How Tariffs Threaten China's Export-Led Growth Model
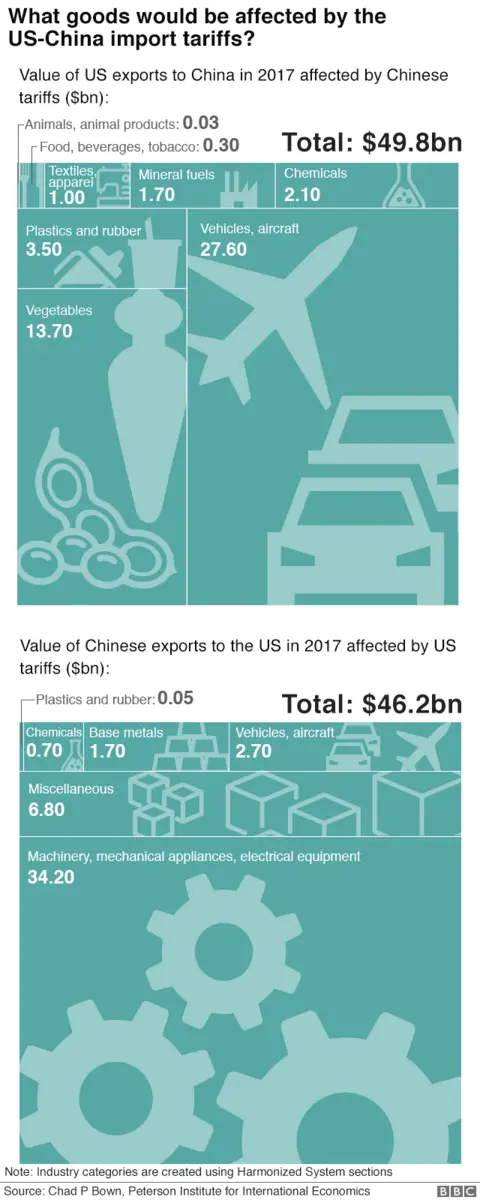
Table of Contents
China's export-oriented economy, the engine of its remarkable economic growth for decades, is facing a significant challenge: escalating tariffs. Recent tariff increases imposed by various countries have had a palpable impact, shrinking export volumes and raising concerns about the long-term sustainability of this model. This article analyzes how tariffs threaten China's export-led growth model, exploring the historical context, the immediate and long-term consequences, and China's responses to this growing threat. The potential consequences for global trade and the Chinese economy are substantial, demanding careful consideration.
H2: The Foundation of China's Export-Oriented Economy
H3: Historical Context: China's export-led growth strategy began to take shape in the late 1970s with the introduction of economic reforms. The strategy focused on attracting foreign investment, developing export-oriented industries, and integrating into the global trading system. This approach fueled rapid economic expansion, lifting millions out of poverty and transforming China into a global manufacturing powerhouse. This reliance on exports, however, has created a vulnerability to external shocks, including trade wars and tariff increases.
H3: Key Export Sectors: China's export success has been driven by several key sectors. Manufacturing, particularly in electronics, textiles, and machinery, has been a cornerstone. Technology exports, encompassing everything from consumer electronics to telecommunications equipment, have also played a crucial role. These sectors are particularly vulnerable to tariffs, as increased costs make Chinese products less competitive in international markets.
- Examples of heavily impacted products: Smartphones, computers, clothing, and solar panels.
- Economic contribution: Manufacturing alone accounts for a significant percentage of China's GDP and employment. The technology sector is a vital driver of innovation and future growth.
H3: Global Trade Dependence: China's economic growth is inextricably linked to its participation in global trade. Its integration into global supply chains means that many industries rely on the seamless flow of goods and services across borders. Tariffs disrupt these chains, creating bottlenecks and increasing costs, making China's export-dependent model increasingly precarious.
H2: The Impact of Tariffs on Chinese Exports
H3: Direct Impact on Export Volume and Revenue: Tariffs directly impact the price competitiveness of Chinese goods. Increased tariffs in target markets, such as the US and EU, lead to higher prices for Chinese products, reducing consumer demand and consequently export volume and revenue.
- Example: A 25% tariff on certain Chinese goods has led to a demonstrable decline in exports of those specific items to the imposing country.
- Data on declining export volumes: Statistical data showing the decrease in exports from China to specific countries following the implementation of tariffs.
H3: Indirect Impacts on Chinese Businesses and Workers: The impact of tariffs extends beyond reduced export earnings. Falling demand leads to factory closures, job losses, and a slowdown in investment. Related industries, such as logistics and transportation, also suffer as the volume of goods being shipped declines.
- Potential factory closures and job losses: Reports on factory closures and job losses in export-oriented industries.
- Impact on related industries: Analysis of the knock-on effects on logistics, transportation, and related support services.
H3: Impact on Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): The uncertainty created by tariffs discourages foreign investment. Businesses are hesitant to invest in countries facing trade tensions and potentially higher costs, impacting China's ability to attract capital for future growth and development.
H2: China's Responses to Tariff Threats
H3: Domestic Market Stimulation: China is actively trying to stimulate domestic consumption to lessen its reliance on exports. This involves policies aimed at raising disposable incomes and promoting domestic tourism and spending.
H3: Trade Diversification: China is actively pursuing trade diversification strategies to reduce its dependence on markets imposing tariffs. This includes strengthening ties with countries in Asia, Africa, and Latin America.
- Initiatives like the Belt and Road Initiative: The Belt and Road Initiative aims to enhance connectivity and trade across Eurasia and beyond.
- Challenges and successes: An assessment of the effectiveness of these diversification efforts.
H3: Technological Advancement and Innovation: China is investing heavily in technological advancement to upgrade its industries and reduce its reliance on low-cost manufacturing. This includes substantial investment in research and development, aiming to move up the value chain and compete in higher-margin sectors.
H2: Long-Term Implications for China's Economic Growth
H3: Shifting Global Economic Landscape: The current geopolitical environment is characterized by increasing protectionism and trade tensions. This makes China’s export-led model even more vulnerable.
H3: Potential for Economic Restructuring: The current challenges highlight the need for economic restructuring and diversification away from a solely export-dependent model. This involves fostering innovation, developing domestic consumption, and strengthening services sector growth.
H3: The Future of "Made in China": The long-term success of "Made in China" hinges on its ability to adapt to the evolving global trade landscape. This requires embracing innovation, improving efficiency, and building resilience to external shocks.
3. Conclusion:
Tariffs pose a significant threat to China's export-led growth model. The direct and indirect impacts on export volumes, employment, investment, and overall economic growth are substantial. While China is taking steps to mitigate these risks through domestic market stimulation, trade diversification, and technological advancement, the long-term implications remain uncertain. Understanding the threats to China's export-led growth model is crucial for comprehending future global economic trends. Learn more about the impact of tariffs on China's economy and the ongoing challenges faced by this major global player. The future of "Made in China" will depend on its ability to successfully navigate this turbulent new era of global trade.

Featured Posts
-
 The Looming Threat Will Google Be Broken Up
Apr 22, 2025
The Looming Threat Will Google Be Broken Up
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Chinas Impact On Luxury Car Sales Bmw Porsche And Beyond
Apr 22, 2025
Chinas Impact On Luxury Car Sales Bmw Porsche And Beyond
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Kyivs Decision Point Evaluating Trumps Plan To End The Ukraine War
Apr 22, 2025
Kyivs Decision Point Evaluating Trumps Plan To End The Ukraine War
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Stock Market Outlook Navigating The Current Challenges
Apr 22, 2025
Stock Market Outlook Navigating The Current Challenges
Apr 22, 2025 -
 A Geographic Overview Of The Countrys Newest Business Hotspots
Apr 22, 2025
A Geographic Overview Of The Countrys Newest Business Hotspots
Apr 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 The Experiences Of Transgender People Under Trumps Executive Orders
May 10, 2025
The Experiences Of Transgender People Under Trumps Executive Orders
May 10, 2025 -
 Trumps Legacy The Transgender Communitys Perspective
May 10, 2025
Trumps Legacy The Transgender Communitys Perspective
May 10, 2025 -
 Bangkok Post Highlights Growing Movement For Transgender Equality
May 10, 2025
Bangkok Post Highlights Growing Movement For Transgender Equality
May 10, 2025 -
 The Impact Of Trumps Transgender Military Ban A Critical Analysis
May 10, 2025
The Impact Of Trumps Transgender Military Ban A Critical Analysis
May 10, 2025 -
 The Trump Presidency And Its Impact On The Transgender Community
May 10, 2025
The Trump Presidency And Its Impact On The Transgender Community
May 10, 2025
