Is Uber Recession-Proof? Analyzing The Stock's Resilience
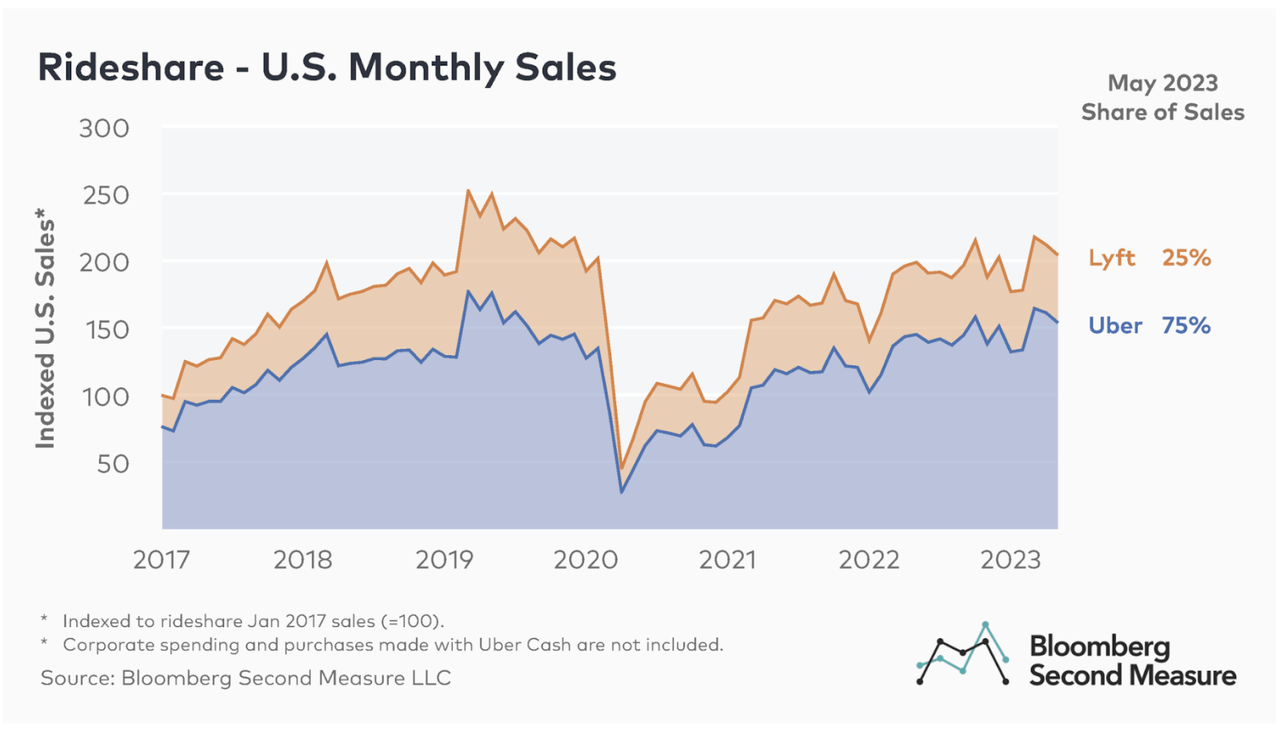
Table of Contents
Uber's Business Model and Recessionary Pressures
Uber's business model, centered around ride-sharing and food delivery, is inherently linked to consumer spending and discretionary income. Understanding Uber's demand elasticity during economic slowdowns is crucial to assessing its recession resilience.
Demand Elasticity During Economic Slowdowns
The demand for ride-sharing and food delivery services is susceptible to fluctuations based on economic conditions. Reduced consumer spending directly impacts Uber's core services.
- Reduced discretionary spending: During a recession, people tend to cut back on non-essential expenses, including ride-hailing and restaurant meals delivered through Uber Eats.
- Price sensitivity: As disposable income shrinks, consumers become more price-sensitive, potentially opting for cheaper alternatives like public transportation or cooking at home. This impacts Uber's pricing strategy and profitability.
- Shift to cheaper alternatives: Economic downturns often see consumers gravitate towards more affordable options, leading to a potential decline in Uber's market share. This requires Uber to adapt pricing and promotional strategies to maintain user engagement.
- Keyword integration: "Uber demand elasticity," "recession impact on Uber," "price sensitivity Uber."
Cost-Cutting Measures and Operational Efficiency
To navigate economic downturns, Uber employs various cost-cutting measures and focuses on operational efficiency.
- Driver incentives: Uber can adjust driver incentives and bonuses to control labor costs during periods of reduced demand.
- Operational optimization: Improving routing algorithms, optimizing delivery routes, and streamlining operations enhance efficiency and reduce expenses.
- Marketing expenditure: Reducing marketing and advertising spending can help conserve resources during economic uncertainty.
- Keyword integration: "Uber cost-cutting," "operational efficiency Uber," "recession response strategies."
Historical Performance During Past Recessions
Examining Uber's historical performance during previous economic slowdowns provides valuable insights into its recession resilience.
Uber's Stock Performance During Previous Economic Slowdowns
While Uber is a relatively young company, analyzing its stock performance since its IPO and comparing it to broader market trends during periods of economic uncertainty offers some clues. (Note: This section would benefit from incorporating specific data and charts showing Uber's stock performance during relevant periods).
- Comparison with market indices: Comparing Uber's stock performance to the performance of broader market indices (like the S&P 500) during past recessions provides context for its relative resilience.
- Specific historical examples: Highlighting specific periods of economic downturn and Uber's performance during those times strengthens the analysis.
- Keyword integration: "Uber stock recession," "historical Uber performance," "Uber stock volatility."
Analyzing Revenue and Earnings Reports
Analyzing Uber's financial statements, specifically revenue, earnings, and profitability during past economic downturns, offers a quantitative assessment of its resilience. (Note: This section requires specific financial data from Uber's financial reports.)
- Revenue trends: Tracking revenue growth or decline during economic downturns reveals the impact of reduced consumer spending.
- Profitability metrics: Examining profitability ratios (e.g., gross margin, operating margin) provides insights into Uber's ability to manage costs and maintain profitability during difficult economic conditions.
- Keyword integration: "Uber financial performance recession," "Uber revenue analysis," "Uber earnings report."
Factors Contributing to Uber's Potential Resilience
Despite its dependence on consumer spending, several factors contribute to Uber's potential resilience during a recession.
Diversification of Revenue Streams
Uber's expansion beyond ride-sharing into food delivery (Uber Eats), freight transportation (Uber Freight), and other services significantly diversifies its revenue streams.
- Reduced reliance on single sector: If demand for ride-sharing declines, Uber can rely on the performance of other sectors like Uber Eats or Uber Freight to cushion the impact.
- Geographic diversification: Operating in multiple geographic markets reduces reliance on any single economy.
- Keyword integration: "Uber diversification," "Uber Eats recession," "Uber Freight resilience."
Technological Innovation and Adaptability
Uber's history demonstrates a commitment to technological innovation and adaptability to changing market conditions.
- Dynamic pricing: Uber's dynamic pricing model helps to optimize pricing based on demand, potentially mitigating revenue losses during economic downturns.
- New service offerings: Continuously introducing new services and features helps to attract and retain customers.
- Technological efficiency: Investments in technology improve operational efficiency and reduce costs.
- Keyword integration: "Uber technology," "Uber innovation," "adaptability Uber."
Potential Risks and Vulnerabilities
Despite its strengths, Uber faces several potential risks and vulnerabilities during a recession.
Dependence on Consumer Spending
Uber's business model is intrinsically linked to discretionary consumer spending. A sharp decline in consumer confidence could significantly impact Uber's revenue.
- Sensitivity to economic downturns: Reduced consumer spending during a recession could lead to a substantial decline in demand for ride-sharing and food delivery services.
- Impact on profitability: Lower demand directly affects Uber's profitability, potentially leading to layoffs and cost-cutting measures.
- Keyword integration: "Uber consumer spending," "discretionary spending Uber," "risk factors Uber."
Competition and Market Saturation
Intense competition from other ride-sharing and food delivery services poses a significant risk to Uber's market share and profitability.
- Price wars: Competitive pressure could lead to price wars, squeezing profit margins.
- Market share erosion: Aggressive competitors could erode Uber's market share during economic downturns, as consumers seek out the cheapest options.
- Keyword integration: "Uber competition," "market saturation Uber," "competitive landscape."
Conclusion
Analyzing Uber's resilience during a potential recession requires a nuanced understanding of its business model, historical performance, and future prospects. While Uber's diversification strategy and commitment to innovation offer considerable potential for resilience, its inherent dependence on consumer spending and the competitive landscape present significant risks. Understanding the factors affecting Uber's recession-proof nature is crucial for informed investment decisions. Continue your research and evaluate the risks and opportunities presented by this dynamic company. Is Uber recession-proof? A deeper dive into its financial performance and market dynamics is necessary to reach a definitive conclusion.

Featured Posts
-
 Nbas Reaction To The Game 4 No Call Against The Pistons
May 17, 2025
Nbas Reaction To The Game 4 No Call Against The Pistons
May 17, 2025 -
 Menganalisis Dan Memahami Laporan Keuangan Untuk Pengambilan Keputusan Bisnis Yang Lebih Baik
May 17, 2025
Menganalisis Dan Memahami Laporan Keuangan Untuk Pengambilan Keputusan Bisnis Yang Lebih Baik
May 17, 2025 -
 Assessing The Effectiveness Of Lockdown Drills In Florida Schools Post Shooting
May 17, 2025
Assessing The Effectiveness Of Lockdown Drills In Florida Schools Post Shooting
May 17, 2025 -
 Zhevago Zayavil O Vozmozhnom Prekraschenii Investitsiy Ferrexpo V Ukrainu
May 17, 2025
Zhevago Zayavil O Vozmozhnom Prekraschenii Investitsiy Ferrexpo V Ukrainu
May 17, 2025 -
 Rethinking Middle Management Their Impact On Company Performance And Employee Satisfaction
May 17, 2025
Rethinking Middle Management Their Impact On Company Performance And Employee Satisfaction
May 17, 2025
