Investigation Into Toxic Chemical Persistence Following Ohio Train Derailment
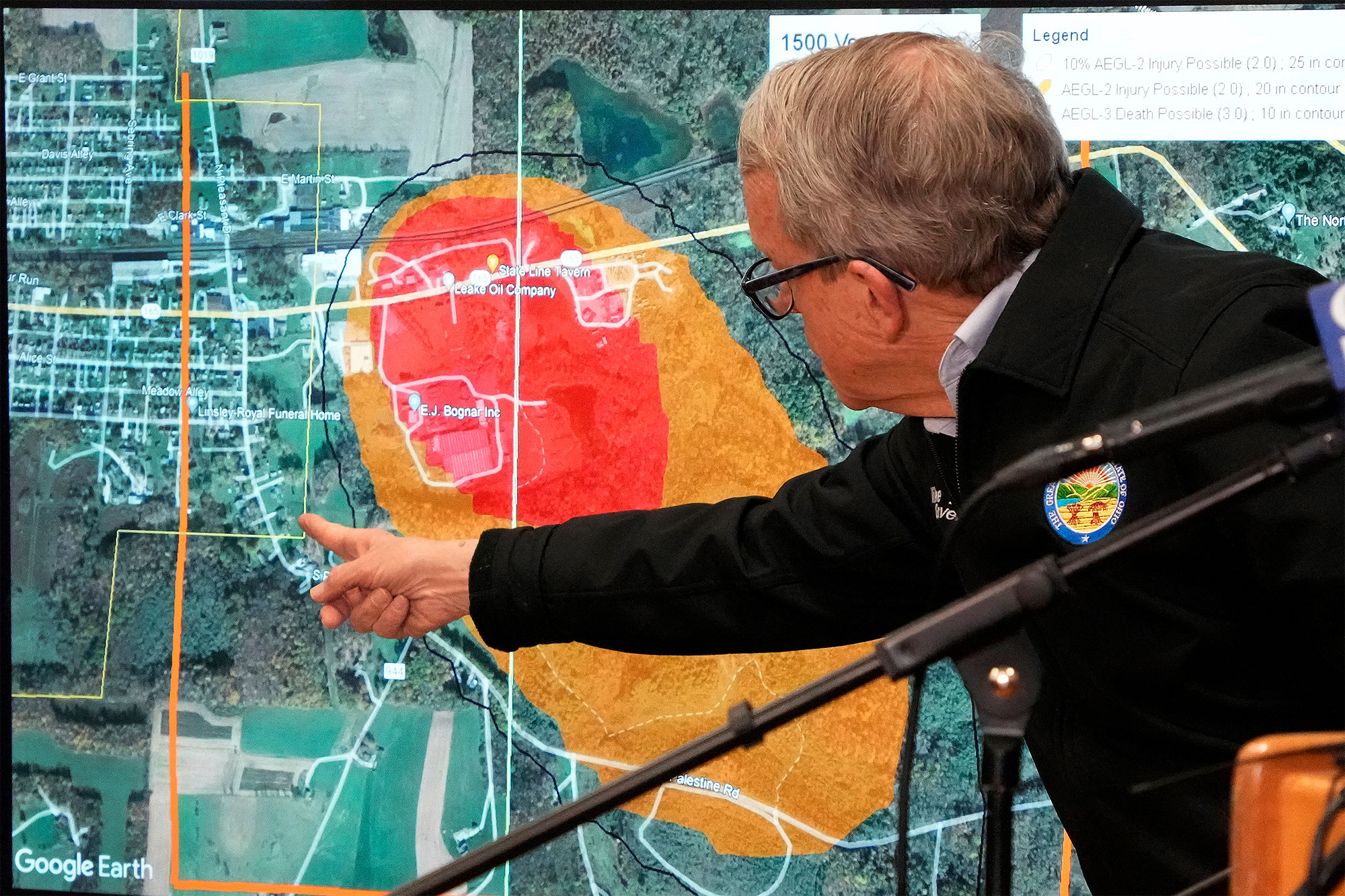
Table of Contents
Identification of Persistent Toxic Chemicals
The Ohio derailment released a cocktail of hazardous chemicals, many known for their persistence in the environment. Understanding the properties of these chemicals is crucial to assessing the long-term risks. Key chemicals of concern include vinyl chloride and butyl acrylate.
- Vinyl Chloride Persistence: Vinyl chloride is a known carcinogen with a relatively short atmospheric half-life but can persist in soil and groundwater for extended periods, depending on factors like soil type and presence of degrading microorganisms. Its high volatility allows for widespread dispersion in the air, leading to potential long-term exposure risks.
- Butyl Acrylate Environmental Impact: Butyl acrylate, while less acutely toxic than vinyl chloride, is persistent in water and soil, potentially bioaccumulating in aquatic organisms. Its slow degradation rate contributes to its long-term environmental impact.
- Half-Life of Toxic Chemicals: The half-life of these chemicals, representing the time it takes for half the substance to break down, varies significantly depending on environmental conditions. However, even relatively short half-lives can translate to significant persistence when large quantities are released, as was the case in the Ohio derailment.
- Bioaccumulation of Pollutants: Many of the released chemicals are hydrophobic, meaning they readily bind to soil particles and organic matter. This characteristic contributes to their bioaccumulation in the food chain, posing a threat to both wildlife and human health through consumption of contaminated food sources. Studies on similar incidents, such as previous chemical spills, have highlighted the long-lasting nature of this bioaccumulation.
Extent of Environmental Contamination
Assessing the extent of contamination from the Ohio train derailment is a complex undertaking, requiring extensive sampling and analysis across various environmental matrices. Initial findings point to widespread contamination:
- Environmental Contamination Assessment: Testing has revealed elevated levels of vinyl chloride and butyl acrylate in soil and water samples within a radius of the derailment site. The precise extent of the plume is still being determined, as the contamination may extend beyond the initially assessed area.
- Soil Pollution: Soil samples show significant levels of contamination, with the potential for long-term persistence due to the chemicals' hydrophobic properties. This necessitates extensive soil remediation efforts.
- Water Contamination: Concerns exist regarding the migration of contaminants into groundwater and nearby surface water systems. Monitoring of water wells and surface water bodies is crucial to track the spread of pollution and its impact on aquatic life.
- Air Quality Monitoring: Although the immediate air quality concerns have lessened, the potential for long-term impact from residual contaminants in the soil and water necessitates ongoing air quality monitoring. Volatile compounds may continue to volatilize over time.
Long-Term Health and Ecological Risks
The long-term health and ecological consequences of the Ohio train derailment remain a major concern. Exposure to the released chemicals carries several risks:
- Long-term Health Effects: Chronic exposure to vinyl chloride and butyl acrylate is linked to various health problems, including liver damage, cancer, respiratory issues, and neurological effects. Long-term, low-level exposure presents significant public health risks.
- Environmental Toxicology: Studies of the released chemicals' impact on various organisms will be crucial to fully understanding the ecological consequences. The potential for biomagnification through the food chain needs close monitoring.
- Ecological Risk Assessment: A comprehensive ecological risk assessment needs to be conducted, addressing potential impacts on aquatic life (fish, invertebrates), terrestrial wildlife (mammals, birds), and plant communities. This requires detailed monitoring and analysis of affected ecosystems.
- Wildlife Toxicology: The effects on wildlife are of particular concern, as the spilled chemicals can have severe impacts on reproduction, development, and survival rates of various species.
Remediation Efforts and Challenges
Remediation efforts are underway, but addressing toxic chemical persistence presents significant challenges:
- Environmental Remediation: Current remediation strategies focus on soil excavation, removal of contaminated water, and the potential use of bioremediation techniques to break down some of the chemicals. However, the extent of the contamination and the persistence of some chemicals make complete remediation a long-term and complex undertaking.
- Soil Cleanup: Excavation and disposal of contaminated soil are costly and time-consuming. In-situ remediation techniques, like bioremediation, may be more sustainable but their efficacy against persistent chemicals needs further evaluation.
- Water Treatment: Contaminated water requires specialized treatment to remove the hazardous substances. Effective water treatment is essential to protect human health and aquatic ecosystems.
- Long-Term Monitoring: Long-term monitoring of contamination levels in soil, water, and air is crucial to assess the effectiveness of remediation efforts and to identify any potential resurgence of contamination. This necessitates robust monitoring protocols and technologies.
Conclusion
The investigation into toxic chemical persistence following the Ohio train derailment reveals significant challenges in mitigating the long-term environmental and health consequences. The persistence of these hazardous substances necessitates ongoing monitoring, effective remediation strategies, and a comprehensive understanding of their long-term impacts. Further research is critical to develop innovative solutions for addressing the issue of toxic chemical persistence in future incidents. We must prioritize proactive measures and stricter regulations to prevent similar disasters and minimize the risk of long-term toxic chemical persistence in our environment. Understanding and mitigating toxic chemical persistence is a critical step towards environmental protection and public safety.

Featured Posts
-
 Apples New I Phone Feature A Must Have For F1 Fans
May 26, 2025
Apples New I Phone Feature A Must Have For F1 Fans
May 26, 2025 -
 The New York Rangers Roster Changes And Their Implications
May 26, 2025
The New York Rangers Roster Changes And Their Implications
May 26, 2025 -
 Catat Jadwal Moto Gp Inggris Rangkaian Balapan Dimulai Hari Ini
May 26, 2025
Catat Jadwal Moto Gp Inggris Rangkaian Balapan Dimulai Hari Ini
May 26, 2025 -
 F1 Rule Changes 2024 Unveiling Hamiltons Contribution
May 26, 2025
F1 Rule Changes 2024 Unveiling Hamiltons Contribution
May 26, 2025 -
 Bayern Goalkeeper Neuer Faces Injury Setback
May 26, 2025
Bayern Goalkeeper Neuer Faces Injury Setback
May 26, 2025
