Britain And Australia's Myanmar Policy: Hypocrisy Or Pragmatism?
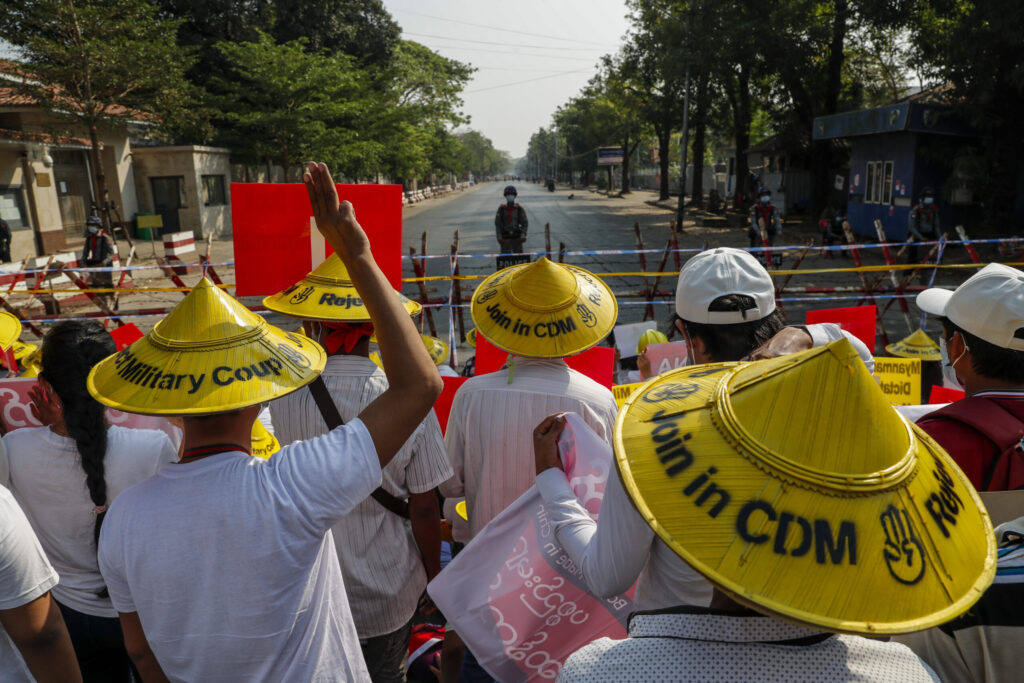

Table of Contents
Historical Context and Colonial Legacy
Britain's historical role in Myanmar
Britain's colonial past in Myanmar casts a long shadow over current relations. British colonialism, spanning from the early 19th century to the mid-20th century, significantly shaped Myanmar's political and economic landscape, leaving a legacy of both positive and negative consequences.
- Positive Impacts: The introduction of infrastructure (though often serving British interests) and a centralized administrative system.
- Negative Impacts: The brutal suppression of local resistance, widespread exploitation of resources, and the artificial division of ethnic groups that sowed the seeds of future conflict. This colonial legacy significantly contributes to the complexities of understanding modern Britain-Myanmar relations. The lasting effects of British colonialism in Burma are undeniable, impacting everything from economic structures to political instability.
Keywords: Myanmar, Burma, British colonialism, colonial legacy, British rule, exploitation.
Australia's engagement with Myanmar
Australia's relationship with Myanmar is more recent and less deeply entrenched than Britain's. However, Australia has engaged with Myanmar through periods of both cooperation and conflict.
- Economic Ties: Australia has maintained some level of economic engagement with Myanmar, albeit with increasing caution in recent years given the deteriorating human rights situation.
- Diplomatic Interventions: Australia has participated in regional diplomatic efforts to address the crisis in Myanmar, often through ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations) channels. However, the effectiveness of these interventions has been questioned, given the limited impact on the military junta.
Keywords: Australia-Myanmar relations, Australia's foreign policy, regional engagement, ASEAN engagement, Australia Myanmar relations.
Current Approaches to Myanmar's Crisis
Britain's policy response
Britain's response to the Myanmar crisis has involved a range of measures, reflecting a multi-pronged approach:
- Targeted Sanctions: The UK has imposed targeted sanctions against individuals and entities within the Myanmar military regime, aiming to restrict their access to international finance and resources.
- Diplomatic Pressure: Britain has actively participated in international efforts to exert diplomatic pressure on the Myanmar military junta, advocating for a return to democracy and an end to violence.
- Humanitarian Aid: The UK has provided significant humanitarian aid to support the people of Myanmar who have been displaced or affected by the ongoing conflict. However, the delivery of aid has been severely hampered by the ongoing instability and restrictions imposed by the military regime.
Keywords: UK Myanmar policy, British sanctions, humanitarian aid, diplomatic pressure, British government, Myanmar military junta.
Australia's policy response
Australia’s response mirrors some aspects of the UK's, yet it also showcases unique considerations:
- Australia Myanmar sanctions: Similar to the UK, Australia has implemented targeted sanctions against individuals and entities linked to the Myanmar military.
- Australian humanitarian aid: Australia has also provided substantial humanitarian aid, but faces the same logistical challenges in delivering it effectively.
- ASEAN engagement: Given its geographical proximity, Australia plays a significant role in engaging with ASEAN in seeking a peaceful resolution. This approach emphasizes regional cooperation and diplomacy.
Keywords: Australia Myanmar sanctions, Australian humanitarian aid, ASEAN engagement, Australian government.
The Argument for Hypocrisy
Economic Interests vs. Human Rights
A strong argument can be made that both Britain and Australia's policies exhibit hypocrisy. The existence of ongoing, albeit often reduced, economic ties with Myanmar, even in the face of egregious human rights violations, raises ethical concerns.
- Trade Relations: While sanctions target specific individuals and entities, broader trade relations often continue, raising questions about the commitment to human rights above economic interests.
- Investment Concerns: Previous investments in Myanmar by British and Australian companies may influence the reluctance to impose more stringent sanctions, showcasing a potential conflict of interest.
Keywords: economic sanctions, trade relations, human rights violations, military junta, ethical concerns, economic interests.
Inconsistency in Policy
Further evidence of hypocrisy lies in the apparent inconsistencies within their policies:
- Selective Condemnation: Criticisms of the Myanmar military junta are not consistently applied to other nations with questionable human rights records, suggesting a degree of selective morality in their foreign policy.
- Delayed or Limited Action: The timing and scope of sanctions and other actions have often been criticized as being too slow or insufficient to effectively address the severity of the human rights abuses.
Keywords: policy inconsistencies, double standards, moral responsibility, ethical dilemmas, delayed action.
The Argument for Pragmatism
The Limits of Sanctions
The pragmatist perspective emphasizes the limitations of sanctions as a sole tool for achieving political change:
- Sanctions Effectiveness: Sanctions can have unintended consequences, potentially harming the civilian population more than the intended targets.
- Regional Stability: A more forceful approach could destabilize the region further, potentially leading to wider conflict. The delicate balancing act of pursuing justice without exacerbating instability necessitates a pragmatic approach.
Keywords: sanctions effectiveness, diplomatic solutions, regional stability, political complexities, unintended consequences.
Balancing Competing Interests
Foreign policy necessitates difficult compromises:
- National Interests: Maintaining regional stability and security may sometimes outweigh immediate concerns about human rights, demanding a pragmatic balancing act.
- Multifaceted Approach: A comprehensive strategy requires a mixture of sanctions, diplomacy, humanitarian aid, and engagement with regional partners, accepting the challenges and limitations of each method.
Keywords: national interests, foreign policy, geopolitical considerations, strategic partnerships, multifaceted approach.
Conclusion: Britain and Australia's Myanmar Policy: A Verdict?
Britain and Australia's Myanmar policies present a complex picture. While their actions demonstrate a commitment to humanitarian aid and some level of condemnation of the military junta through sanctions and diplomatic pressure, the existence of ongoing economic ties and instances of seemingly inconsistent responses lends credence to accusations of hypocrisy. However, a purely pragmatic perspective acknowledges the limitations of sanctions, the complexities of regional politics, and the need to balance competing national interests. The reality likely lies in a nuanced blend of both pragmatism and, at times, unavoidable compromise, reflecting the difficult ethical dilemmas inherent in navigating such a multifaceted international crisis. Further research and sustained pressure on both governments are needed to ensure their policies adequately reflect the severity of the human rights crisis and to promote a more just and equitable outcome in Myanmar. Continued scrutiny of Britain and Australia's Myanmar policy is crucial to pushing for meaningful change.

Featured Posts
-
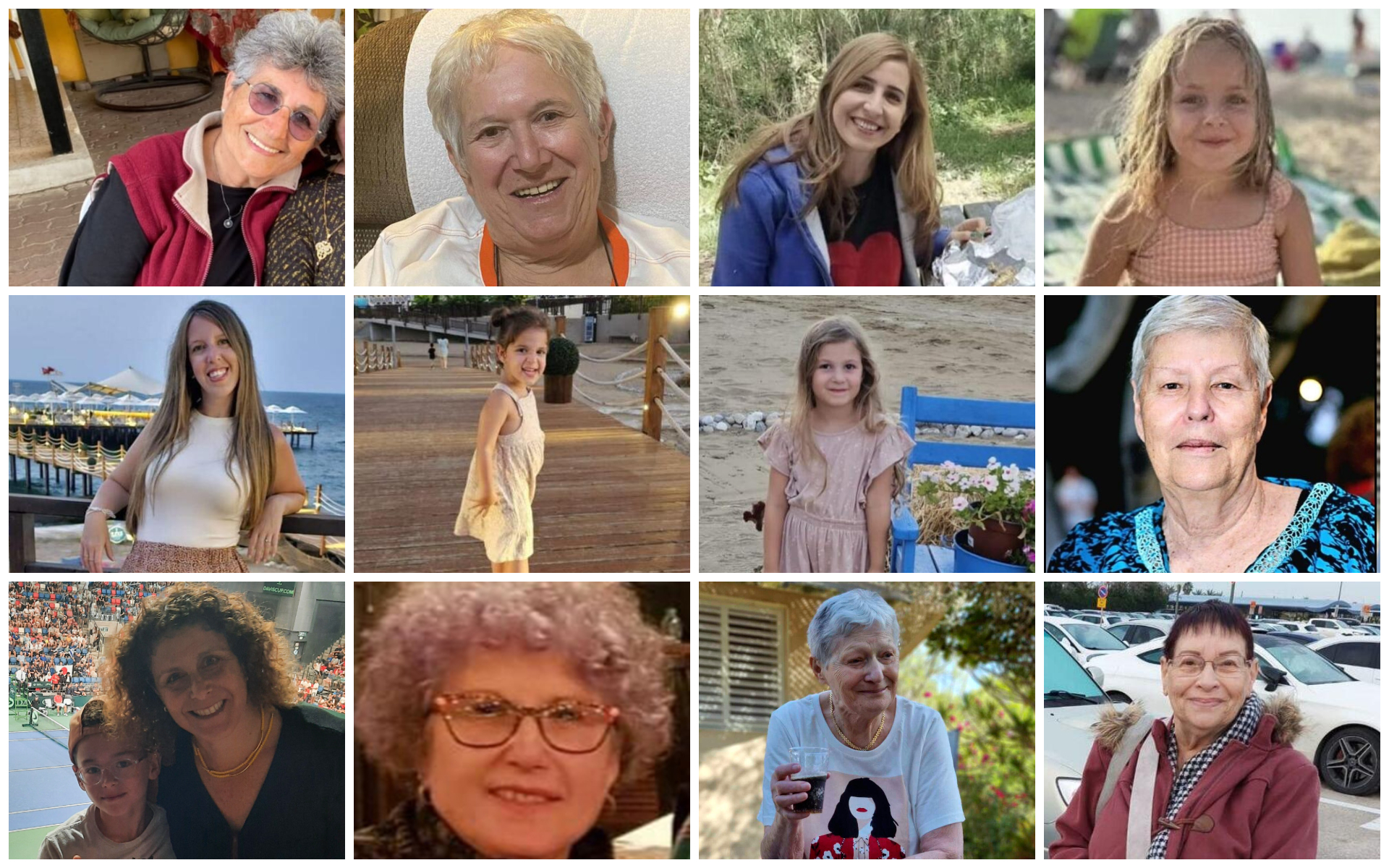 Prolonged Nightmare The Suffering Of Families With Hostages In Gaza
May 13, 2025
Prolonged Nightmare The Suffering Of Families With Hostages In Gaza
May 13, 2025 -
 Kemenangan Telak Persipura Jayapura 8 0 Atas Rans Fc Di Playoff Liga 2
May 13, 2025
Kemenangan Telak Persipura Jayapura 8 0 Atas Rans Fc Di Playoff Liga 2
May 13, 2025 -
 Den Epistrefei I Skarlet Gioxanson Os Black Widow I Anakoinosi Poy Prokalese Thyella
May 13, 2025
Den Epistrefei I Skarlet Gioxanson Os Black Widow I Anakoinosi Poy Prokalese Thyella
May 13, 2025 -
 Byds International Growth Benin Seychelles Croatia Slovakia Cambodia And Record Breaking Ship
May 13, 2025
Byds International Growth Benin Seychelles Croatia Slovakia Cambodia And Record Breaking Ship
May 13, 2025 -
 Texas Rangers 2025 Season Complete Guide To Watching Every Game
May 13, 2025
Texas Rangers 2025 Season Complete Guide To Watching Every Game
May 13, 2025
