Gas Prices Surge: Nearly 20-Cent Increase Per Gallon
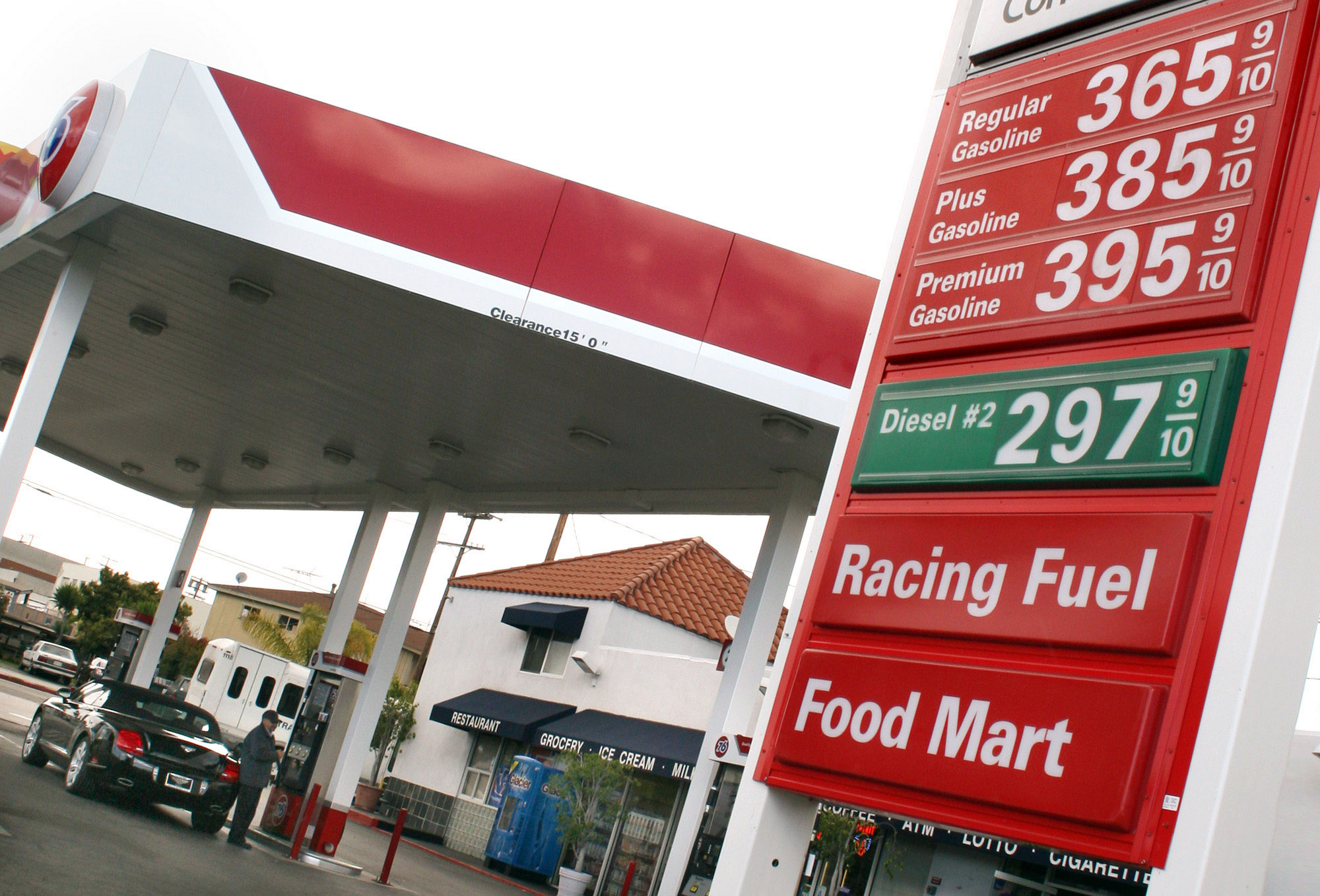

Table of Contents
Reasons Behind the Gas Price Surge
Several interconnected factors have contributed to this recent and dramatic gas prices surge. Understanding these complexities is crucial to grasping the current situation and predicting potential future fluctuations.
Geopolitical Factors
Global events significantly influence oil prices, the primary component of gasoline. Geopolitical instability, sanctions, and conflicts often disrupt oil supply chains, leading to price increases.
- The ongoing conflict in Eastern Europe: This has created significant uncertainty in the global energy market, impacting oil production and distribution.
- OPEC+ production cuts: Decisions by the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) and its allies to reduce oil production have also contributed to tightening supply and driving up prices.
- Increased demand from recovering economies: As global economies recover from the pandemic, demand for oil has increased, further pressuring prices. This increased global energy demand is putting upward pressure on the oil barrel price.
These geopolitical factors are not isolated events; they create a complex web of interconnected challenges that impact oil prices and, consequently, gas prices at the pump. Continued instability in these regions could lead to further price increases in the future.
Refinery Capacity and Production
The capacity and efficiency of oil refineries directly impact the availability of gasoline and other fuels. Reduced refinery output, due to various factors, can quickly lead to price increases.
- Planned and unplanned refinery maintenance: Scheduled maintenance and unexpected outages at refineries can temporarily reduce fuel production, impacting supply and driving prices higher.
- Supply chain disruptions: Difficulties in securing necessary parts, materials, or labor for refinery operations can also hinder production and contribute to price increases.
- Aging infrastructure: Many refineries are aging, leading to increased maintenance needs and potentially reducing their overall output capacity. Investments in new refinery capacity are crucial to meet future demands and stabilize prices.
These issues highlight the vulnerabilities within the fuel production and distribution networks. Any further disruptions to refinery operations could exacerbate the current gas prices surge.
Seasonal Demand and Increased Travel
Seasonal changes in consumer behavior significantly impact fuel demand, particularly during peak travel seasons. Increased travel during summer months naturally leads to higher demand for gasoline, resulting in increased prices.
- Summer vacation travel: The summer months consistently see a surge in road trips and leisure travel, driving up demand for gasoline.
- Increased commuting: Changes in weather patterns or other factors can also impact commuting patterns and daily fuel consumption.
- Back-to-school season: The start of the school year also often leads to increased fuel consumption due to children's activities and school transportation needs.
Predicting future seasonal demand is crucial for anticipating potential fluctuations in gas prices. Understanding these trends allows consumers and businesses to better prepare for anticipated price changes.
Impact of the Gas Price Increase on Consumers
The nearly 20-cent increase in gas prices has wide-ranging consequences for consumers and the overall economy.
Increased Transportation Costs
Higher gas prices directly translate into increased transportation costs for consumers. This impact ripples across many aspects of daily life:
- Commuting costs: Daily commutes become more expensive, impacting household budgets. The increase in gas prices can lead to an extra $20-$50 per month depending on the driving distance.
- Grocery shopping and other expenses: The cost of transporting goods increases, leading to potentially higher prices for consumers at the grocery store and other retail outlets.
- Reduced discretionary spending: Increased transportation costs can reduce the amount of money available for other expenses, impacting overall consumer spending. This reduction in discretionary spending can have broader impacts on the economy.
Strategies for Managing Increased Fuel Costs
While gas prices are beyond individual control, consumers can take steps to mitigate the impact on their wallets:
- Carpool or use public transportation: Sharing rides with colleagues or utilizing public transit can significantly reduce fuel consumption and expenses.
- Drive less: Consolidate errands, walk or cycle when feasible, and work from home if possible to decrease fuel consumption.
- Maintain your vehicle: Regularly scheduled vehicle maintenance, including proper tire inflation, ensures optimal fuel efficiency.
- Consider a fuel-efficient vehicle: Explore fuel-efficient vehicles or hybrids as long-term options to save money on fuel in the future.
- Use gas price comparison apps: Many apps can help find the lowest gas prices in your area, potentially saving money on every fill-up.
Impact on Businesses and the Economy
Rising gas prices also impact businesses and the broader economy:
- Increased operational costs: Businesses reliant on transportation, such as delivery services and trucking companies, face increased operational costs. This could lead to higher prices for consumers.
- Inflationary pressures: Increased transportation costs contribute to inflationary pressures, potentially impacting the overall cost of goods and services.
- Reduced economic growth: Higher fuel costs can hamper economic growth by reducing consumer spending and impacting business profitability.
Conclusion
The recent nearly 20-cent gas prices surge is a complex issue driven by a confluence of geopolitical events, refinery constraints, and seasonal demand. This increase significantly impacts consumers through higher transportation costs, reduced discretionary spending, and potentially higher prices for goods and services. Businesses also face increased operational costs and inflationary pressures. To mitigate the effects, consumers should adopt fuel-saving strategies and remain informed about future gas price fluctuations. Stay informed about future gas prices surge updates and adopt strategies to mitigate the rising costs.

Featured Posts
-
 Analysis Of Core Weave Crwv Stocks Positive Movement On Wednesday
May 22, 2025
Analysis Of Core Weave Crwv Stocks Positive Movement On Wednesday
May 22, 2025 -
 Gender Reveal Peppa Pigs Parents Announce Babys Sex
May 22, 2025
Gender Reveal Peppa Pigs Parents Announce Babys Sex
May 22, 2025 -
 Ap Photos Israeli Embassy Staff Killed In Dc Shooting Near Jewish Museum
May 22, 2025
Ap Photos Israeli Embassy Staff Killed In Dc Shooting Near Jewish Museum
May 22, 2025 -
 Former Ukrainian Official Shot Dead Outside Madrid American School
May 22, 2025
Former Ukrainian Official Shot Dead Outside Madrid American School
May 22, 2025 -
 Peppa Pig A New Baby Sister Arrives
May 22, 2025
Peppa Pig A New Baby Sister Arrives
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Zimbabwe Test Englands Confirmed Lineup
May 23, 2025
Zimbabwe Test Englands Confirmed Lineup
May 23, 2025 -
 Dan Lawrences England Test Opening Prospects A Look At His Future Ambitions
May 23, 2025
Dan Lawrences England Test Opening Prospects A Look At His Future Ambitions
May 23, 2025 -
 Sam Cook Englands New Test Bowler For Zimbabwe Series
May 23, 2025
Sam Cook Englands New Test Bowler For Zimbabwe Series
May 23, 2025 -
 Englands Playing Xi For Zimbabwe Test Revealed
May 23, 2025
Englands Playing Xi For Zimbabwe Test Revealed
May 23, 2025 -
 Cook Selected For Englands Zimbabwe Test Tour
May 23, 2025
Cook Selected For Englands Zimbabwe Test Tour
May 23, 2025
