How Rising Federal Debt Influences The Mortgage Lending Landscape
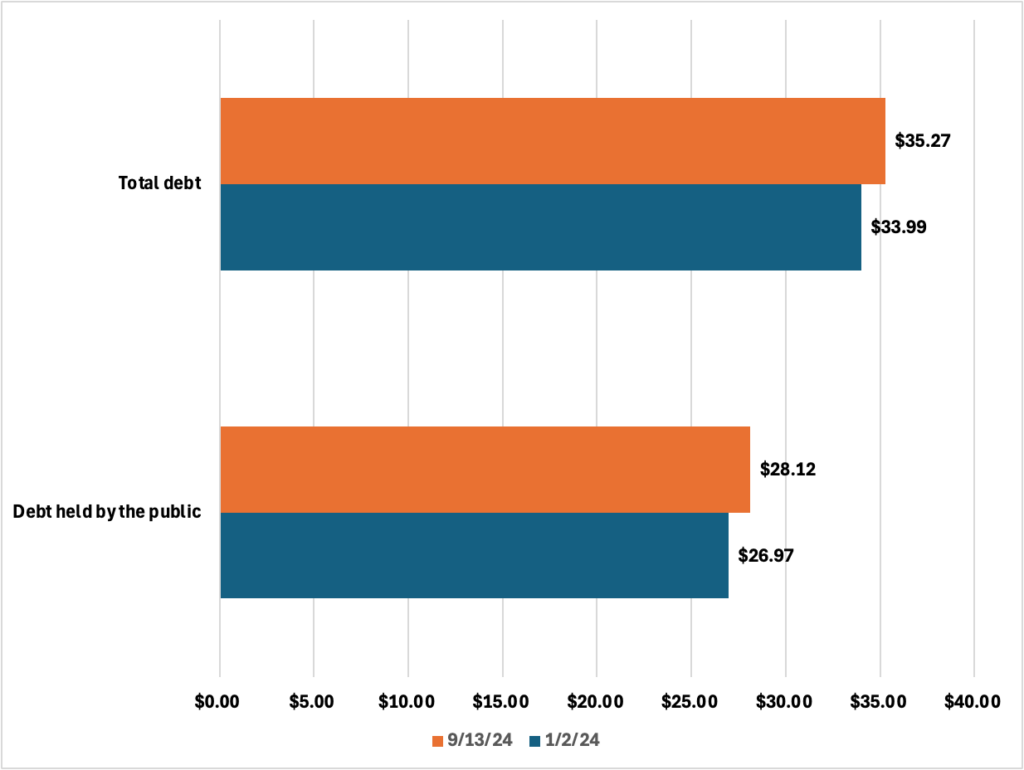
Table of Contents
The Impact of Federal Debt on Interest Rates
The connection between rising federal debt and mortgage rates is largely indirect, but significant. It primarily works through its influence on interest rates set by the Federal Reserve and investor sentiment.
The Federal Reserve's Role
The Federal Reserve (the Fed) plays a crucial role in managing interest rates. When the national debt rises, the government needs to borrow more money, increasing the demand for Treasury bonds.
- Increased government borrowing can drive up Treasury yields. Higher demand pushes up the price of these bonds, inversely impacting their yields (returns).
- Higher Treasury yields influence the prime rate and other benchmark rates. These benchmark rates serve as the foundation for many other interest rates, including those for mortgages.
- Inflation, exacerbated by increased government spending to finance the debt, further impacts interest rates. The Fed often raises rates to combat inflation, indirectly impacting mortgage rates.
Investor Sentiment and Risk
Rising national debt also affects investor confidence and risk perception. Uncertainty about the future of the economy can significantly impact the bond market and mortgage rates.
- Uncertainty about the future of the economy impacts the bond market. Investors may demand higher returns (yields) on bonds to compensate for the perceived increased risk.
- Increased risk premiums can translate into higher mortgage rates. Lenders pass these increased costs onto borrowers through higher interest rates.
- Credit rating downgrades on US debt can further increase borrowing costs. A downgrade signals increased risk, making it more expensive for the government and private entities to borrow money.
Changes in Mortgage Availability and Lending Standards
Economic uncertainty fueled by rising federal debt often leads to changes in mortgage availability and stricter lending standards. Lenders become more cautious, protecting their own financial stability.
Increased Scrutiny from Lenders
The increased risk associated with rising national debt translates into stricter lending practices.
- Higher credit score requirements: Lenders demand higher credit scores to minimize the risk of defaults.
- Stricter debt-to-income ratio limits: Borrowers with higher debt relative to their income are less likely to qualify for a mortgage.
- Decreased availability of certain mortgage products: Some riskier mortgage products, such as subprime loans, may become less available or disappear entirely.
Impact on Government-Backed Loans
Rising federal debt can also impact government-backed loan programs like FHA and VA loans.
- Potential budget constraints affecting these programs: Increased national debt could lead to reduced funding for these programs.
- Potential changes in eligibility requirements: To manage risk, eligibility criteria might become stricter.
- Impact on loan limits: Budgetary concerns might lead to lower loan limits, making homeownership less accessible for some.
The Long-Term Effects on Homeownership
The combined effects of rising federal debt on interest rates and lending standards create significant challenges for homeownership.
Affordability Challenges
Higher mortgage rates directly impact affordability.
- Effect on first-time homebuyers: Rising rates make it significantly harder for first-time homebuyers to enter the market.
- Impact on housing market demand: Reduced affordability can lead to decreased demand, potentially slowing down market growth.
- Potential shifts in geographic preferences: Buyers might shift their focus to more affordable areas.
Potential for Market Corrections
Sustained increases in interest rates and reduced affordability can lead to market corrections.
- Possible price adjustments: Housing prices may need to adjust downward to match reduced buyer demand.
- Potential for a market slowdown or correction: A slowdown or even a correction in the housing market could occur.
- Impact on the real estate industry: A market slowdown could negatively affect the real estate industry, impacting jobs and investment.
Conclusion
Rising federal debt significantly influences the mortgage lending landscape by impacting interest rates, lending standards, and overall home affordability. Understanding how rising federal debt and mortgage rates are interconnected is vital for both borrowers and lenders. The increased scrutiny from lenders, coupled with higher interest rates, creates significant affordability challenges, particularly for first-time homebuyers. This could lead to market corrections and broader impacts on the real estate industry. Staying informed about economic trends and consulting with financial advisors is crucial to navigate this evolving landscape of rising federal debt and mortgage rates. Make informed decisions about homeownership by understanding the interplay between national debt and mortgage market conditions.

Featured Posts
-
 Help Build Pickleball Courts In Olive Branch Donation And Bid Process
May 19, 2025
Help Build Pickleball Courts In Olive Branch Donation And Bid Process
May 19, 2025 -
 Cne Anuncia Elecciones Primarias 2025 Fechas Candidatos Y Proceso Electoral
May 19, 2025
Cne Anuncia Elecciones Primarias 2025 Fechas Candidatos Y Proceso Electoral
May 19, 2025 -
 Ufc Fight Night 226 Gilbert Burns Vs Michael Morales Recap And Analysis
May 19, 2025
Ufc Fight Night 226 Gilbert Burns Vs Michael Morales Recap And Analysis
May 19, 2025 -
 Acc Tournament Unc Secures Important Win Against Notre Dame
May 19, 2025
Acc Tournament Unc Secures Important Win Against Notre Dame
May 19, 2025 -
 Music Festival Cancellations Court Decision Impacts Parks
May 19, 2025
Music Festival Cancellations Court Decision Impacts Parks
May 19, 2025
