Increased Alcohol Use In Women: Health Risks And Expert Concerns
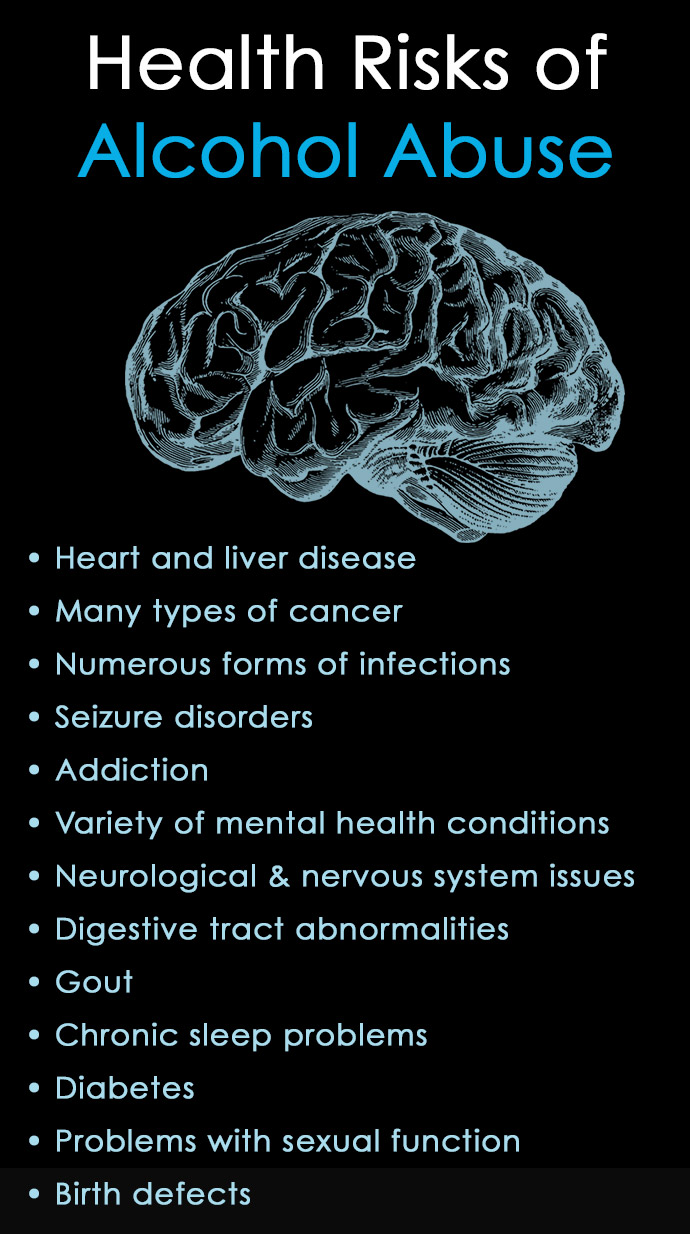
Table of Contents
Physical Health Risks Associated with Increased Alcohol Use in Women
The biological differences between men and women significantly impact how the body processes alcohol, leading to heightened vulnerability to various health problems in women. Increased alcohol use in women translates to a disproportionately higher risk of serious health complications.
Liver Disease and Damage
Women are more susceptible to liver damage from alcohol than men. This is partly due to differences in metabolic processes and enzyme activity. They tend to have lower levels of alcohol dehydrogenase, an enzyme that breaks down alcohol in the stomach. This means a larger portion of ingested alcohol reaches the liver, increasing the risk of:
- Higher risk of cirrhosis and alcoholic hepatitis: Cirrhosis, a severe scarring of the liver, and alcoholic hepatitis, a form of liver inflammation, are significantly more prevalent in women who consume excessive alcohol.
- Different metabolic processes contributing to greater vulnerability: Women generally have less body water and more body fat than men, resulting in higher blood alcohol concentrations (BAC) for the same amount of alcohol consumed.
- Statistics on the prevalence of alcohol-related liver disease in women: Studies show a growing number of women hospitalized and diagnosed with alcohol-related liver diseases, underscoring the severity of this issue.
Cardiovascular Problems
Increased alcohol use in women is strongly linked to an elevated risk of cardiovascular problems. Even moderate drinking can contribute to:
- Increased risk of heart attack and stroke: Alcohol consumption disrupts heart rhythm and increases blood pressure, putting women at a greater risk of these life-threatening events.
- Impact on blood lipid levels: Alcohol can negatively impact cholesterol and triglyceride levels, further increasing the risk of heart disease.
- Specific cardiovascular risks for women: Hormonal fluctuations throughout a woman's life may exacerbate the impact of alcohol on the cardiovascular system.
Cancer Risk
Excessive alcohol intake significantly increases the risk of several cancers in women. The link is well-established for:
- Specific cancer types with higher risk associated with alcohol: Breast cancer, liver cancer, colorectal cancer, and other cancers show a stronger correlation with alcohol consumption in women.
- Mechanisms by which alcohol increases cancer risk: Alcohol can damage DNA and interfere with the body's ability to repair this damage, leading to uncontrolled cell growth.
- Relevant studies and statistics: Numerous large-scale studies have confirmed the strong association between increased alcohol intake and various cancer types in women.
Reproductive Health Issues
The impact of increased alcohol use in women extends to reproductive health, causing several serious problems:
- Effects of alcohol on ovulation and conception: Alcohol can disrupt hormone production and negatively affect ovulation, making it harder to conceive.
- Risks to fetal development during pregnancy: Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASDs) are a group of conditions that can occur in babies exposed to alcohol during pregnancy, causing lifelong physical, mental, and behavioral problems.
- Long-term reproductive health consequences: Excessive alcohol use can lead to menstrual irregularities, early menopause, and reduced fertility.
Mental Health Impacts of Increased Alcohol Use in Women
The relationship between alcohol and mental health is complex, especially for women. Increased alcohol use in women can worsen existing conditions or trigger new ones.
Increased Risk of Depression and Anxiety
Alcohol initially may seem to alleviate anxiety and depression, but it's a temporary effect. Long-term use:
- The link between alcohol consumption and depression/anxiety disorders: Studies show a strong correlation between alcohol misuse and an increased risk of depression and anxiety disorders in women.
- The cyclical relationship between alcohol use and mental health struggles: Alcohol use can worsen mental health symptoms, leading to increased drinking to cope, creating a vicious cycle.
- Data on the prevalence of co-occurring disorders: A significant portion of women with alcohol use disorders also suffer from depression, anxiety, or other mental health conditions.
Alcohol Dependence and Addiction
Women often develop alcohol dependence more quickly than men, and they may face unique challenges in treatment.
- Factors contributing to alcohol addiction in women: Hormonal factors, stress, trauma, and social pressures can contribute to a higher risk of alcohol addiction in women.
- The unique challenges women face in accessing treatment: Societal stigma, lack of specialized treatment programs for women, and childcare responsibilities can create barriers to seeking help.
- Importance of early intervention and support: Early identification and intervention are crucial in preventing alcohol dependence and addiction from escalating.
Social Consequences of Increased Alcohol Use in Women
The consequences of increased alcohol use in women extend beyond physical and mental health, impacting their social lives and well-being.
Impact on Relationships and Family
Heavy alcohol consumption can severely strain personal relationships and family dynamics:
- Strain on relationships with partners, children, and friends: Alcohol abuse can lead to conflict, isolation, and damaged relationships with loved ones.
- Increased likelihood of domestic violence or abuse: Alcohol use is often a factor in domestic violence and abuse, with women disproportionately affected.
- Negative impact on parenting and family stability: Alcohol abuse can impair parenting skills, causing instability and harm to children.
Professional and Financial Implications
Increased alcohol use in women can have detrimental consequences for their careers and financial stability:
- Impact on work performance and productivity: Alcohol use can affect job performance, attendance, and overall productivity.
- Financial difficulties due to alcohol-related expenses or job loss: The costs associated with alcohol abuse, along with potential job loss, can lead to significant financial strain.
- The overall economic burden of alcohol abuse: The societal costs of alcohol abuse are substantial, including healthcare expenses, lost productivity, and social welfare support.
Conclusion
The evidence overwhelmingly demonstrates that increased alcohol use in women presents a serious and growing public health concern. The unique physical, mental, and social consequences highlight the urgent need for increased awareness and targeted interventions. From the heightened risk of liver disease and cancer to the devastating impacts on mental health and relationships, the dangers are significant and cannot be ignored. Women struggling with alcohol use are not alone; resources are available to provide support and guidance. It is crucial to recognize the signs of alcohol abuse and seek professional help promptly. Understanding the specific risks associated with increased alcohol use in women is the first step towards prevention and effective treatment. Take control of your health and well-being. Learn more about managing increased alcohol use in women and find support today. Contact your doctor, a therapist, or a support group specializing in addiction for guidance and assistance.

Featured Posts
-
 Xong Hoi Dung Cach Huong Dan Thoi Gian Va Nhung Luu Y Quan Trong
May 15, 2025
Xong Hoi Dung Cach Huong Dan Thoi Gian Va Nhung Luu Y Quan Trong
May 15, 2025 -
 Jaylen Wells Scary Fall Taken Off On Stretcher
May 15, 2025
Jaylen Wells Scary Fall Taken Off On Stretcher
May 15, 2025 -
 Trumps Egg Price Prediction From Fiction To Reality
May 15, 2025
Trumps Egg Price Prediction From Fiction To Reality
May 15, 2025 -
 Dodgers Left Handed Hitters A Look At Their Recent Slump And Potential For Improvement
May 15, 2025
Dodgers Left Handed Hitters A Look At Their Recent Slump And Potential For Improvement
May 15, 2025 -
 Grizzlies Jaylen Wells Suffers Scary Fall Needs Stretcher
May 15, 2025
Grizzlies Jaylen Wells Suffers Scary Fall Needs Stretcher
May 15, 2025
