Inflation's Heat: The Bank Of Canada's Response

Table of Contents
The Bank of Canada's Mandate and Inflation Targets
The Bank of Canada's primary mandate is to promote the economic and financial well-being of Canadians. This involves two key objectives: maintaining price stability and fostering sustainable economic growth, which often translates to full employment. Price stability is typically defined by the Bank's inflation target, currently set within a range of 1 to 3 percent. This target provides a benchmark for the Bank's monetary policy decisions.
- Historical Context: Canada adopted an explicit inflation-targeting framework in 1991, significantly improving the country's inflation performance. Prior to this, inflation was significantly higher and more volatile.
- Setting Inflation Targets: The Bank of Canada sets its inflation targets through a comprehensive process involving economic modelling, consultations with experts, and consideration of global economic factors. The goal is to balance price stability with sustainable economic growth.
- Challenges in a Volatile Market: Achieving the inflation target is challenging, especially in a volatile global market. External shocks, such as supply chain disruptions or geopolitical events, can significantly impact inflation and require the Bank to adjust its monetary policy accordingly. The current inflationary pressures are partially driven by global factors like the war in Ukraine and pandemic-related supply chain issues.
Interest Rate Hikes as a Key Tool
One of the Bank of Canada's most powerful tools to combat inflation is adjusting interest rates. By raising interest rates, borrowing becomes more expensive. This discourages businesses and consumers from taking on new debt, reducing demand and ultimately cooling down inflation. Higher interest rates also make saving more attractive, further dampening spending.
- Timeline of Rate Increases: The Bank of Canada has implemented a series of interest rate increases since early 2022, responding to rising inflation. These increases have been relatively aggressive, reflecting the seriousness of the inflationary pressures. You can find a detailed timeline of these increases on the Bank of Canada's website.
- Effectiveness of Rate Hikes: The effectiveness of these rate hikes in curbing inflation is still being assessed. While there are indications of slowing inflation, it's a complex process with a time lag between interest rate changes and their impact on the overall economy.
- Potential Negative Consequences: Aggressive interest rate increases carry the risk of triggering an economic slowdown or even a recession. Higher borrowing costs can impact investment, hinder business growth, and lead to job losses. The Bank of Canada carefully balances the need to control inflation with the risk of harming economic growth.
Quantitative Tightening and Other Monetary Policy Measures
Beyond interest rate adjustments, the Bank of Canada utilizes quantitative tightening (QT) and other monetary policy measures to manage inflation. Quantitative tightening involves reducing the money supply by selling government bonds held on its balance sheet. This decreases the amount of money circulating in the economy, further dampening inflationary pressures.
- Quantitative Tightening Explained: QT works by reducing the liquidity in the financial system. When the Bank sells bonds, it absorbs money from banks, reducing their capacity to lend and ultimately decreasing overall spending.
- Other Monetary Policy Tools: Other tools employed by the Bank of Canada include forward guidance (communicating future policy intentions to influence market expectations) and the buying and selling of government bonds to influence the overall money supply.
- Effectiveness Assessment: The combined effectiveness of these measures is continuously monitored and evaluated by the Bank. The Bank's decisions are data-driven, using a variety of economic indicators to guide its actions.
The Impact on the Canadian Economy
The Bank of Canada's actions to combat inflation have significant implications for the Canadian economy. These policies impact various sectors, including the housing market, employment, and consumer spending.
- Impact on Housing and Spending: Higher interest rates directly affect the housing market, increasing mortgage payments and potentially cooling down price growth. Increased borrowing costs also reduce consumer spending, as individuals have less disposable income available for purchases.
- Effect on Employment: While controlling inflation is crucial, tighter monetary policy can lead to job losses in certain sectors as economic activity slows. The Bank carefully monitors employment figures as it adjusts its policies.
- Overall Economic Growth Outlook: The overall economic growth outlook for Canada depends on a multitude of factors, including global economic conditions and the effectiveness of the Bank of Canada's monetary policy response to inflation. A delicate balancing act is required to curb inflation without triggering a significant economic downturn.
Conclusion
The Bank of Canada is actively combating inflation through a multifaceted approach involving interest rate hikes, quantitative tightening, and other monetary policy tools. While these measures aim to stabilize prices and protect the purchasing power of Canadians, they also carry the risk of slowing economic growth. The success of the Bank of Canada's strategy will depend on various interconnected factors, including global economic conditions and the resilience of the Canadian economy.
Call to Action: Stay informed about the Bank of Canada's response to inflation and its impact on the Canadian economy. Regularly check the Bank of Canada's website and follow reputable financial news sources for updates on inflation and monetary policy. Understanding the Bank of Canada's actions is crucial for navigating the current economic climate and making informed financial decisions during this period of high inflation. Staying aware of inflation trends and the Bank's response is vital for both personal financial planning and broader economic understanding.

Featured Posts
-
 Sydney Sweeney Projects After Echo Valley The Housemaid And Her Recent Split
May 22, 2025
Sydney Sweeney Projects After Echo Valley The Housemaid And Her Recent Split
May 22, 2025 -
 Understanding The Federal Results A Saskatchewan Political Perspective
May 22, 2025
Understanding The Federal Results A Saskatchewan Political Perspective
May 22, 2025 -
 Abn Amro Kamerbrief Certificaten Een Verkoopprogramma Overzicht
May 22, 2025
Abn Amro Kamerbrief Certificaten Een Verkoopprogramma Overzicht
May 22, 2025 -
 Tuerkiye Ve Italya Nin Ortak Nato Goerevi Planin Ayrintilari
May 22, 2025
Tuerkiye Ve Italya Nin Ortak Nato Goerevi Planin Ayrintilari
May 22, 2025 -
 Peppa Pigs New Baby When Will We Meet The Newborn
May 22, 2025
Peppa Pigs New Baby When Will We Meet The Newborn
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
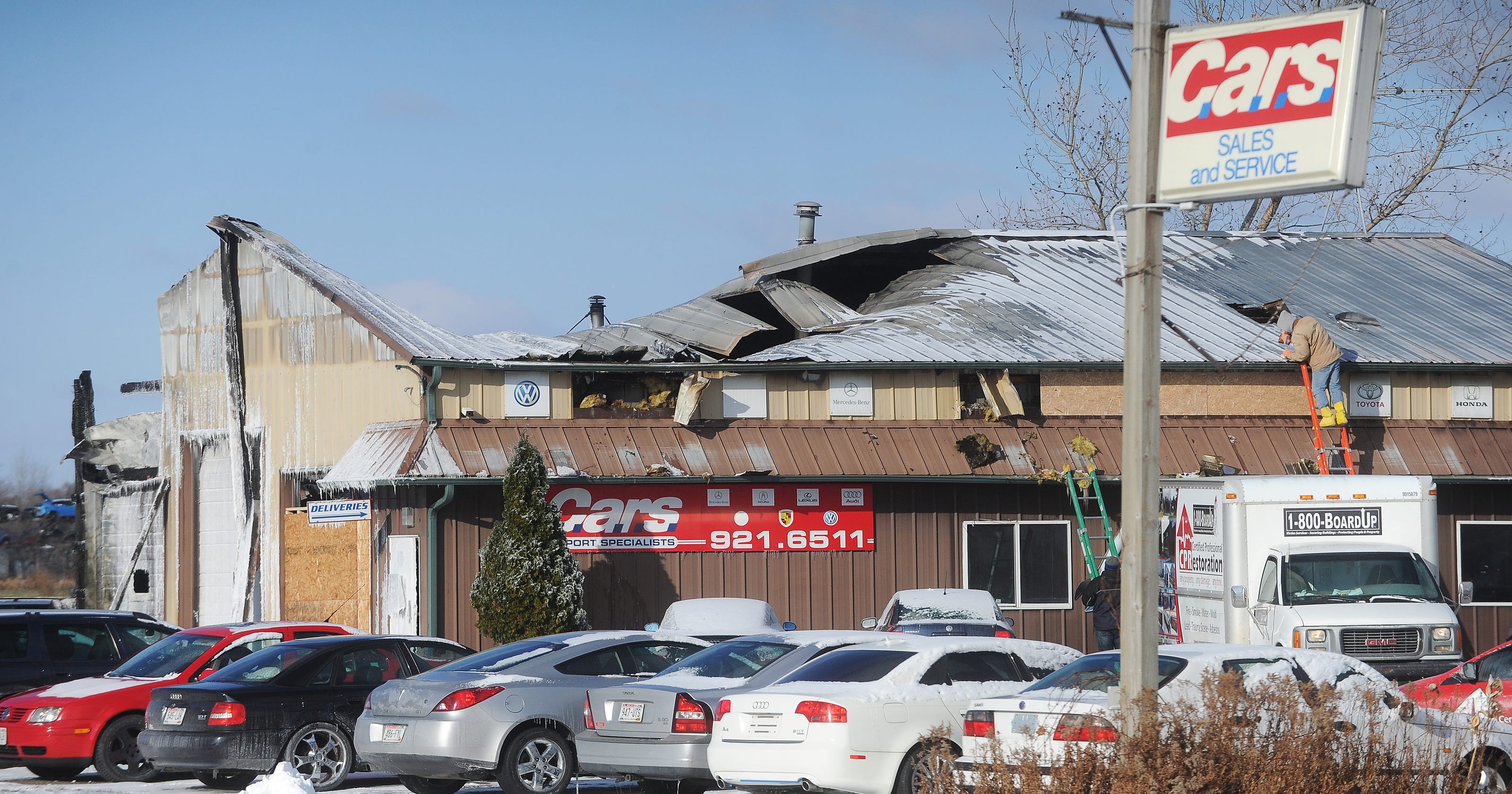 Large Fire Engulfs Used Car Dealership
May 22, 2025
Large Fire Engulfs Used Car Dealership
May 22, 2025 -
 Used Car Lot Fire Extensive Damage Reported
May 22, 2025
Used Car Lot Fire Extensive Damage Reported
May 22, 2025 -
 Crews Battle Blaze At Used Car Dealership
May 22, 2025
Crews Battle Blaze At Used Car Dealership
May 22, 2025 -
 Recent Susquehanna Valley Storm Damage Cleanup Repairs And Community Support
May 22, 2025
Recent Susquehanna Valley Storm Damage Cleanup Repairs And Community Support
May 22, 2025 -
 Urgent Severe Thunderstorm Watch In Effect South Central Pennsylvania
May 22, 2025
Urgent Severe Thunderstorm Watch In Effect South Central Pennsylvania
May 22, 2025
