Discussions Heat Up: EU Plans For Russian Gas Spot Market Elimination
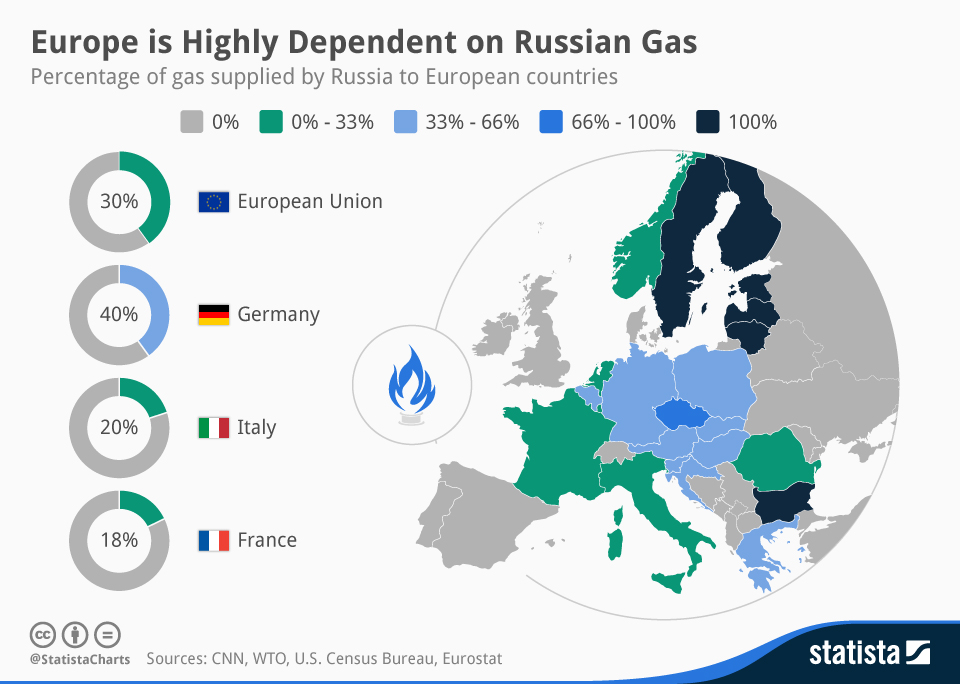
Table of Contents
The Rationale Behind the EU's Proposal
The EU's proposal to eliminate the Russian gas spot market stems from a multifaceted need to bolster its energy security and reduce its dependence on a single, unreliable supplier.
Reducing Dependence on Russian Energy
Relying heavily on one energy source, especially from a politically volatile region, presents significant risks.
- Vulnerability to Supply Disruptions: The war in Ukraine dramatically highlighted the vulnerability of relying on a single supplier. Russia's weaponization of energy supplies underscores the need for diversification.
- Past Energy Crises: Previous energy crises, such as the 2009 gas dispute between Russia and Ukraine, demonstrated the economic and social ramifications of energy supply disruptions.
- Political Leverage: Russia's control over gas supplies has given it considerable political leverage over EU member states. Eliminating this leverage is a key strategic goal.
These factors underscore the urgent need for energy independence and diversification of energy sources. The EU aims to establish a resilient energy system less susceptible to geopolitical pressures.
Sanctions and Geopolitical Implications
The EU's sanctions against Russia play a crucial role in the plan to eliminate the Russian gas market.
- Impact on Russian Gas Exports: Sanctions have significantly impacted Russian gas exports, forcing the Kremlin to seek alternative markets and causing considerable revenue loss.
- Enforcement Challenges: Enforcing sanctions effectively presents significant challenges, particularly given the complexities of international gas trade and the potential for circumvention.
- Retaliatory Measures: Russia has responded to sanctions with retaliatory measures, further impacting gas supplies and highlighting the geopolitical tensions involved.
The interplay between sanctions and the elimination of the Russian gas market is a complex and evolving situation, with far-reaching geopolitical implications.
Challenges and Obstacles to Implementation
The EU's plan to eliminate Russian gas faces numerous obstacles.
Finding Alternative Gas Suppliers
Replacing Russian gas is a considerable challenge.
- LNG Imports: The EU is increasing LNG imports, but this requires significant investment in port infrastructure and regasification facilities.
- Alternative Gas Suppliers: While Norway and other countries are increasing their gas exports to the EU, these sources might not fully compensate for the loss of Russian gas.
- Gas Infrastructure: The EU's existing gas infrastructure is largely designed for pipeline gas, requiring substantial adjustments to accommodate increased LNG imports.
- Price Volatility: The transition to alternative gas suppliers is likely to lead to increased price volatility in the short term.
Economic and Social Impacts
Eliminating Russian gas will have significant economic and social consequences for some EU member states.
- Energy Prices: Increased energy prices are a major concern, potentially leading to inflation and impacting household budgets.
- Impact on Industries: Energy-intensive industries could face significant challenges, requiring adjustments to their operations and potentially leading to job losses.
- Social Safety Nets: EU member states will need to implement robust social safety nets to mitigate the impact of rising energy costs on vulnerable populations. The affordability of energy will be key.
Internal EU Disagreements
The EU's plan is not without internal disagreements.
- Varying Levels of Dependence: EU member states have varying levels of dependence on Russian gas, leading to different perspectives on the speed and methods of elimination.
- National Interests: National interests often clash, impacting the EU's ability to implement a unified energy policy.
- Potential Compromises: Finding compromises that satisfy all member states will require careful negotiation and consideration of diverse national circumstances. Coordination of EU energy policy is vital for success.
Potential Long-Term Impacts and Strategies
The elimination of Russian gas presents both challenges and opportunities.
Accelerated Green Transition
The crisis might accelerate the EU's transition to renewable energy sources.
- Investments in Renewables: The urgency of reducing reliance on fossil fuels will likely lead to increased investments in renewable energy technologies, such as solar, wind, and geothermal power.
- Energy Efficiency Measures: Energy efficiency improvements in buildings and industries will play a key role in reducing overall energy consumption.
- Technological Innovation: The drive for energy independence will stimulate technological innovation in renewable energy and energy storage. The sustainable energy transition is crucial.
Strengthening Energy Partnerships
The EU needs to strengthen its energy partnerships with other countries.
- Collaborations with Gas-Producing Countries: Developing closer relationships with other gas-producing countries will help to diversify the EU's energy supply.
- New Pipelines and LNG Infrastructure: Investments in new pipelines and the expansion of LNG infrastructure are vital for a secure and diverse energy supply. International energy cooperation is key.
- Energy Diplomacy: Active energy diplomacy will be necessary to secure reliable and affordable energy supplies from diverse sources.
Conclusion: The Future of the EU's Energy Independence
The EU's plan to eliminate the Russian gas spot market represents a significant shift in its energy policy, driven by geopolitical realities and a commitment to energy independence. While the transition faces considerable challenges, including economic impacts, internal disagreements, and the need to find reliable alternative suppliers, the long-term benefits of reduced reliance on a volatile energy source are undeniable. The EU’s plans for Russian gas spot market elimination will ultimately shape the future of its energy security and geopolitical standing. Stay informed about further developments in this crucial area, and engage in ongoing discussions regarding the EU's energy future. Explore relevant resources and continue to learn about the evolving landscape of EU energy policy.

Featured Posts
-
 Elite Universities Facing Funding Challenges Under Trump Administration
Apr 24, 2025
Elite Universities Facing Funding Challenges Under Trump Administration
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Hollywood Production Grinds To Halt Amidst Joint Actors And Writers Strike
Apr 24, 2025
Hollywood Production Grinds To Halt Amidst Joint Actors And Writers Strike
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Selling Sunset Star Condemns La Landlord Price Gouging After Fires
Apr 24, 2025
Selling Sunset Star Condemns La Landlord Price Gouging After Fires
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Child Actor Sophie Nyweide Known For Mammoth And Noah Passes Away At 24
Apr 24, 2025
Child Actor Sophie Nyweide Known For Mammoth And Noah Passes Away At 24
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Hong Kongs Chinese Stock Market A Rally Driven By Trade Talks
Apr 24, 2025
Hong Kongs Chinese Stock Market A Rally Driven By Trade Talks
Apr 24, 2025
