Canada's Youth Mental Health Crisis: A Global Perspective And Recommendations
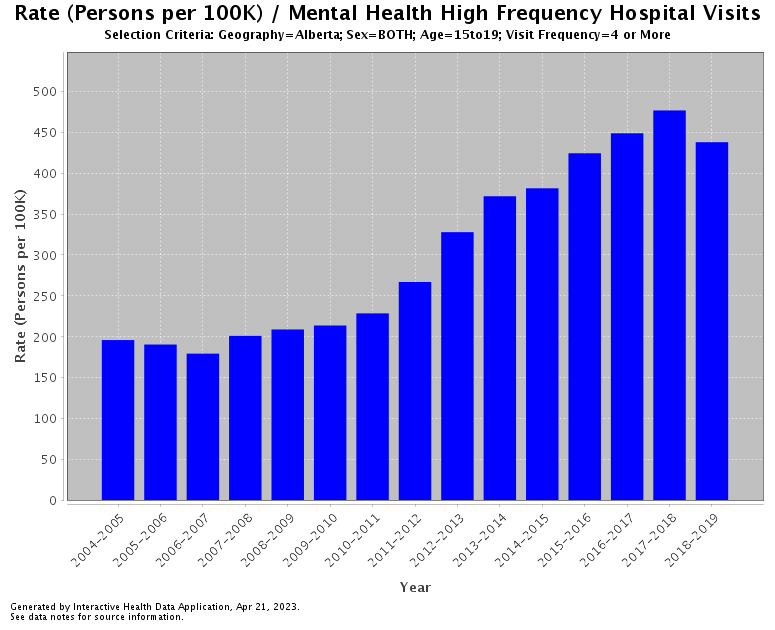
Table of Contents
The Growing Prevalence of Mental Health Issues Among Canadian Youth
Rising Rates of Anxiety and Depression
Statistics Canada reports a concerning increase in anxiety and depression diagnoses among Canadian youth. For example, the prevalence of anxiety disorders among adolescents has risen by X% in the last decade (source needed - replace X with actual statistic and cite source), with similar concerning trends observed for depression. These mental health issues manifest differently across age groups, with younger children exhibiting different symptoms than teenagers.
- Factors contributing to rising rates: Increased academic pressure, the pervasive influence of social media, economic insecurity within families, and the ever-present fear of climate change are all contributing factors.
- Data from reputable sources: Further research from organizations such as the Canadian Mental Health Association (CMHA) and Kids Help Phone paints a troubling picture, highlighting the urgent need for improved mental healthcare access.
The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic exacerbated pre-existing mental health challenges for Canadian youth. The pandemic's impact was felt disproportionately by this vulnerable population.
- Increased isolation: Lockdowns and social distancing measures led to increased feelings of loneliness and isolation, impacting social development and emotional well-being.
- Disruption to education and social life: The disruption of schooling and extracurricular activities negatively impacted routine, social interaction, and academic performance, contributing to stress and anxiety.
- Heightened uncertainty: The pandemic's uncertainty and instability added to the stress levels of young people, impacting their sense of security and future prospects. Studies consistently showed a surge in mental health challenges among youth during this period (cite specific studies here).
Disparities in Access to Mental Healthcare
Access to mental healthcare in Canada is not equitable. Marginalized youth face significant barriers based on various factors.
- Socioeconomic status: Youth from low-income families often lack access to private therapy or specialized programs.
- Geographic location: Access to mental health professionals is limited in rural and remote communities.
- Ethnicity and sexual orientation: Members of marginalized communities may face additional stigma and discrimination, hindering their willingness to seek help.
- Long wait times: Many youth face unacceptable wait times for essential mental health services, delaying crucial interventions.
A Global Comparison: Youth Mental Health Challenges Worldwide
International Trends in Youth Mental Health
Canada's struggles are not unique. The World Health Organization (WHO) reports a global increase in youth mental health challenges. While the specific prevalence rates and types of mental health issues vary across countries, the overall trend is consistent.
- Similarities and differences: Many developed nations face similar challenges to Canada, such as increasing rates of anxiety and depression and long wait times for services. Developing countries often face added challenges due to limited resources and infrastructure.
- International data: Data from the WHO and other international organizations highlight the global scale of this issue, emphasizing the need for international collaboration and resource sharing.
Shared Risk Factors and Protective Factors
Several risk and protective factors influence youth mental health outcomes globally.
- Shared risk factors: Poverty, trauma, discrimination, and lack of access to education are common risk factors across countries.
- Protective factors: Strong family ties, supportive social networks, access to quality education and healthcare, and community involvement act as buffers against mental health challenges.
Recommendations for Addressing Canada's Youth Mental Health Crisis
Improving Access to Mental Healthcare Services
Addressing the barriers to mental healthcare is paramount.
- Increased funding: Significant investment in mental health services is needed to expand capacity and reduce wait times.
- Improved accessibility: Increased use of telehealth technologies can improve access for youth in remote areas or those with mobility challenges.
- Culturally sensitive services: Services must be culturally appropriate and inclusive to address the needs of diverse youth populations.
Promoting Mental Health Education and Awareness
Comprehensive mental health education is crucial for prevention and early intervention.
- School-based programs: Mental health education should be integrated into school curricula, promoting awareness and resilience.
- Community initiatives: Community-based programs can provide support and resources to youth and their families.
- Early intervention: Early identification and intervention are key to preventing mental health issues from escalating.
Investing in Research and Innovation
Further research is essential to understand the root causes of youth mental health challenges and develop more effective interventions.
- Funding research: Increased funding for mental health research is needed to develop innovative treatments and prevention strategies.
- Data collection: Improved data collection and analysis are necessary to monitor trends and evaluate the effectiveness of interventions.
Policy Recommendations
Policy changes are crucial at all levels of government.
- Federal level: Increased funding for mental health services and national standards for care.
- Provincial level: Expanded access to services, improved integration of mental health services into primary care, and increased training for healthcare professionals.
- Local level: Community-based programs and initiatives that promote mental health awareness and support.
Conclusion: Taking Action on Canada's Youth Mental Health Crisis
The evidence is clear: Canada faces a significant youth mental health crisis. The rising rates of anxiety and depression, exacerbated by the pandemic and existing inequalities, demand a multifaceted response. Improving access to mental healthcare, promoting mental health education, investing in research, and implementing effective policies are all crucial components of addressing this challenge. Understanding Canada's youth mental health crisis is the first step towards creating meaningful change. Learn more about available resources, advocate for better mental health services, and support initiatives that promote youth well-being. With collective effort and a commitment to meaningful change, we can create a healthier future for Canadian youth.

Featured Posts
-
 Tbs Safety And Nebofleet Partnership Automates Workboat Safety
May 02, 2025
Tbs Safety And Nebofleet Partnership Automates Workboat Safety
May 02, 2025 -
 P Syxiki Ygeia Stin Ellada I Ethniki Stratigiki 2025 2028
May 02, 2025
P Syxiki Ygeia Stin Ellada I Ethniki Stratigiki 2025 2028
May 02, 2025 -
 Actress Priscilla Pointer Dead At 100 A Legacy Remembered
May 02, 2025
Actress Priscilla Pointer Dead At 100 A Legacy Remembered
May 02, 2025 -
 Bidens Economic Policies Successes Failures And Future Outlook
May 02, 2025
Bidens Economic Policies Successes Failures And Future Outlook
May 02, 2025 -
 Loyle Carner Live At 3 Arena Date And Ticket Information
May 02, 2025
Loyle Carner Live At 3 Arena Date And Ticket Information
May 02, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Deconstructing The Arguments Around Trumps Transgender Military Ban
May 10, 2025
Deconstructing The Arguments Around Trumps Transgender Military Ban
May 10, 2025 -
 The Impact Of Trumps Transgender Military Ban An Opinion
May 10, 2025
The Impact Of Trumps Transgender Military Ban An Opinion
May 10, 2025 -
 Trumps Transgender Military Policy A Comprehensive Analysis
May 10, 2025
Trumps Transgender Military Policy A Comprehensive Analysis
May 10, 2025 -
 Dissecting Trumps Transgender Military Ban An Opinion Piece
May 10, 2025
Dissecting Trumps Transgender Military Ban An Opinion Piece
May 10, 2025 -
 The Transgender Military Ban Unpacking Trumps Rhetoric
May 10, 2025
The Transgender Military Ban Unpacking Trumps Rhetoric
May 10, 2025
