Los Angeles Wildfires: A Reflection Of Societal Attitudes Towards Gambling And Risk

Table of Contents
The Gamble with Nature: Understanding Wildfire Risk Factors
The increasing frequency and intensity of Los Angeles wildfires are not solely acts of nature; they are a consequence of choices we make as a society. Understanding these choices is crucial to mitigating future risks.
WUI Development: A High-Stakes Bet
The expansion of the Wildland-Urban Interface (WUI) – the zone where urban development meets wildlands – is a primary driver of wildfire risk. Rising property values incentivize development in increasingly fire-prone areas, leading to urban sprawl and increased vulnerability.
- Rising property values: The allure of owning a home with stunning views often overshadows the inherent risks.
- Lack of adequate fire-resistant building codes: Many existing structures lack the necessary fire-resistant materials and design features to withstand intense wildfires.
- Insufficient planning and zoning regulations: Inadequate land-use planning allows development in areas highly susceptible to wildfires, exacerbating the problem.
This unchecked WUI development necessitates a comprehensive review of wildfire risk assessment, stricter enforcement of fire-resistant building materials, and smarter urban planning strategies to minimize future losses. The consequences of ignoring this risk are catastrophic, as seen in numerous Los Angeles wildfires.
Ignoring Early Warning Signs: A Risky Proposition
The tendency to downplay or ignore early warning signs of wildfire danger is another significant contributor to the devastating impact of these events. This behavior is strikingly similar to a gambler ignoring warning signs of impending losses.
- Failure to heed evacuation orders: Delays in evacuating endangered areas can lead to tragic consequences.
- Underestimation of fire spread potential: The unpredictable nature of wildfires often leads to underestimation of their destructive power.
- Neglecting fire prevention measures: Failing to clear brush, maintain defensible space around homes, and implement other preventative measures significantly increases risk.
Effective wildfire prediction models and improved early warning systems are critical. However, equally important is enhancing public understanding of wildfire prevention strategies and promoting responsible risk perception. This involves educating the public about the real dangers and encouraging proactive participation in fire prevention efforts.
Climate Change as a High-Stakes Bet: The Long-Term Gamble
Climate change is dramatically increasing the frequency and intensity of wildfires in Los Angeles and across the globe. This is a high-stakes gamble with long-term, potentially irreversible consequences.
- Increased frequency and intensity of droughts: Drier conditions create abundant fuel for wildfires, making them more easily ignited and harder to control.
- Higher temperatures leading to drier vegetation: Increased heat exacerbates drought conditions, creating a tinderbox environment ready to ignite.
- Changes in wind patterns: Shifting wind patterns can rapidly spread wildfires, making containment efforts more challenging.
Addressing climate change is paramount to mitigating wildfire risk. This necessitates a global effort to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and implement sustainable practices to protect our environment. Ignoring this challenge is a gamble we cannot afford to lose.
The Psychology of Risk: Parallels with Gambling Behavior
Understanding the psychological factors influencing our response to wildfire risk is essential for developing effective mitigation strategies. These factors often mirror the cognitive biases observed in gambling behavior.
The Gambler's Fallacy and Wildfire Risk: A False Sense of Security
The gambler's fallacy – the mistaken belief that past events influence future probabilities – is frequently observed in relation to wildfire risk. People may believe that because their area has not experienced a major fire in the past, they are safe.
- Ignoring historical fire data: Failing to acknowledge past fire events increases vulnerability.
- Assuming past safety equates to future safety: This false sense of security can lead to complacency and a lack of preparedness.
- The illusion of control over uncontrollable events: Wildfires are inherently unpredictable, yet many attempt to exert control where it is impossible.
Addressing this cognitive bias requires promoting a realistic understanding of wildfire risk, emphasizing the inherent unpredictability of these events, and promoting preparedness regardless of past experience.
Confirmation Bias and Selective Attention: Choosing What to Believe
Confirmation bias – the tendency to favor information confirming pre-existing beliefs – plays a significant role in shaping our perception of wildfire risk.
- Dismissing scientific evidence: Ignoring expert warnings and scientific data about wildfire risk leads to unpreparedness.
- Focusing on anecdotal evidence: Relying on personal experiences or isolated incidents can lead to a skewed perception of risk.
- Ignoring expert warnings: Disregarding the advice of fire professionals can have severe consequences.
Effective risk communication strategies must aim to counteract these biases by presenting clear, accurate, and unbiased information in an accessible manner.
The Role of Media in Shaping Risk Perception: A Double-Edged Sword
Media coverage significantly influences public perception of wildfire risk, serving as both an informative tool and a potential source of misinformation.
- Sensationalized reporting vs. factual reporting: Overly dramatic reporting can heighten fear and anxiety, while downplaying the risk can lead to complacency.
- The influence of social media: Social media can spread both accurate information and misinformation, creating confusion and hindering effective response.
- Spread of misinformation: False or misleading information can undermine trust in official sources and hinder effective preparedness efforts.
Responsible media reporting is crucial, emphasizing factual information while avoiding sensationalism. Public awareness campaigns can help counteract misinformation and promote critical thinking about information shared online.
Conclusion: Stop Gambling with Our Future
The devastating Los Angeles wildfires serve as a stark reminder of the high-stakes gamble we play with nature. Our societal attitudes towards risk, often mirroring the gambler's fallacy and other cognitive biases, contribute significantly to the increasing vulnerability to wildfires. By understanding the parallels between gambling behavior and our response to wildfire risk, we can adopt more responsible approaches to land management, disaster preparedness, and public education. Let's stop gambling with our future and work towards a more informed and proactive approach to wildfire prevention and mitigation in Los Angeles and beyond. Addressing the root causes of wildfire risk is not a gamble; it’s an investment in a safer and more sustainable future. Let's make responsible choices and mitigate the risk of future Los Angeles wildfires.

Featured Posts
-
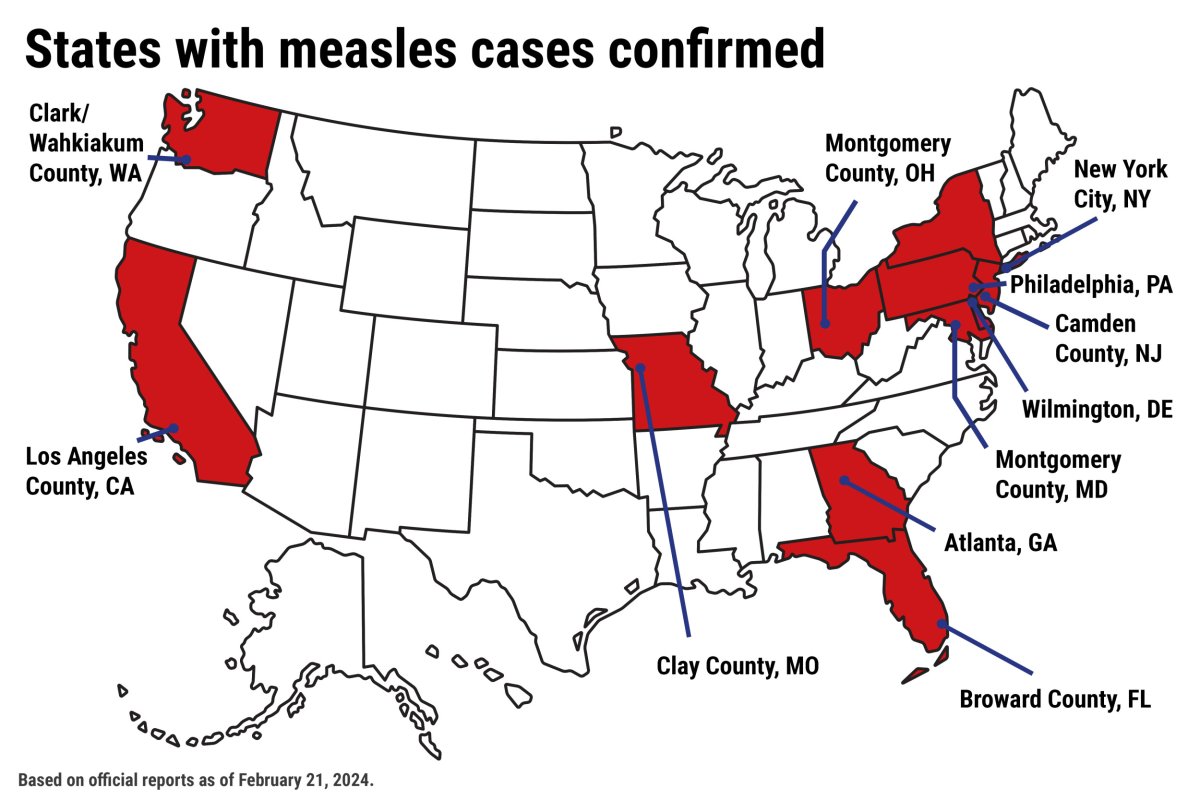 Slight Increase In Us Measles Cases Total Reaches 1 046
May 30, 2025
Slight Increase In Us Measles Cases Total Reaches 1 046
May 30, 2025 -
 Appel Rn Jacobelli Salue La Rapidite De La Justice
May 30, 2025
Appel Rn Jacobelli Salue La Rapidite De La Justice
May 30, 2025 -
 Wildfire Speculation Analyzing The Market For Los Angeles Fire Bets
May 30, 2025
Wildfire Speculation Analyzing The Market For Los Angeles Fire Bets
May 30, 2025 -
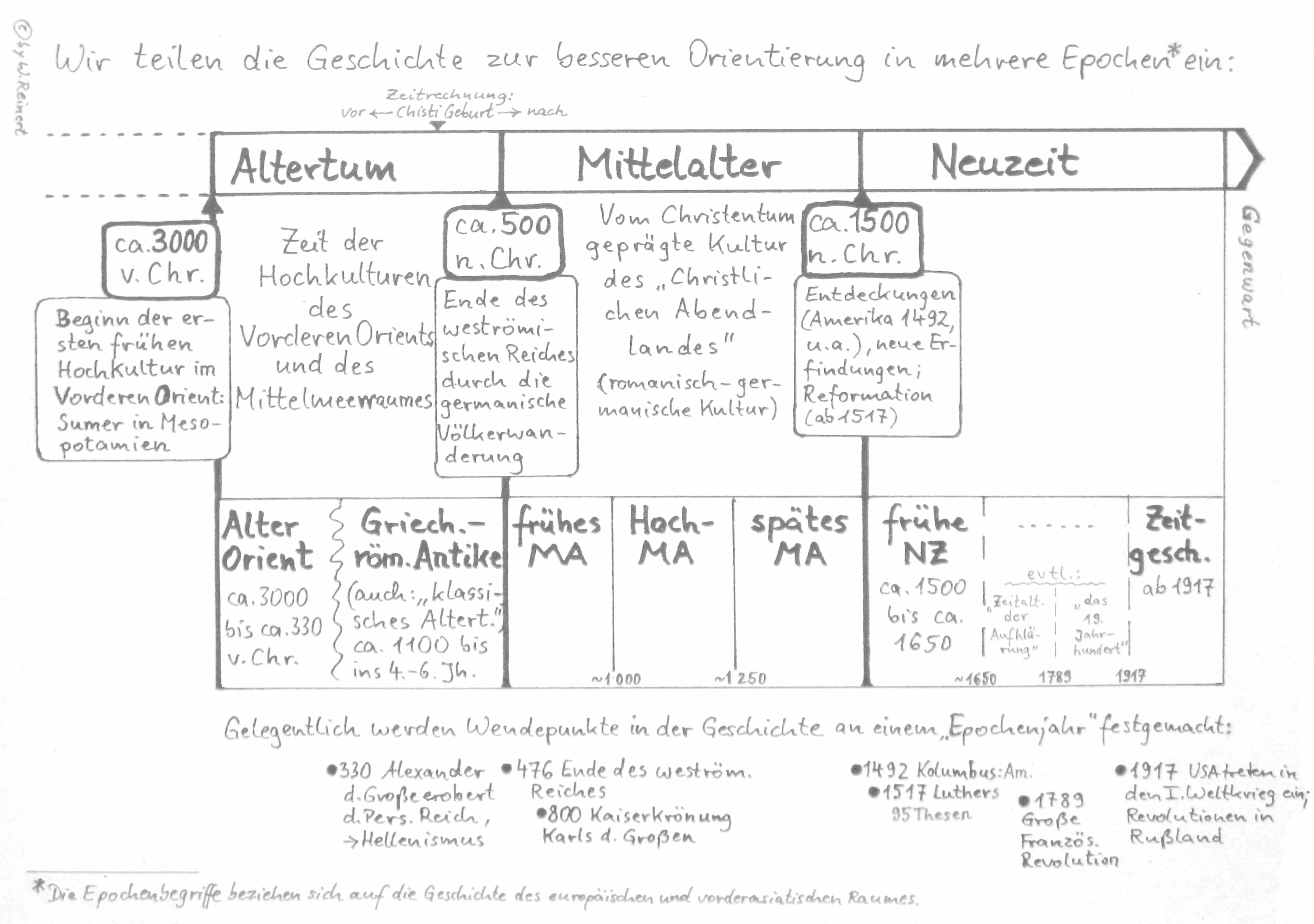 Der 10 April In Der Geschichte Daten Fakten Und Ereignisse
May 30, 2025
Der 10 April In Der Geschichte Daten Fakten Und Ereignisse
May 30, 2025 -
 French Rape Survivors Story Gisele Pelicots Book Headed To Hbo
May 30, 2025
French Rape Survivors Story Gisele Pelicots Book Headed To Hbo
May 30, 2025
