COVID-19 Case Increase: A New Variant's Potential Role, According To The WHO

Table of Contents
Identifying the Contributing Factors to the COVID-19 Case Increase
The recent rise in COVID-19 infections is not solely attributable to new variants. Several interconnected factors contribute to this increase. While new variants play a role, understanding the broader context is essential for effective mitigation strategies. Attributing the surge solely to one factor would be an oversimplification.
-
Decreased Vaccination Rates and Booster Uptake: Lower-than-ideal vaccination rates globally, coupled with a decline in booster shot uptake, have left many individuals with waning immunity. This makes populations more vulnerable to infection, even from less severe variants.
-
Relaxation of Public Health Measures: The easing of restrictions, including mask mandates and social distancing guidelines, has facilitated increased viral transmission. This relaxation, while aimed at returning to normalcy, increases the risk of outbreaks.
-
Increased Social Gatherings and Travel: Increased social interaction and international travel during periods of reduced public health vigilance provide ample opportunities for viral spread. The higher the density of individuals in close proximity, the greater the risk of transmission.
-
Potential for Underreporting of Cases: With reduced testing and surveillance in many regions, the actual number of COVID-19 cases might be significantly higher than officially reported. This underreporting makes it difficult to accurately assess the scale of the increase and implement targeted interventions. Improved testing and surveillance are key to a more accurate picture.
Analysis of New COVID-19 Variants and their Characteristics
Several new variants of concern have emerged, contributing to the COVID-19 case increase. These variants exhibit characteristics that influence their spread and severity. The WHO closely monitors these developments, issuing regular updates.
-
Increased Transmissibility: Some new variants demonstrate significantly higher transmissibility than previous strains. This increased ability to spread rapidly contributes significantly to the overall case increase. Higher transmissibility necessitates more robust preventative measures.
-
Potential for Immune Evasion: Certain variants exhibit the capacity to evade the immune response generated by previous infections or vaccinations. This immune evasion means that even previously infected or vaccinated individuals are at risk of reinfection.
-
Severity of Illness: While some variants might not cause more severe illness, the sheer volume of infections caused by their increased transmissibility can still overwhelm healthcare systems. The overall impact on public health is dependent on both transmissibility and severity.
-
Geographic Spread and Prevalence: Tracking the geographic distribution and prevalence of each variant is vital. Some variants might be concentrated in specific regions, while others exhibit a wider global spread, influencing the overall global COVID-19 case increase.
-
WHO Classification and Risk Assessment: The WHO constantly assesses new variants, classifying them according to their potential risk to public health. These classifications guide international responses and inform public health strategies globally. Understanding the WHO's risk assessments is critical for informed decision-making.
WHO's Response to the COVID-19 Case Increase
The WHO plays a crucial role in coordinating the global response to the increased COVID-19 cases. Their actions are pivotal in mitigating the pandemic's impact.
-
Global Monitoring of New Variants: The WHO maintains a rigorous global surveillance system to monitor the emergence and spread of new variants. This surveillance is crucial for early detection and rapid response.
-
Guidance on Vaccination, Testing, and Public Health Measures: The WHO provides evidence-based guidance to countries on vaccination strategies, testing protocols, and appropriate public health measures. This guidance helps to harmonize responses across nations.
-
Collaboration with Member States to Contain the Spread: The WHO facilitates collaboration among member states, promoting information sharing and coordinated responses to outbreaks. International cooperation is essential for effective pandemic management.
-
Communication Strategies to Inform the Public: The WHO communicates regularly with the public, providing updates on the evolving situation and dispelling misinformation. Clear, consistent communication is crucial in public health emergencies.
Implications for Public Health Strategies and Individual Actions
Managing the COVID-19 case increase requires a multifaceted approach involving public health strategies and individual actions.
-
Importance of Vaccination and Boosters: Vaccination and booster shots remain critical for protecting individuals and reducing the severity of illness. Staying up-to-date with vaccinations is a personal responsibility.
-
Continued Hand Hygiene and Mask-Wearing in High-Risk Settings: Basic preventive measures, such as frequent handwashing and wearing masks in crowded or poorly ventilated areas, remain essential. Simple measures can significantly reduce transmission.
-
Maintaining Social Distancing Where Appropriate: Maintaining physical distance in crowded settings helps to reduce the risk of transmission. Situational awareness and appropriate distancing are vital.
-
Seeking Testing and Medical Care When Symptoms Appear: Prompt testing and seeking medical attention when symptoms appear helps to prevent further spread and ensures access to appropriate care. Early intervention is crucial.
-
The Role of Genomic Surveillance in Tracking Variants: Continuous genomic surveillance is critical for identifying emerging variants and tracking their spread. Data-driven insights are essential for informing public health responses.
Conclusion
The recent COVID-19 case increase is a complex issue with multiple contributing factors, including the emergence of new variants and waning immunity. The WHO's role in monitoring, assessing, and responding to these developments is critical. Understanding the characteristics of new variants and implementing appropriate public health strategies are essential for managing the pandemic effectively. The collective effort of governments, healthcare professionals, and individuals is vital in controlling the COVID-19 case increase.
Call to Action: Stay informed about the latest developments regarding the COVID-19 case increase by regularly checking the WHO website and following public health guidelines. Your actions play a vital role in protecting yourself and your community from this evolving situation. Stay vigilant and contribute to reducing the spread of COVID-19. Let's work together to manage this ongoing challenge.

Featured Posts
-
 Zverev Fights Back To Reach Munich Open Semifinals
May 31, 2025
Zverev Fights Back To Reach Munich Open Semifinals
May 31, 2025 -
 Skubals Focus Shifts Ahead Of Crucial Rematch Following Grand Slam
May 31, 2025
Skubals Focus Shifts Ahead Of Crucial Rematch Following Grand Slam
May 31, 2025 -
 Jannik Sinner Tro Lai Rome Masters San Sang Doi Dau Carlos Alcaraz
May 31, 2025
Jannik Sinner Tro Lai Rome Masters San Sang Doi Dau Carlos Alcaraz
May 31, 2025 -
 Large Scale Fire On East London High Street Requires 100 Firefighters
May 31, 2025
Large Scale Fire On East London High Street Requires 100 Firefighters
May 31, 2025 -
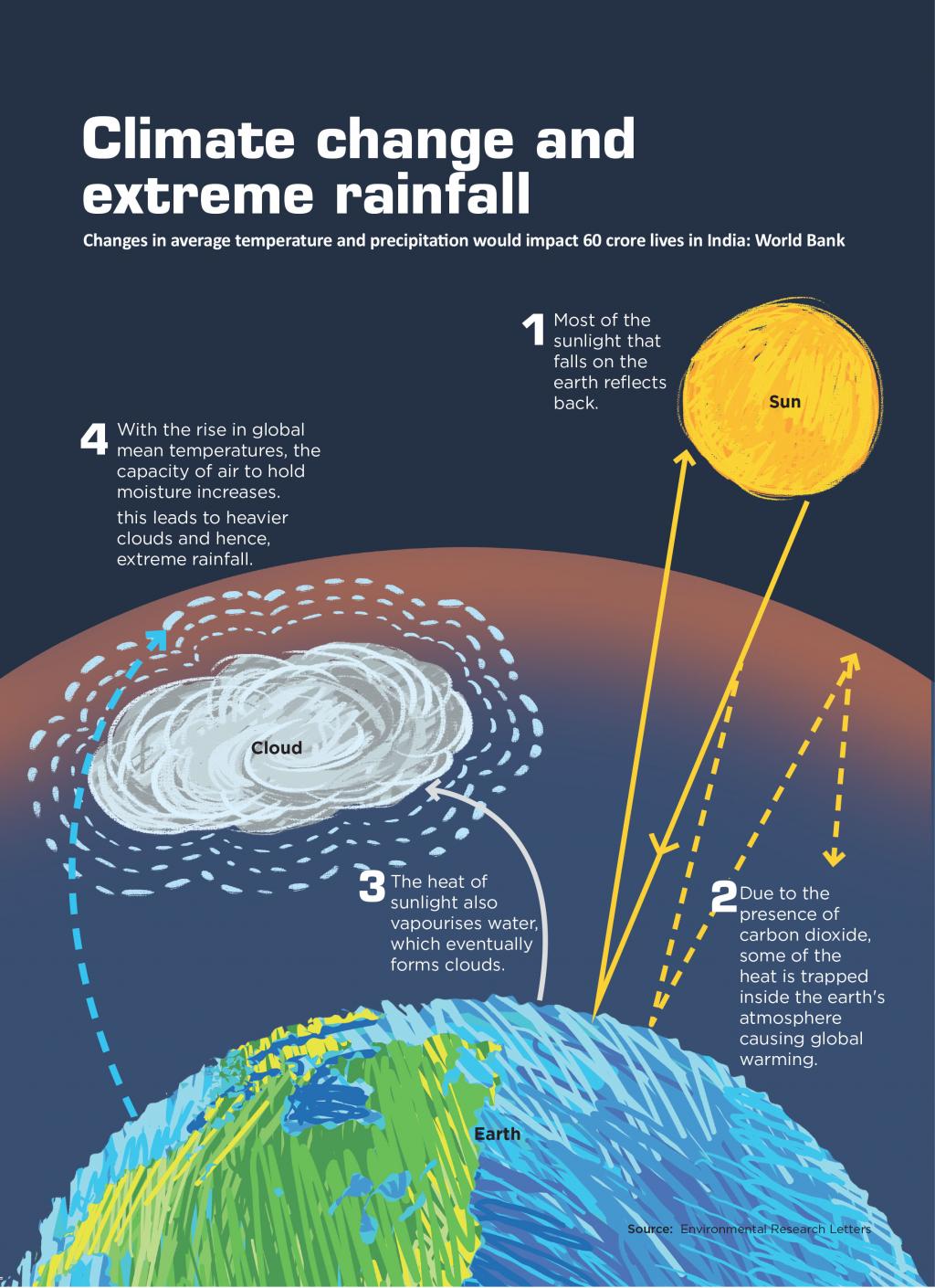 Climate Changes Effect On Rainfall The Case Of Western Massachusetts
May 31, 2025
Climate Changes Effect On Rainfall The Case Of Western Massachusetts
May 31, 2025
