EV Mandate Opposition: Car Dealers Push Back Again

Table of Contents
Economic Concerns Fueling EV Mandate Opposition
The economic implications of EV mandates are a primary source of concern for car dealerships. The substantial financial burden associated with transitioning to an EV-centric model is proving to be a major obstacle.
High Upfront Investment Costs for Dealerships
Adapting to the EV market requires significant upfront investments for dealerships, particularly smaller, independent ones.
- Need for specialized EV training: Dealership staff needs extensive training on EV technology, maintenance, and repair, adding to labor costs.
- Costly infrastructure upgrades: Installing EV charging stations, acquiring specialized tools for EV maintenance, and modifying service bays represent substantial capital expenditures.
- Inventory management challenges: Managing EV inventory alongside traditional gasoline-powered vehicles introduces complexities in logistics, storage, and sales strategies.
The financial burden of these upgrades can be crippling for many dealerships. Securing loans to cover these expenses can be challenging, especially for those already operating on tight margins. The lack of sufficient government support for these crucial infrastructure upgrades in many regions further exacerbates the problem, fueling EV mandate opposition.
Uncertainty Surrounding Consumer Demand and Market Readiness
Dealerships are expressing significant uncertainty regarding consumer demand for EVs and the overall market readiness for a widespread EV transition.
- Concerns about consumer acceptance of EVs: Range anxiety, charging infrastructure limitations, and the higher initial cost of EVs remain significant barriers to consumer adoption.
- Range anxiety: Consumers are still concerned about the driving range of EVs and the availability of charging stations, particularly on long journeys.
- Charging infrastructure limitations: The uneven distribution and reliability of public charging networks add to consumer hesitancy.
- Overall maturity of the EV market: The EV market is still relatively young, and there are concerns about the long-term reliability and residual value of EVs compared to gasoline-powered cars.
This uncertainty makes it difficult for dealerships to accurately predict demand and manage their inventory effectively, increasing the risk of overstocking EVs and suffering financial losses. The potential for lower residual values compared to internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles adds to the financial risk.
Logistical Challenges and Infrastructure Gaps Pose Obstacles
Beyond the economic concerns, logistical challenges and significant gaps in the necessary infrastructure are further contributing to EV mandate opposition.
Lack of Sufficient Charging Infrastructure
The lack of a robust and widespread charging infrastructure is a major impediment to both EV adoption and the success of EV mandates.
- Uneven distribution of charging stations: Charging stations are not evenly distributed across all regions, leaving many areas underserved.
- Lengthy charging times: Charging times for EVs can be significantly longer than refueling gasoline vehicles, creating inconvenience for consumers.
- Reliability issues with public charging networks: The reliability and availability of public charging stations can be inconsistent, causing further frustration for EV owners.
The absence of readily available and reliable charging infrastructure severely limits the practicality of EV ownership for many consumers, hindering the success of any EV mandate. This highlights the urgent need for government investment in charging infrastructure to support the transition to EVs.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Parts Shortages
The automotive industry is facing ongoing supply chain disruptions and parts shortages, which are particularly acute in the EV sector.
- Difficulties in obtaining EV components: Securing essential EV components, such as batteries and semiconductors, is a major challenge for manufacturers and dealerships.
- Battery shortages: The limited availability of batteries is a significant bottleneck in EV production.
- Potential delays in vehicle deliveries: Supply chain issues lead to delays in the delivery of new EVs, affecting dealerships' ability to meet customer demand.
These supply chain problems are exacerbating the challenges faced by dealerships in transitioning to EVs and fulfilling their sales quotas under any EV mandate. The resulting delays and uncertainties are further adding to the EV mandate opposition.
Concerns Regarding Consumer Choice and Market Competition
Dealerships also express concerns about the impact of EV mandates on consumer choice and market competition.
Limited EV Model Variety and High Prices
Currently, the variety of EV models available is limited, and the prices of EVs tend to be higher than comparable gasoline-powered cars.
- Lack of affordable EV options: The lack of affordable EVs limits the accessibility of this technology for many consumers.
- Limited choices in vehicle types and features: The range of EV models available is still relatively narrow compared to gasoline-powered cars.
- Overall higher price point compared to gasoline cars: The higher initial cost of EVs remains a major barrier to adoption for many consumers.
These limitations could be exacerbated by EV mandates, as they might unintentionally favor certain manufacturers and models, reducing competition and limiting consumer choice.
Fear of Reduced Consumer Autonomy and Market Distortion
Dealerships fear that EV mandates could lead to government overreach and distort the free market.
- Concerns about government overreach: Mandatory quotas could be seen as excessive government intervention in the market.
- Potential for market manipulation: Mandates could favor certain manufacturers or technologies over others, leading to market manipulation.
- Negative impact on consumer purchasing decisions: Consumers might resent being forced to buy EVs before they are ready or before sufficient infrastructure is in place.
This concern about reduced consumer autonomy and market distortion is a significant aspect of the EV mandate opposition. A free and competitive market is vital for innovation and consumer satisfaction.
Conclusion
The opposition to EV mandates is complex and driven by legitimate concerns within the car dealership network. Economic uncertainties, logistical hurdles, and apprehensions about consumer choice and fair market competition all contribute to this pushback. Finding solutions requires collaborative efforts between governments, manufacturers, and dealerships. Instead of rigid mandates, a balanced strategy that promotes sustainable growth, addresses infrastructure gaps, and supports dealerships in their transition is crucial. Prioritizing incentives for EV adoption rather than imposing mandates might be a more effective and less disruptive way to achieve widespread EV adoption, ultimately mitigating the ongoing EV mandate opposition.

Featured Posts
-
 Kyle Stowers And The Marlins The Power Of Journaling
May 28, 2025
Kyle Stowers And The Marlins The Power Of Journaling
May 28, 2025 -
 The Importance Of Middle Managers A Key To Employee Engagement And Productivity
May 28, 2025
The Importance Of Middle Managers A Key To Employee Engagement And Productivity
May 28, 2025 -
 Vente Flash Samsung Galaxy S25 Ultra 256 Go 5 Etoiles A 1196 50 E
May 28, 2025
Vente Flash Samsung Galaxy S25 Ultra 256 Go 5 Etoiles A 1196 50 E
May 28, 2025 -
 Alcarazs Dominance Swiateks Uncertainties Road To Roland Garros
May 28, 2025
Alcarazs Dominance Swiateks Uncertainties Road To Roland Garros
May 28, 2025 -
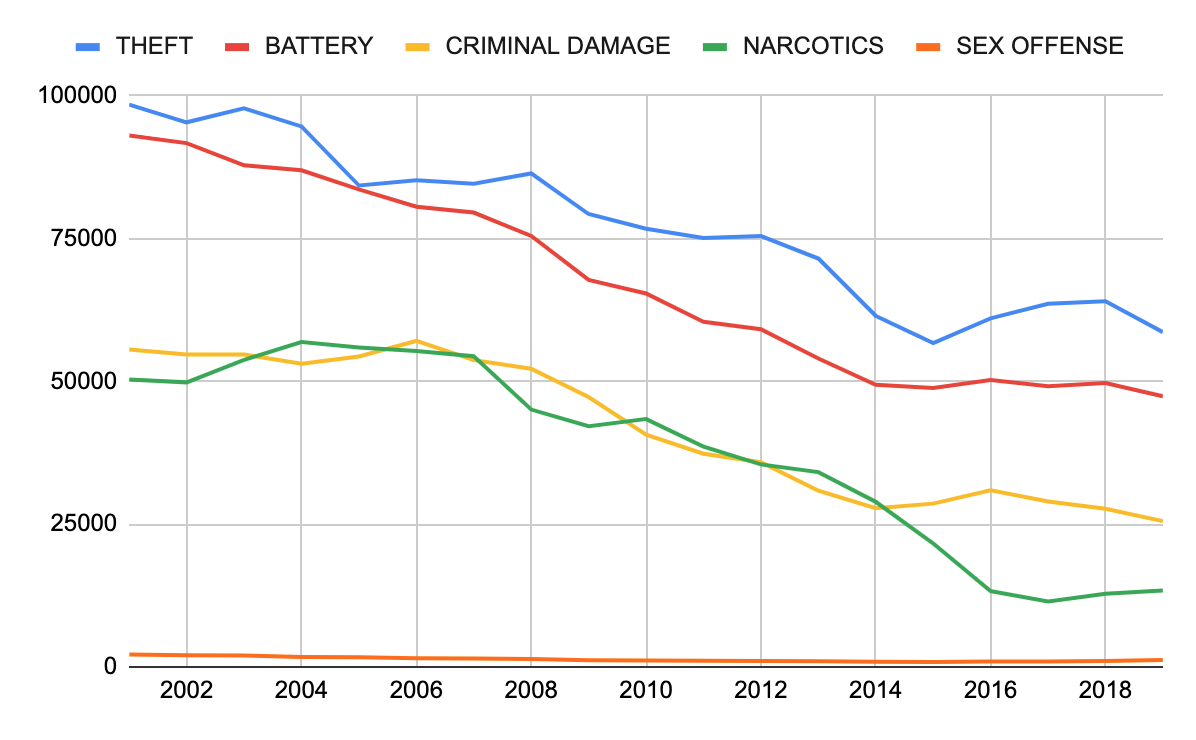 Chicago Crime Rate A Belated But Significant Decrease Whats Behind It
May 28, 2025
Chicago Crime Rate A Belated But Significant Decrease Whats Behind It
May 28, 2025
