuts, it was less than projected, insufficient to offset the revenue shortfall.
- Projected vs. Realized Growth: The CBO's projections of economic growth consistently underestimated the impact of the tax cuts.
- Laffer Curve Relevance: The validity of the Laffer Curve in the context of this tax plan remains highly debated.
Unfunded Tax Cuts and Their Contribution to the Deficit
The tax cuts were largely unfunded, meaning there were no corresponding spending cuts to offset the revenue loss.
- Long-Term Impact: The lack of offsetting spending cuts led to a significant and sustained increase in the national debt.
- Absence of Spending Cuts: No significant spending cuts accompanied the tax reductions, increasing the deficit substantially.
- Projected Increase in National Debt: The CBO projected a significant increase in the national debt as a direct consequence of the tax plan.
- Comparison to Previous Tax Cuts: Comparing this tax plan to previous tax cuts reveals a similar pattern: large tax cuts without offsetting spending cuts typically lead to increased national debt.
- Visual Representation: Charts and graphs illustrating the projected and actual increase in the national debt clearly demonstrate the fiscal impact.
Alternative Analyses and Criticisms of the GOP Tax Plan
Independent analyses and criticisms further highlight the shortcomings of the GOP tax plan.
Independent Analyses and Their Findings
Several independent organizations offered alternative analyses of the tax plan's impact.
- Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget: This group consistently criticized the lack of fiscal responsibility in the plan.
- Brookings Institution: The Brookings Institution's research highlighted the negative impact on income inequality.
- Comparison to Official Projections: Independent analyses generally found a more negative impact on the deficit than the official government projections.
- Key Disagreements: Key disagreements centered around the accuracy of dynamic scoring and the magnitude of the economic growth stimulated by the tax cuts.
Criticisms Regarding Economic Inequality and Distributional Effects
The tax cuts disproportionately benefited high-income earners, exacerbating income inequality.
- Disproportionate Benefits: The majority of the tax cuts went to the wealthiest Americans.
- Impact on Income Inequality: The tax cuts widened the gap between the rich and the poor.
- Arguments Against Fairness: Critics argued the plan was unfair and regressive, benefiting the wealthy at the expense of lower- and middle-income taxpayers.
Conclusion
This analysis of the GOP tax plan reveals a complex picture regarding its impact on deficit reduction. While proponents argued that tax cuts would stimulate economic growth, leading to increased tax revenue, the reality shows a significant increase in the national debt. Independent analyses largely corroborate this finding, highlighting concerns about the plan's distributional effects and long-term fiscal sustainability. Ultimately, a thorough examination of the GOP tax plan and its impact on deficit reduction necessitates a critical review of both projected and actual outcomes. For a deeper understanding of the long-term fiscal consequences, further analysis of the GOP tax plan's effects is crucial.

Featured Posts
-
 Bangladeshinfo Com The Ultimate Resource For Information On Bangladesh
May 20, 2025
Bangladeshinfo Com The Ultimate Resource For Information On Bangladesh
May 20, 2025 -
 Retired Admirals Bribery Conviction A Four Count Guilty Verdict
May 20, 2025
Retired Admirals Bribery Conviction A Four Count Guilty Verdict
May 20, 2025 -
 Todays Nyt Mini Crossword Solutions March 18
May 20, 2025
Todays Nyt Mini Crossword Solutions March 18
May 20, 2025 -
 Todays Nyt Mini Crossword Solutions March 31
May 20, 2025
Todays Nyt Mini Crossword Solutions March 31
May 20, 2025 -
 Tragicheskaya Situatsiya Novye Podrobnosti O Sostoyanii Mikhaelya Shumakhera Ot Blizkogo Druga
May 20, 2025
Tragicheskaya Situatsiya Novye Podrobnosti O Sostoyanii Mikhaelya Shumakhera Ot Blizkogo Druga
May 20, 2025
