Assessing The Damage: How Much Is The Trade War Really Costing China?
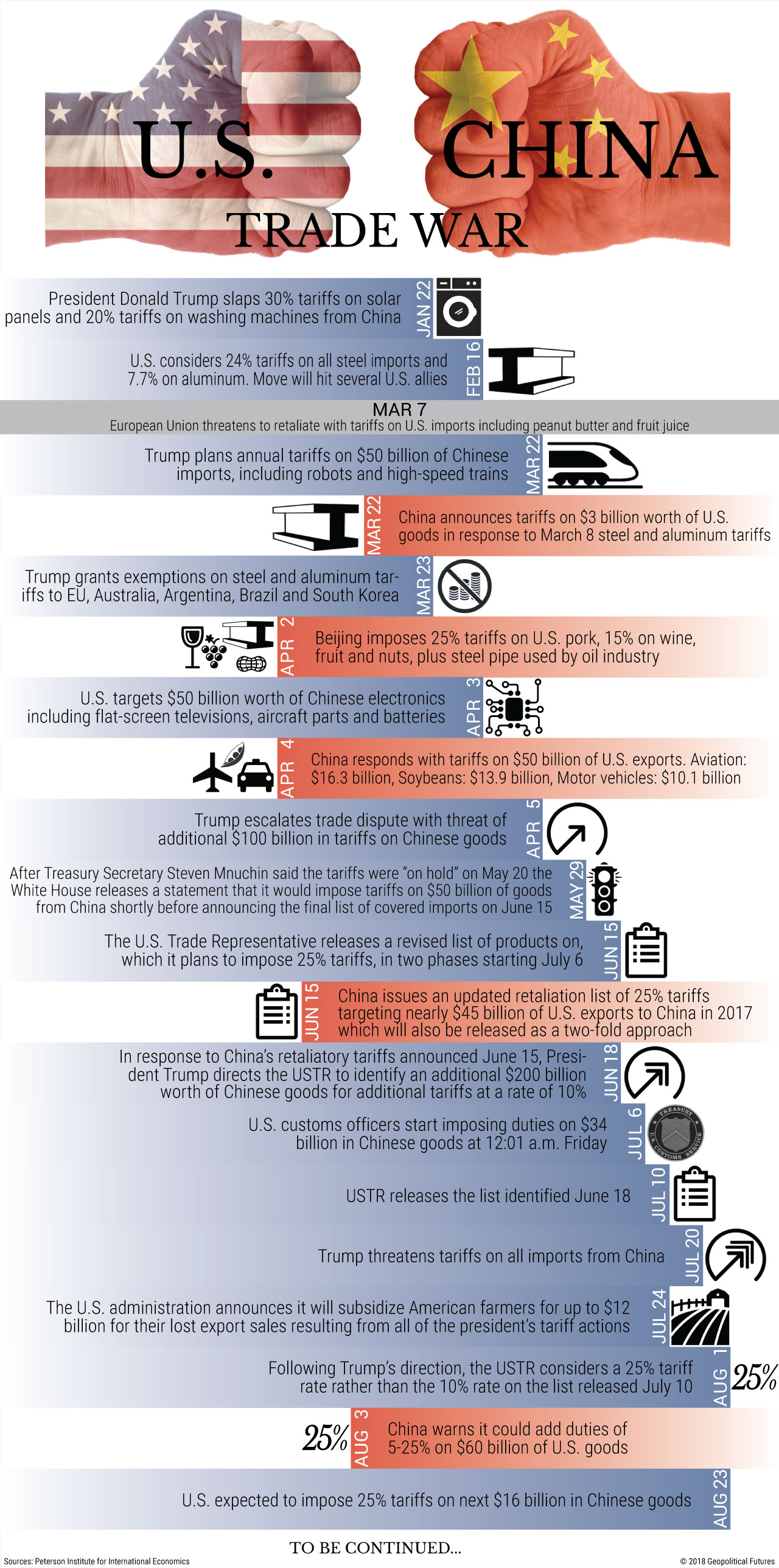
Table of Contents
Direct Costs: Tariffs and Reduced Exports
The most immediate and tangible impact of the trade war was the imposition of tariffs by the US on a vast range of Chinese goods. These tariffs, levied on everything from electronics and agricultural products to textiles and machinery, directly increased the cost of Chinese exports to the US market. This resulted in a significant decrease in export revenue for numerous Chinese industries.
-
Decreased export revenue for specific industries: Sectors like technology, where tariffs targeted high-value components, experienced particularly sharp declines. The agricultural sector also suffered, with tariffs impacting exports of soybeans and other products.
-
Increased prices for Chinese consumers due to tariffs: The tariffs didn't just affect exports; some were passed on to Chinese consumers in the form of higher prices for imported goods. This further dampened domestic consumption.
-
Loss of market share to competitors: With Chinese goods becoming more expensive in the US market, competitors from other countries gained a significant advantage, capturing market share previously held by Chinese firms. This loss of market share had long-lasting consequences for certain industries.
-
Examples of specific industries significantly affected: The electronics industry, a cornerstone of China's manufacturing prowess, faced considerable challenges. Similarly, the textile industry, already facing global competition, experienced a further decline in its export performance due to the added tariffs.
Indirect Costs: Supply Chain Disruptions and Investment Uncertainty
Beyond the direct impact of tariffs, the trade war generated significant indirect costs. The escalating tensions disrupted global supply chains, creating uncertainty and volatility in the market. This uncertainty deterred foreign direct investment (FDI) in China, as businesses hesitated to commit capital to a potentially unstable environment.
-
Increased costs for Chinese businesses relying on imported components: Many Chinese businesses relied on imported components for their production processes. The tariffs and trade disruptions increased the costs of these inputs, squeezing profit margins and impacting competitiveness.
-
Delayed or canceled investment projects due to uncertainty: The trade war’s unpredictability led to a postponement or cancellation of numerous investment projects, both domestic and foreign. This further hindered economic growth.
-
Impact on employment in export-oriented industries: The decline in exports and investment directly impacted employment in export-oriented industries. Job losses and reduced income further impacted domestic consumption and economic activity.
-
Shift of manufacturing and investment to other countries: Facing higher costs and uncertainty, some businesses shifted manufacturing operations and investment to other countries, particularly in Southeast Asia, seeking more stable and cost-effective environments. This resulted in a loss of jobs and economic activity for China.
Long-Term Costs: Technological Dependence and Economic Slowdown
The trade war also had profound implications for China's long-term economic prospects. The restrictions on technology transfers and access to advanced components hampered China's technological ambitions. Moreover, the overall economic growth rate was affected, with predictions of slower growth compared to pre-trade war projections.
-
Increased reliance on domestic technology, potentially hindering innovation: The trade war spurred efforts to foster domestic technological innovation, but this increased reliance on homegrown technology, in some cases, may have inadvertently slowed down innovation by limiting access to global best practices and competition.
-
Slowdown in GDP growth compared to pre-trade war projections: The combined effect of direct and indirect costs resulted in a slower pace of economic growth compared to projections before the trade war. The precise extent of this slowdown is debatable but undeniably significant.
-
Long-term consequences for Chinese industries' competitiveness: The trade war created long-term challenges to the competitiveness of several key Chinese industries, impacting their ability to participate in the global market effectively.
-
Potential impact on China's global influence and standing: The economic consequences of the trade war could have long-term implications for China's global influence and geopolitical standing, affecting its strategic relationships with other nations.
Attempts at Mitigation: Government Policies and Economic Adjustments
The Chinese government responded to the trade war with various policy measures aimed at mitigating its negative impacts. These included government subsidies to affected industries, stimulus packages to boost domestic demand, an increased emphasis on technological self-reliance and innovation, and efforts to diversify export markets.
-
Government subsidies to affected industries: Financial assistance was provided to sectors heavily impacted by tariffs, helping to prevent widespread bankruptcies and job losses.
-
Stimulus packages to boost domestic demand: Measures were introduced to stimulate domestic consumption and reduce reliance on exports, aiming to offset the decline in external demand.
-
Emphasis on technological self-reliance and innovation: The trade war highlighted the need for greater technological independence. Significant investments were made in research and development to foster innovation and reduce reliance on foreign technology.
-
Diversification of export markets: Efforts were undertaken to diversify export markets, reducing dependence on the US and exploring opportunities in other regions.
Conclusion: The Enduring Impact – Quantifying the Trade War's Cost to China
The US-China trade war inflicted significant economic damage on China, encompassing both direct costs from tariffs and reduced exports, and indirect costs from supply chain disruptions and investment uncertainty. The long-term consequences, including the impact on technological ambitions and economic growth, are still unfolding. While precisely calculating the total cost remains difficult, the negative impacts are undeniable and will likely continue to be felt for years to come. Understanding the true ramifications of the "Trade War Costing China" requires a comprehensive analysis of these multifaceted economic effects. To further delve into the intricacies of this complex issue, explore more related articles on our website for a deeper understanding of the economic repercussions and their long-term implications.

Featured Posts
-
 Celebrity Traitors On Bbc Filming Delays After Sibling Withdrawals
May 02, 2025
Celebrity Traitors On Bbc Filming Delays After Sibling Withdrawals
May 02, 2025 -
 Broadcoms Proposed V Mware Price Hike A 1050 Increase For At And T
May 02, 2025
Broadcoms Proposed V Mware Price Hike A 1050 Increase For At And T
May 02, 2025 -
 Fortnite Game Mode Removal A Sign Of Things To Come
May 02, 2025
Fortnite Game Mode Removal A Sign Of Things To Come
May 02, 2025 -
 Scotlands Six Nations 2025 Prospects Realism Vs Optimism
May 02, 2025
Scotlands Six Nations 2025 Prospects Realism Vs Optimism
May 02, 2025 -
 Nigel Farage And Rupert Lowe Their Public Feud Reaches A Boiling Point
May 02, 2025
Nigel Farage And Rupert Lowe Their Public Feud Reaches A Boiling Point
May 02, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Singer Wynne Evans Reveals Recent Health Struggle Hints At Stage Return
May 10, 2025
Singer Wynne Evans Reveals Recent Health Struggle Hints At Stage Return
May 10, 2025 -
 Wynne Evans Shares Health Battle Recovery Update And Future Plans
May 10, 2025
Wynne Evans Shares Health Battle Recovery Update And Future Plans
May 10, 2025 -
 Elizabeth Stewarts Spring Designs A Collaboration With Lilysilk
May 10, 2025
Elizabeth Stewarts Spring Designs A Collaboration With Lilysilk
May 10, 2025 -
 A Look At Elizabeth Stewart And Lilysilks Collaborative Spring Line
May 10, 2025
A Look At Elizabeth Stewart And Lilysilks Collaborative Spring Line
May 10, 2025 -
 New Spring Collection Elizabeth Stewarts Designs For Lilysilk
May 10, 2025
New Spring Collection Elizabeth Stewarts Designs For Lilysilk
May 10, 2025
