Income Needed For Middle Class Status By US State
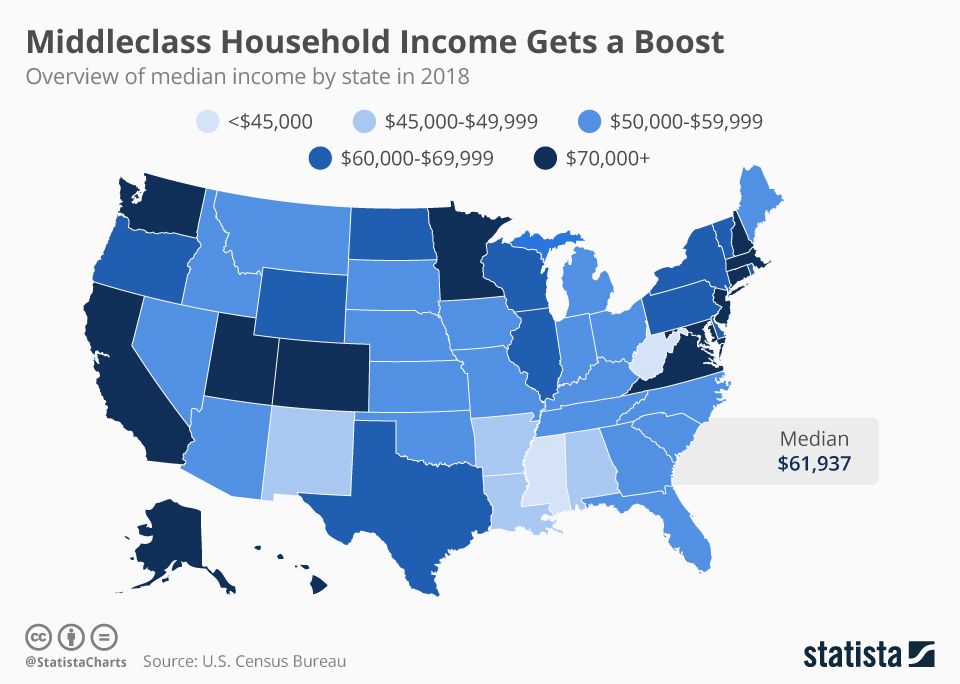
Table of Contents
Understanding Cost of Living Variations Across US States
The cost of living is the most significant factor influencing the income needed for middle-class status. This encompasses various expenses, including:
- Housing: Rent or mortgage payments often constitute the largest expense. Prices vary drastically based on location, housing type, and market conditions.
- Transportation: Fuel costs, car insurance, public transportation fares, and potential car payments all contribute. States with extensive public transportation networks may have lower transportation costs than those heavily reliant on personal vehicles.
- Healthcare: Healthcare expenses, including insurance premiums, deductibles, co-pays, and prescription drugs, can be substantial. Access to affordable healthcare varies significantly across states.
- Taxes: State and local taxes, including income tax, sales tax, and property tax, can significantly impact disposable income.
- Groceries: Food costs fluctuate depending on location, availability of fresh produce, and local market dynamics.
The differences are stark. For example, the cost of living in California, particularly in major metropolitan areas like San Francisco and Los Angeles, is significantly higher than in many Midwest states like Iowa or Nebraska. We've utilized data from reputable sources like the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and the Council for Community and Economic Research (C2ER) to inform our analysis.
- High Cost of Living States: California, New York, Hawaii, Massachusetts (driven by high housing costs and taxes).
- Low Cost of Living States: Mississippi, West Virginia, Arkansas, Oklahoma (often characterized by lower housing costs and taxes).
These variations highlight the need for a state-by-state approach when determining the income needed for middle-class status.
State-Specific Income Thresholds for Middle Class Status
The table below provides estimated income thresholds for middle-class status by state. These figures are based on median household income adjusted for cost of living using a weighted average of the factors discussed above. Remember that this is an estimate, and individual circumstances can significantly alter these numbers.
(Insert interactive map or table here. Each row should include: State, Estimated Middle-Class Income Range, Methodology used for calculation.)
Example Table Row:
| State | Estimated Middle-Class Income | Methodology |
|---|---|---|
| California | $100,000 - $150,000 | Median household income adjusted for COL index of 130 |
| Iowa | $60,000 - $90,000 | Median household income adjusted for COL index of 90 |
The income range considered "middle class" shows significant regional differences. The Northeast and West Coast typically require substantially higher incomes than the South and Midwest.
Factors Influencing Middle Class Income Needs Beyond Cost of Living
While cost of living is a primary factor, several other elements influence the actual income required to achieve middle-class status:
- Family Size and Number of Dependents: Larger families with more children face significantly higher expenses related to childcare, food, clothing, and education.
- Household Debt: High levels of student loan debt, credit card debt, or other loans reduce disposable income and make it harder to maintain a middle-class lifestyle.
- Healthcare Costs: Unexpected medical expenses can devastate even well-planned household budgets. High healthcare costs, particularly deductibles and co-pays, can impact middle-class families disproportionately.
- Education Expenses: College tuition, private school fees, and other educational expenses can significantly strain household finances.
These factors highlight the complexity of defining a universal "middle-class income." Two families in the same state might have vastly different income needs based on these individual circumstances.
The Future of Middle-Class Income in the US
Predicting the future of middle-class income is challenging. However, several trends will likely influence future income needs:
- Inflation: Persistent inflation erodes purchasing power, requiring higher incomes to maintain the same standard of living.
- Wage Growth: The rate of wage growth compared to inflation will significantly impact the affordability of middle-class living.
- Job Market Changes: Automation and shifts in the job market may affect employment opportunities and income levels for middle-class workers.
These economic factors suggest that the income needed for middle-class status by US state is likely to increase in the coming years.
Conclusion: Achieving Financial Security – Determining Your Income Needs
This article has explored the significant variations in the income needed for middle-class status by US state. Understanding the cost of living in your specific location is crucial for setting realistic financial goals. Use the information provided to assess your financial situation and plan accordingly. Consider your individual circumstances, including family size, debt levels, and healthcare costs, when evaluating your income needs. Use our state-by-state guide to determine the income needed for middle-class status in your area and start planning your financial future. For further assistance, consider using a cost of living calculator or seeking advice from a financial advisor.

Featured Posts
-
 Doktorluk Hayalinden Boks Arenalarina Bir Sporcunun Yolculugu
Apr 30, 2025
Doktorluk Hayalinden Boks Arenalarina Bir Sporcunun Yolculugu
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Yate Recycling Centre Incident Air Ambulance Called
Apr 30, 2025
Yate Recycling Centre Incident Air Ambulance Called
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Understanding Middle Class Income Levels Across The United States
Apr 30, 2025
Understanding Middle Class Income Levels Across The United States
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Trtyb Hdafa Albrymyrlyj Bed Hdf Haaland
Apr 30, 2025
Trtyb Hdafa Albrymyrlyj Bed Hdf Haaland
Apr 30, 2025 -
 The Reality Of Farming Amanda Owens Honest Account
Apr 30, 2025
The Reality Of Farming Amanda Owens Honest Account
Apr 30, 2025
