De Minimis Tariffs On Chinese Goods: Examining The G-7's Approach To Trade Policy
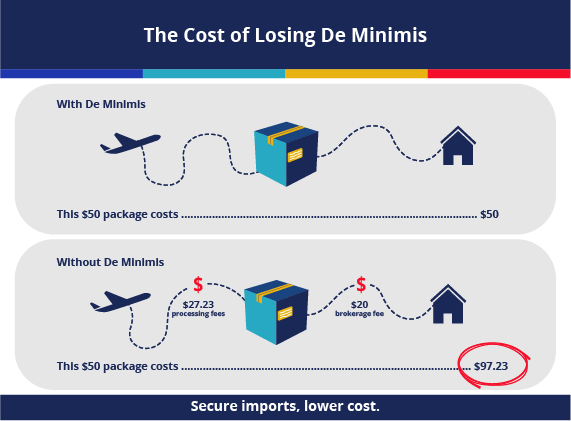
Table of Contents
The Current Landscape of De Minimis Tariffs within the G7
The G7 nations—the US, UK, Canada, France, Germany, Italy, and Japan—each employ their own de minimis tariff thresholds. These thresholds determine the value of goods imported from countries like China that can enter a country duty-free. The lack of uniformity presents a significant challenge for businesses and policymakers alike.
Variation in De Minimis Thresholds Across G7 Nations
The inconsistencies in de minimis thresholds across the G7 create a fragmented and uneven playing field for businesses. These differences can lead to trade imbalances and competitive disadvantages.
- United States: $800
- United Kingdom: £135
- Canada: CAD 40
- France: €150
- Germany: €22
- Italy: €22
- Japan: ¥16,000
These varying thresholds have far-reaching implications. For example, a small business in the UK might find it easier to import goods from China under its relatively higher threshold compared to a similar business in Germany, creating an uneven playing field within the EU and impacting China trade significantly. This disparity creates complications for businesses seeking to import goods consistently across multiple G7 markets. The lack of harmonization impacts import tariffs and necessitates navigating complex regulatory frameworks, increasing compliance costs and administrative burdens.
Impact of De Minimis Tariffs on Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs)
SMEs, often lacking the resources of larger corporations, are disproportionately affected by inconsistent de minimis tariffs. Navigating the differing thresholds across G7 nations adds to their already substantial administrative burdens.
- Increased Compliance Costs: SMEs must dedicate resources to understand and comply with various regulations across different markets, consuming time and resources that could be invested in growth.
- Reduced Competitiveness: Inconsistent tariffs can make it difficult for SMEs to compete with larger companies that may have greater capacity to manage complex regulations.
- Limited Access to Markets: The varying thresholds can effectively limit SMEs' access to certain G7 markets, hindering their potential for international expansion and China trade.
Policy recommendations to mitigate these challenges include: providing targeted support and training programs for SMEs in navigating international trade regulations, advocating for greater harmonization of de minimis thresholds amongst G7 nations, and simplifying customs procedures to reduce the administrative burden.
The Economic and Geopolitical Implications of De Minimis Tariffs on China-G7 Trade
De minimis tariffs, seemingly minor, carry significant economic and geopolitical weight within the China-G7 trade relationship. Their impact extends beyond simple import costs, influencing trade balances and shaping international relations.
Trade Balance and its Relationship to De Minimis Tariffs
The impact of de minimis tariffs on the overall trade balance between the G7 and China is complex and not fully understood. However, it's clear that inconsistencies in thresholds can create an environment ripe for manipulation. A country with a lower threshold could potentially attract a larger share of imports from China, impacting the overall trade balance. The use of de minimis tariffs, therefore, needs to be carefully considered within the larger context of trade negotiations and agreements. Furthermore, the influence of these tariffs on overall import tariffs is often overlooked, needing more transparent data and thorough economic analysis.
Geopolitical Considerations and the Use of De Minimis Tariffs as a Trade Weapon
De minimis tariffs can serve as tools in geopolitical strategies. Adjustments to thresholds can be used to exert pressure, reward allies, or penalize perceived adversaries. This can lead to escalating trade tensions, especially in the context of already strained G7-China relations. The possibility of using these seemingly minor adjustments as trade weapons raises concerns about the fairness and predictability of international trade. Cooperation and harmonization amongst G7 nations are crucial in mitigating the potential for escalation and ensuring a level playing field.
Future Trends and Potential Reforms in De Minimis Tariff Policies
Looking forward, there's a growing need for reform and harmonization in de minimis tariff policies. The current landscape is unsustainable, particularly given the rise of e-commerce and the increasing interconnectedness of global trade.
Calls for Harmonization and Standardization of De Minimis Thresholds
Harmonizing de minimis tariffs across the G7 is a complex but potentially beneficial undertaking. While some argue it would simplify trade and foster greater predictability, others worry it could lead to unintended consequences. A standardized threshold could reduce the administrative burden for businesses, but setting a universally acceptable value is a significant challenge, requiring comprehensive negotiations and potentially compromising individual national interests. The feasibility of such an undertaking is influenced heavily by existing trade agreements and the political will of the G7 nations. Therefore, achieving harmonization requires careful consideration of the potential benefits and drawbacks.
The Role of Technology and E-commerce in Shaping Future De Minimis Tariff Policies
The rise of e-commerce has further complicated the enforcement and relevance of de minimis tariffs. Online marketplaces facilitate the easy import of smaller, lower-value goods that often fall under the de minimis threshold. This presents significant challenges for customs authorities in tracking and regulating these imports. The speed and scale of e-commerce necessitates new approaches to ensuring compliance with de minimis rules. Future policies must address these challenges, potentially involving advanced technologies such as data analytics and automation, to manage the complexities of cross-border e-commerce while still supporting the development of online marketplaces.
Conclusion: Understanding the Significance of De Minimis Tariffs on Chinese Goods and the G7's Approach
The G7's approach to de minimis tariffs on Chinese goods reveals inconsistencies that create economic and geopolitical challenges. The lack of harmonization disproportionately impacts SMEs, creates potential for trade imbalances, and raises concerns about the use of tariffs as tools in geopolitical strategies. Understanding these complexities is vital for navigating the current trade landscape. By understanding the intricacies of de minimis tariffs on Chinese goods and their impact on G7 trade policy, we can foster more informed discussions and advocate for fairer, more predictable trade relations. Continue to research and stay informed on developments in de minimis tariffs on Chinese goods to contribute to a more balanced global trade system.

Featured Posts
-
 Muzarabanis Nine Wicket Haul Zimbabwe Celebrate Historic First Test Win Over Bangladesh
May 23, 2025
Muzarabanis Nine Wicket Haul Zimbabwe Celebrate Historic First Test Win Over Bangladesh
May 23, 2025 -
 Scrutiny Of Thames Water Executive Bonuses Were They Justified
May 23, 2025
Scrutiny Of Thames Water Executive Bonuses Were They Justified
May 23, 2025 -
 Flintoffs Story New Disney Documentary Details Career And Near Fatal Crash
May 23, 2025
Flintoffs Story New Disney Documentary Details Career And Near Fatal Crash
May 23, 2025 -
 Karate Kid 6 Ralph Macchios Return And A Controversial Film Revival
May 23, 2025
Karate Kid 6 Ralph Macchios Return And A Controversial Film Revival
May 23, 2025 -
 Critics Praise Jackie Chan And Ralph Macchio In Karate Kid Legend
May 23, 2025
Critics Praise Jackie Chan And Ralph Macchio In Karate Kid Legend
May 23, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 The Jonas Brothers Joe Jonas And A Hilarious Marital Dispute
May 23, 2025
The Jonas Brothers Joe Jonas And A Hilarious Marital Dispute
May 23, 2025 -
 Joe Jonas Handling A Unique Fan Interaction
May 23, 2025
Joe Jonas Handling A Unique Fan Interaction
May 23, 2025 -
 How Joe Jonas Responded To A Couple Fighting Over Him
May 23, 2025
How Joe Jonas Responded To A Couple Fighting Over Him
May 23, 2025 -
 Joe Jonas Responds To Married Couples Public Dispute
May 23, 2025
Joe Jonas Responds To Married Couples Public Dispute
May 23, 2025 -
 Couple Fights Over Joe Jonas His Hilarious Reaction
May 23, 2025
Couple Fights Over Joe Jonas His Hilarious Reaction
May 23, 2025
