Economists Forecast Bank Of Canada Rate Cuts Following Tariff-Induced Job Losses
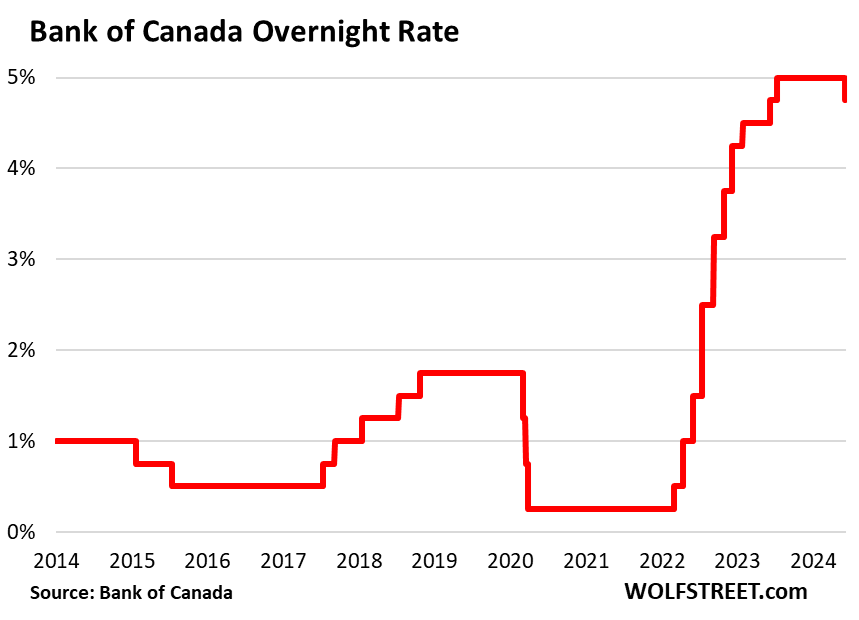
Table of Contents
The Impact of Tariffs on Canadian Employment
The increased tariffs have undeniably had a negative impact on Canadian employment. Industries heavily reliant on international trade, particularly manufacturing and agriculture, have been disproportionately affected. The "tariff impact" is being felt across various sectors, with the job market struggling to absorb the resulting job losses.
- Manufacturing: A recent report indicates a 3% decline in manufacturing jobs, impacting approximately 60,000 workers.
- Agriculture: The agricultural sector, already facing challenges, saw a 2% reduction in employment, further straining rural communities.
- Overall Unemployment Rate: The Canadian unemployment rate has climbed to 6.2%, a significant increase from 5.5% before the tariff implementation.
- Regional Disparities: The impact isn't uniform across the country, with provinces heavily reliant on specific sectors experiencing more significant job losses. Ontario and Quebec, for example, are facing steeper job losses in manufacturing.
These statistics highlight the severe strain on Canadian employment caused by the tariffs, creating a compelling case for government intervention and emphasizing the need for effective solutions to mitigate the "sectoral impact" of these trade policies.
Economists' Predictions and Analysis
A growing consensus among economists points towards the likelihood of Bank of Canada rate cuts in response to the economic slowdown and tariff-induced job losses. Several prominent economists have publicly predicted a reduction in interest rates within the next quarter.
- Dr. Anya Sharma, Chief Economist at XYZ Financial: "Given the weakening economic growth and rising unemployment, a rate cut of at least 0.25% is highly probable in the upcoming monetary policy announcement. The Bank of Canada needs to act swiftly to stimulate the economy."
- Professor David Lee, University of Toronto: "Our economic forecast models predict a significant contraction in consumer spending due to job losses. This necessitates a proactive monetary policy response from the Bank of Canada to prevent a deeper recession."
The rationale behind these predictions centers on several key factors:
- Dampened Inflation: While inflation remains a concern, the economic slowdown caused by tariff-induced job losses has eased inflationary pressure, creating some leeway for interest rate cuts.
- Weakening Economic Growth: The decreased economic activity necessitates a stimulative measure to reignite growth and bolster consumer confidence.
- Stimulating the Economy: The Bank of Canada is likely to prioritize stimulating economic activity and preventing a prolonged recession, even at the potential cost of increased inflation.
These varied projections, employing diverse economic models, all indicate a strong probability of "Bank of Canada policy" changes involving "interest rate prediction" adjustments.
Potential Consequences of Rate Cuts
Implementing "monetary easing" through "Bank of Canada rate cuts" could have several potential effects.
Potential Positive Effects:
- Stimulated Borrowing and Investment: Lower interest rates make borrowing more attractive for businesses and consumers, potentially boosting investment and consumption.
- Increased Economic Growth: The increased borrowing and spending could lead to a revival of economic activity and job creation.
Potential Negative Effects:
- Increased Inflationary Pressure: Lower interest rates can fuel inflation if demand outpaces supply.
- Canadian Dollar Devaluation: Reduced interest rates can make the Canadian dollar less attractive to foreign investors, leading to devaluation.
The Bank of Canada needs to carefully weigh the potential benefits of stimulating the economy against the risks of increased inflation and currency devaluation. The trade-offs involved are complex and require a nuanced understanding of the current economic climate. This balancing act is crucial for achieving a sustainable "economic stimulus" without creating further instability.
Alternative Policy Responses Considered by the Bank of Canada
Besides rate cuts, the Bank of Canada might consider alternative "monetary policy tools" to address the economic slowdown.
- Quantitative Easing (QE): The Bank of Canada could implement QE by purchasing government bonds to inject liquidity into the financial system. This could lower long-term interest rates and stimulate lending.
- Targeted Lending Programs: The Bank of Canada could create specialized lending programs to support specific sectors heavily impacted by the tariffs.
The effectiveness of these alternative measures compared to interest rate adjustments depends on various factors, including the severity of the economic downturn and the overall state of the financial system. The "Bank of Canada response" will need to be tailored to the specific needs of the Canadian economy. Choosing the most effective tools for "economic recovery" is crucial.
Conclusion
Economists overwhelmingly predict "Bank of Canada rate cuts" in response to the "tariff-induced job losses" and the resulting economic slowdown. While rate cuts offer the potential for stimulating borrowing, investment, and growth, they also carry risks, including inflation and currency devaluation. The Bank of Canada must carefully consider these trade-offs and potentially explore alternative "monetary policy tools" to navigate this complex economic situation. The potential implications of both action and inaction are significant, making continuous monitoring of the situation crucial. To stay informed about the Bank of Canada's decisions and their impact, we encourage you to follow reputable news sources, economic analysis reports, and leading economists’ commentary on "Bank of Canada rate cuts" and the broader impact of "tariff-induced job losses" on the Canadian economy. Subscribe to leading financial publications or follow key economists on social media for updates and insights.

Featured Posts
-
 Captain America Brave New World Box Office A Disappointing Start For The Mcu
May 14, 2025
Captain America Brave New World Box Office A Disappointing Start For The Mcu
May 14, 2025 -
 Tommy Fury Challenges Jake Paul To A Rematch Hours After Denying It
May 14, 2025
Tommy Fury Challenges Jake Paul To A Rematch Hours After Denying It
May 14, 2025 -
 Icelandic Eurovision Boycott Call Over Israels Actions In Gaza
May 14, 2025
Icelandic Eurovision Boycott Call Over Israels Actions In Gaza
May 14, 2025 -
 Eurovision 2025 Contestants Uk Representative Semi Finals And Final Schedule
May 14, 2025
Eurovision 2025 Contestants Uk Representative Semi Finals And Final Schedule
May 14, 2025 -
 Franca E Haiti A Injustica Da Divida Da Independencia
May 14, 2025
Franca E Haiti A Injustica Da Divida Da Independencia
May 14, 2025
