Global Forest Destruction: A Record Year Fueled By Wildfires
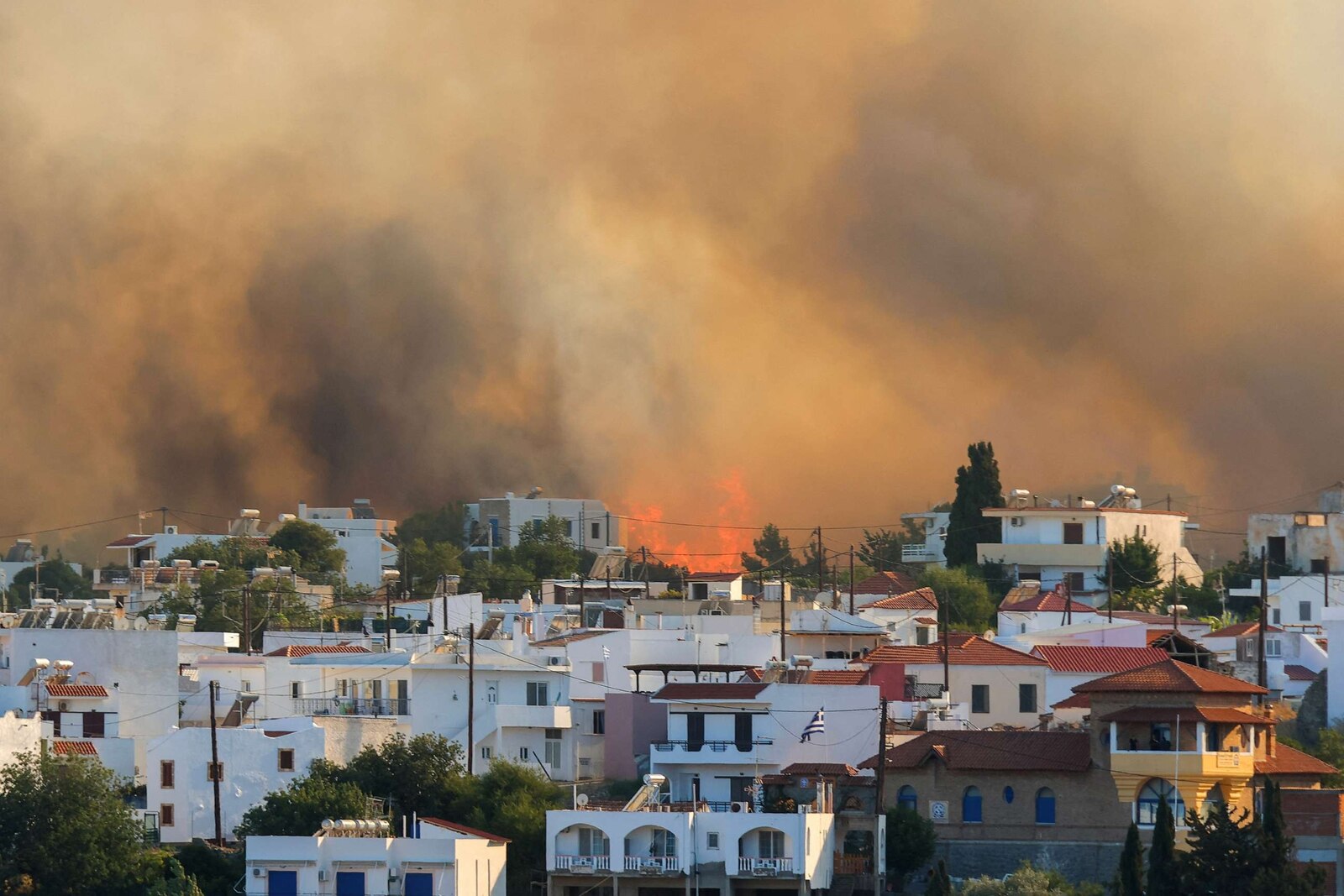

Table of Contents
The Role of Wildfires in Global Forest Destruction
Wildfires are a significant driver of global forest destruction, and their impact is worsening due to climate change. Increased temperatures and prolonged droughts create ideal conditions for wildfires to ignite and spread rapidly. The consequences are devastating, leading to widespread habitat loss and contributing significantly to global carbon emissions.
-
Increased frequency and intensity: Climate change-induced drought and heatwaves have led to a dramatic increase in the frequency and intensity of wildfires globally. Longer, hotter summers extend wildfire seasons, leaving forests vulnerable for longer periods.
-
Uncontainable infernos: The sheer scale of some wildfires, combined with remote locations and challenging terrain, makes them incredibly difficult to contain, leading to extensive forest destruction.
-
Biodiversity devastation: Wildfires devastate biodiversity, destroying habitats and killing countless plant and animal species. The loss of these ecosystems has cascading effects throughout the food web.
-
Carbon emissions surge: Burning forests release massive amounts of stored carbon into the atmosphere, significantly contributing to global warming and further exacerbating the climate crisis. This creates a dangerous feedback loop, accelerating the cycle of wildfires and deforestation.
According to Global Forest Watch, preliminary data suggests that [Insert statistic on hectares burned in 2023 compared to previous years, citing source]. Devastating examples include the [mention specific examples of major wildfires in different regions, e.g., Canadian wildfires of 2023, Australian bushfires of 2019-2020].
Deforestation Beyond Wildfires: Driving Forces and Impacts
While wildfires are a major contributor to global forest destruction, deforestation driven by human activities remains a critical issue. The clearing of forests for various purposes releases stored carbon, destroys habitats, and has far-reaching environmental consequences.
-
Illegal logging: Illegal logging and timber extraction remain a significant driver of deforestation, particularly in tropical regions. Weak governance and enforcement contribute to this illegal activity.
-
Agricultural expansion: The conversion of forests for agricultural purposes, such as palm oil plantations and cattle ranching, is a major cause of deforestation, particularly in the Amazon and Southeast Asia.
-
Mining operations: Mining operations often involve extensive clearing of forests for access roads, mining sites, and processing facilities, resulting in significant habitat destruction.
-
Urban sprawl: Rapid urbanization and infrastructure development continue to encroach on forested areas, leading to further forest loss.
-
Biodiversity loss: Deforestation leads to significant biodiversity loss, pushing numerous plant and animal species towards extinction due to habitat destruction and fragmentation.
The rate of deforestation in key regions remains alarming. For instance, the Amazon rainforest is experiencing [Insert statistic on deforestation rate in the Amazon, citing source], while the Congo Basin is facing [Insert statistic on deforestation rate in the Congo Basin, citing source]. International agreements like REDD+ aim to address this issue, but more robust implementation and enforcement are crucial.
The Environmental Consequences of Unprecedented Forest Loss
The unprecedented levels of forest loss have profound and interconnected environmental consequences, impacting the entire planet.
-
Accelerated climate change: The release of vast amounts of carbon dioxide from deforestation and wildfires accelerates climate change, leading to more frequent and intense extreme weather events.
-
Biodiversity collapse: Habitat loss and fragmentation lead to widespread biodiversity loss, threatening countless plant and animal species with extinction. This loss of biodiversity weakens ecosystems and reduces their resilience.
-
Disrupted water cycle: Forests play a vital role in regulating the water cycle. Deforestation can lead to altered rainfall patterns, increased droughts, and decreased water availability.
-
Soil erosion and degradation: The removal of forest cover exposes soil to erosion, leading to decreased soil fertility and impacting agricultural productivity.
-
Increased air pollution: Wildfires release significant amounts of air pollutants, impacting air quality and human health.
Combating Global Forest Destruction: Solutions and Strategies
Combating global forest destruction requires a multifaceted approach involving various stakeholders and strategies.
-
Sustainable forestry: Investing in sustainable forestry practices and responsible timber harvesting are crucial steps to reduce deforestation. Certification schemes, like the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC), can help ensure responsible forest management.
-
Enhanced wildfire management: Improving wildfire prevention and management strategies, including early detection systems and improved firefighting capabilities, is critical to minimizing wildfire damage.
-
Reforestation and afforestation: Large-scale reforestation and afforestation initiatives are necessary to restore degraded forests and increase carbon sequestration.
-
International cooperation: Strengthening international cooperation to combat illegal logging and deforestation is vital, involving stricter enforcement of regulations and collaborative efforts to monitor forest resources.
-
Policy changes: Implementing policies that incentivize forest conservation and sustainable land management, such as carbon pricing and payments for ecosystem services, can help shift incentives away from deforestation.
-
Public awareness: Raising public awareness about the importance of forest conservation and the devastating consequences of deforestation is crucial for driving behavioral change and supporting conservation efforts. The use of technology, such as satellite monitoring, plays an important role in tracking deforestation and informing conservation strategies.
Conclusion
The record-breaking levels of global forest destruction in 2023, largely driven by devastating wildfires and unsustainable practices, highlight the urgent need for concerted global action. The environmental consequences are far-reaching and pose a significant threat to the planet's future. By addressing the root causes of deforestation, improving wildfire management, and investing in reforestation efforts, we can work towards mitigating this crisis. We must collectively commit to protecting our forests and adopting sustainable practices to ensure the long-term health of our planet. Let's act now to curb global forest destruction and secure a sustainable future for generations to come.

Featured Posts
-
 En Cimri 3 Burc Paranizi Nasil Yoenetiyorlar
May 23, 2025
En Cimri 3 Burc Paranizi Nasil Yoenetiyorlar
May 23, 2025 -
 The Champions Trophy Beckons Englands Winter Countdown
May 23, 2025
The Champions Trophy Beckons Englands Winter Countdown
May 23, 2025 -
 Siren Film Review Analyzing The Performances Of Moore Fahy And Alcock
May 23, 2025
Siren Film Review Analyzing The Performances Of Moore Fahy And Alcock
May 23, 2025 -
 Jasprit Bumrah Remains Worlds Top Test Bowler
May 23, 2025
Jasprit Bumrah Remains Worlds Top Test Bowler
May 23, 2025 -
 Cat Deeleys Mint Velvet Dress Spotted At Liverpool One
May 23, 2025
Cat Deeleys Mint Velvet Dress Spotted At Liverpool One
May 23, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Unexpected Joe Jonas Concert Thrills Fort Worth Stockyards Crowd
May 23, 2025
Unexpected Joe Jonas Concert Thrills Fort Worth Stockyards Crowd
May 23, 2025 -
 Fort Worth Stockyards An Unforgettable Night With Joe Jonas
May 23, 2025
Fort Worth Stockyards An Unforgettable Night With Joe Jonas
May 23, 2025 -
 Dc Legends Of Tomorrow Frequently Asked Questions And Answers
May 23, 2025
Dc Legends Of Tomorrow Frequently Asked Questions And Answers
May 23, 2025 -
 The Last Rodeo Exploring Neal Mc Donoughs Character
May 23, 2025
The Last Rodeo Exploring Neal Mc Donoughs Character
May 23, 2025 -
 A Deep Dive Into Dc Legends Of Tomorrow
May 23, 2025
A Deep Dive Into Dc Legends Of Tomorrow
May 23, 2025
