China's Drive To Reduce Reliance On US Pharmaceutical Imports

Table of Contents
Government Policies and Initiatives
The Chinese government has implemented a series of ambitious policies and initiatives aimed at bolstering domestic pharmaceutical production and reducing import reliance. These efforts represent a significant investment in national drug security.
National Drug Security Strategy
China's national drug security strategy is a multifaceted approach encompassing various policy levers. The government has actively pursued:
- Increased funding for R&D: Massive investments in research and development, both through direct government funding and tax incentives for private companies, are driving innovation in domestic pharmaceutical production.
- Streamlined drug approval processes: Efforts to expedite the approval process for new drugs, both domestically developed and imported, aim to accelerate the availability of essential medicines.
- Tax breaks and subsidies for domestic manufacturers: Significant tax breaks and subsidies are provided to incentivize domestic companies to increase production capacity and compete with foreign imports.
- Protectionist measures: While debated internationally, some measures aim to protect domestic companies from foreign competition and support the growth of the domestic pharmaceutical industry.
These initiatives collectively aim to foster "pharmaceutical independence" and ensure a reliable supply of essential medicines for the Chinese population, effectively reducing reliance on foreign pharmaceutical imports.
Investment in Domestic Research and Development (R&D)
China's investment in pharmaceutical R&D has skyrocketed in recent years. Both the government and the private sector are significantly increasing their spending, leading to:
- Growth in domestic pharmaceutical innovation: This increased investment fuels the development of novel drugs and treatments, lessening dependence on foreign technology.
- Successful domestic drug development: Several Chinese pharmaceutical companies have achieved significant breakthroughs in drug development, including in areas like oncology and infectious diseases.
- International collaborations: To accelerate innovation, Chinese pharmaceutical companies are increasingly collaborating with international partners on research and development projects. This allows them to access cutting-edge technologies and expertise.
This focus on "indigenous drug development" is central to China’s strategy to reduce its reliance on foreign pharmaceutical technology and ultimately reduce reliance on US pharmaceutical imports.
Growth of Domestic Pharmaceutical Companies
The expansion of domestic pharmaceutical companies is another key pillar of China’s strategy to achieve pharmaceutical self-sufficiency.
Expansion of Manufacturing Capacity
Chinese pharmaceutical manufacturers are rapidly expanding their production capacity, investing heavily in advanced technologies to enhance efficiency and competitiveness.
- Increased domestic manufacturing: A significant number of new pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities have been built across China, significantly boosting the country's overall production capacity.
- Technological advancements: Chinese companies are adopting advanced manufacturing technologies, including artificial intelligence and automation, to improve production efficiency and quality.
- Major players expanding: Companies like Sinopharm and CSPC are leading the expansion, investing billions in new facilities and equipment. This "increased domestic manufacturing" is crucial for reducing reliance on imports.
This rapid expansion of manufacturing capabilities ensures that China can meet its growing domestic demand for pharmaceuticals and, eventually, export to international markets.
Development of Generic Drugs and Biosimilars
China is aggressively pursuing the development and manufacturing of generic drugs and biosimilars. This strategy provides a cost-effective way to compete with more expensive brand-name drugs.
- Increased market share of generics: Generic and biosimilar drugs are gaining significant market share in China, driven by government price controls and increased affordability.
- Reducing drug costs: The widespread adoption of generics and biosimilars has contributed to a significant reduction in drug costs for Chinese consumers.
This focus on "generic drug production" and "biosimilar development" directly contributes to the goal of reducing reliance on expensive imported pharmaceuticals.
Challenges and Obstacles
Despite significant progress, China still faces several challenges in its drive to reduce reliance on US pharmaceutical imports.
Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) Concerns
Concerns regarding intellectual property rights (IPR) protection remain a significant obstacle. This impacts foreign investment and the transfer of advanced pharmaceutical technologies.
- IPR disputes: Disputes over IPR have occasionally hampered the transfer of technology from foreign companies to domestic firms.
- Impact on foreign investment: Concerns about IPR protection can deter foreign pharmaceutical companies from investing in China, hindering the transfer of cutting-edge technologies and expertise.
Strengthening "IP protection" is crucial for attracting foreign investment and accelerating technological advancements in the Chinese pharmaceutical industry.
Maintaining Quality and Safety Standards
Maintaining high quality and safety standards in domestically produced pharmaceuticals is paramount to build both domestic and international trust.
- Regulatory framework: China's regulatory framework for pharmaceutical quality and safety is continuously evolving to meet international standards.
- Quality control measures: Strengthening quality control measures at every stage of the manufacturing process is crucial to ensure product safety and efficacy.
Ensuring "pharmaceutical quality control" and adherence to stringent "drug safety regulations" are vital to building confidence in the quality and reliability of Chinese-produced pharmaceuticals.
Conclusion
China's drive to reduce reliance on US pharmaceutical imports is a complex and multifaceted undertaking. The government's strategic policies, combined with the rapid growth of domestic pharmaceutical companies, are driving significant progress toward self-sufficiency. However, challenges regarding intellectual property rights and maintaining stringent quality and safety standards remain. The success of this ambitious endeavor will have significant implications for the global pharmaceutical landscape, impacting international trade and healthcare access worldwide. To stay informed about the ongoing developments in China's pharmaceutical sector, continue researching the latest developments related to China's drive to reduce reliance on US pharmaceutical imports and the future of China's pharmaceutical independence. Further research into the specific policies and company strategies involved is highly recommended.

Featured Posts
-
 Becciu Condannato Dal Vaticano Il Risarcimento Agli Accusatori
Apr 30, 2025
Becciu Condannato Dal Vaticano Il Risarcimento Agli Accusatori
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Novoe O Bolezni Materi Beyonse Poslednie Izvestiya
Apr 30, 2025
Novoe O Bolezni Materi Beyonse Poslednie Izvestiya
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Alkwnghw Aldymqratyt Tetmd Ela Bakambw Fy Mshwarha Nhw Kas Alealm 2026
Apr 30, 2025
Alkwnghw Aldymqratyt Tetmd Ela Bakambw Fy Mshwarha Nhw Kas Alealm 2026
Apr 30, 2025 -
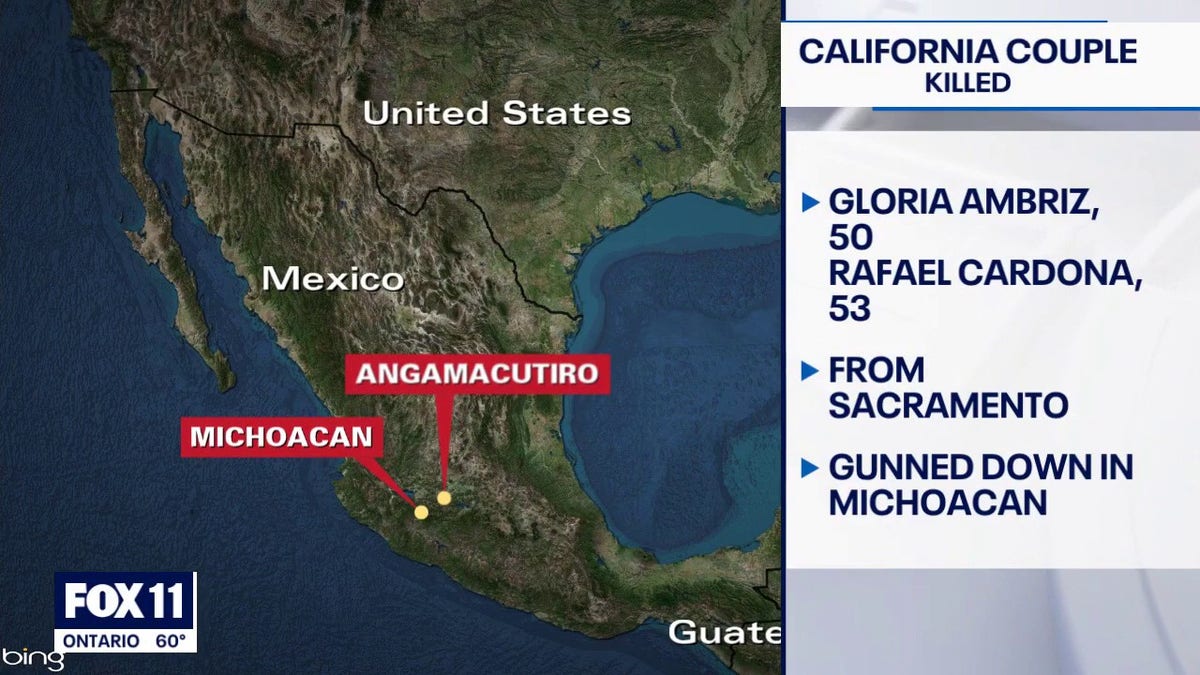 Mexican Human Rights Couple Found Dead Investigation Into Disappearance
Apr 30, 2025
Mexican Human Rights Couple Found Dead Investigation Into Disappearance
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Beyonce And Jay Zs Daughters Show Stopping Super Bowl Fashion
Apr 30, 2025
Beyonce And Jay Zs Daughters Show Stopping Super Bowl Fashion
Apr 30, 2025
