Global Warming: The Rise Of Dangerous Fungi
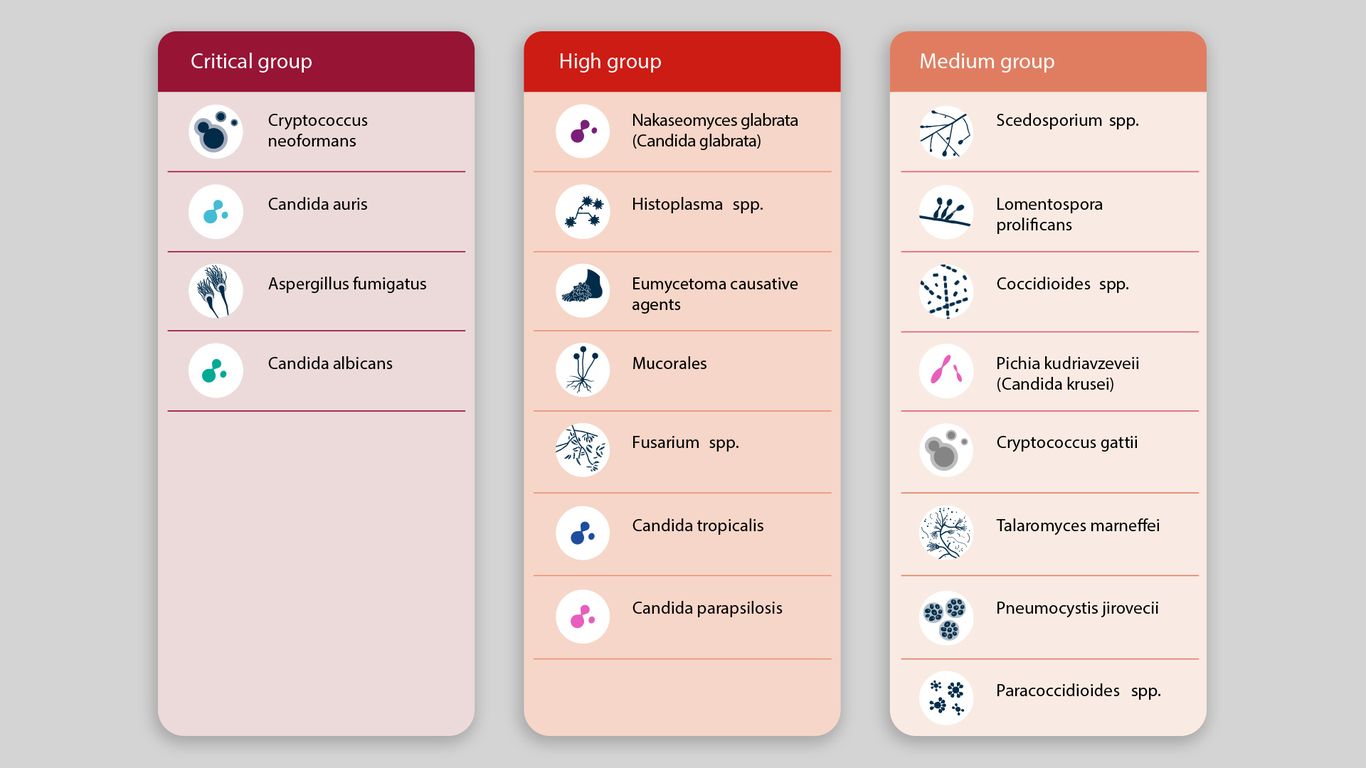
Table of Contents
The Impact of Rising Temperatures on Fungal Growth
Many fungi thrive within specific temperature ranges. Global warming is shifting these optimal ranges, expanding the geographical distribution and growth potential of dangerous species previously confined to smaller, warmer regions. This expansion poses a significant threat to both human and environmental health.
Optimal Temperature Ranges for Pathogenic Fungi
Many pathogenic fungi find their ideal growth temperatures increasing with global warming. Areas previously too cold now support their proliferation.
- Examples: Candida auris, a multi-drug-resistant yeast causing serious bloodstream infections, and Aspergillus fumigatus, a common cause of opportunistic pulmonary infections in immunocompromised individuals, are exhibiting expanded ranges.
- Temperature Thresholds: While specific thresholds vary by species, many pathogenic fungi show accelerated growth rates at temperatures just a few degrees Celsius above their historical optima. Climate change models predict exceeding these thresholds in numerous regions globally.
- Geographic Expansion: Mapping studies demonstrate the clear northward expansion of several fungal species' habitats, directly correlating with rising temperatures. This means increased human exposure in regions previously unaffected. (Imagine a map here visually illustrating this expansion).
Increased Humidity and Rainfall Favoring Fungal Spore Dispersion
Warmer temperatures frequently lead to increased humidity and rainfall. These conditions are ideal for fungal spore production and dispersal.
- Spore Germination: High humidity provides the necessary moisture for fungal spores to germinate and establish colonies.
- Extreme Weather Events: Floods and hurricanes, exacerbated by climate change, can act as potent vectors for fungal spores, leading to widespread outbreaks in their wake. Consider the increased mold growth after hurricanes, for example.
- Outbreak Examples: Several fungal outbreaks have been linked to extreme weather events, highlighting the direct connection between climate change, increased humidity, and fungal disease emergence.
Emerging Fungal Diseases and their Link to Climate Change
Higher temperatures are directly linked to an increase in the incidence of invasive fungal infections, particularly impacting vulnerable populations. This poses a serious public health concern.
Increased Incidence of Invasive Fungal Infections
Invasive fungal infections are becoming more common, and climate change is a contributing factor.
- Emerging Diseases: Coccidioidomycosis (Valley Fever), a respiratory illness caused by the fungus Coccidioides, is expanding its geographic range due to increasing temperatures and drought conditions.
- Geographic Range Shift: Many fungal diseases are shifting their ranges towards higher latitudes and altitudes, exposing new populations to these pathogens.
- Vulnerable Populations: Immunocompromised individuals (those with HIV/AIDS, undergoing chemotherapy, or organ transplant recipients), the elderly, and those with pre-existing conditions are particularly vulnerable to severe fungal infections.
Impact on Agriculture and Food Security
Climate change is severely impacting global food security through increased fungal diseases affecting major crops.
- Crop Losses: Fungal diseases like rusts, blights, and wilts are causing significant yield losses in wheat, rice, corn, and other staple crops.
- Economic Impact: Crop losses due to fungal infections translate to significant economic losses for farmers and increased food prices for consumers worldwide.
- Mitigation Strategies: Developing resistant crop varieties, implementing improved agricultural practices, and employing biocontrol agents are crucial strategies for mitigating the effects of fungal diseases on agriculture.
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies
Addressing the threat of dangerous fungi necessitates a two-pronged approach: mitigation and adaptation.
Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The most effective long-term strategy is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to mitigate the effects of climate change.
- Global Cooperation: International collaboration is essential for implementing effective climate change mitigation policies.
- Emission Reduction Technologies: Transitioning to renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and implementing carbon capture technologies are crucial steps.
Developing Antifungal Treatments and Prevention Strategies
Investing in research and development of new antifungal drugs and preventative measures is crucial to combat the rising threat.
- Improved Diagnostics: Early and accurate diagnosis is critical for effective treatment of invasive fungal infections. Better diagnostic tools are urgently needed.
- New Antifungal Therapies: Research into new antifungal drugs, especially those targeting multi-drug resistant species, is paramount.
- Public Health Initiatives: Public health awareness campaigns and improved prevention strategies are crucial for reducing the incidence of fungal infections.
Conclusion:
The rise of dangerous fungi, exacerbated by global warming, presents a significant and growing threat. From increased incidence of deadly fungal infections to devastating impacts on agriculture, the consequences are far-reaching. Addressing this requires a multifaceted approach: reducing greenhouse gas emissions through global cooperation and investing heavily in research and development of new antifungal treatments and preventative measures. Understanding the link between global warming and the rise of dangerous fungi is the first step toward mitigating this emerging threat. Let's act now to combat the effects of global warming and the dangerous fungi it breeds. Ignoring this interconnected issue will only amplify the risks we face.

Featured Posts
-
 The Naomi Campbell Anna Wintour Feud Implications For The 2025 Met Gala
May 25, 2025
The Naomi Campbell Anna Wintour Feud Implications For The 2025 Met Gala
May 25, 2025 -
 Rowing For A Cure A Fathers 2 2 Million Mission For His Son
May 25, 2025
Rowing For A Cure A Fathers 2 2 Million Mission For His Son
May 25, 2025 -
 Ardisson Vs Baffie Les Dessous D Une Relation Tendue
May 25, 2025
Ardisson Vs Baffie Les Dessous D Une Relation Tendue
May 25, 2025 -
 Shopping Mall Acquisition B C Billionaire Seeks Hudsons Bay Properties
May 25, 2025
Shopping Mall Acquisition B C Billionaire Seeks Hudsons Bay Properties
May 25, 2025 -
 Elon Musks Return To Form Positive Impact On Tesla
May 25, 2025
Elon Musks Return To Form Positive Impact On Tesla
May 25, 2025
