Market Volatility And Investor Behavior: Professionals Vs. Individuals
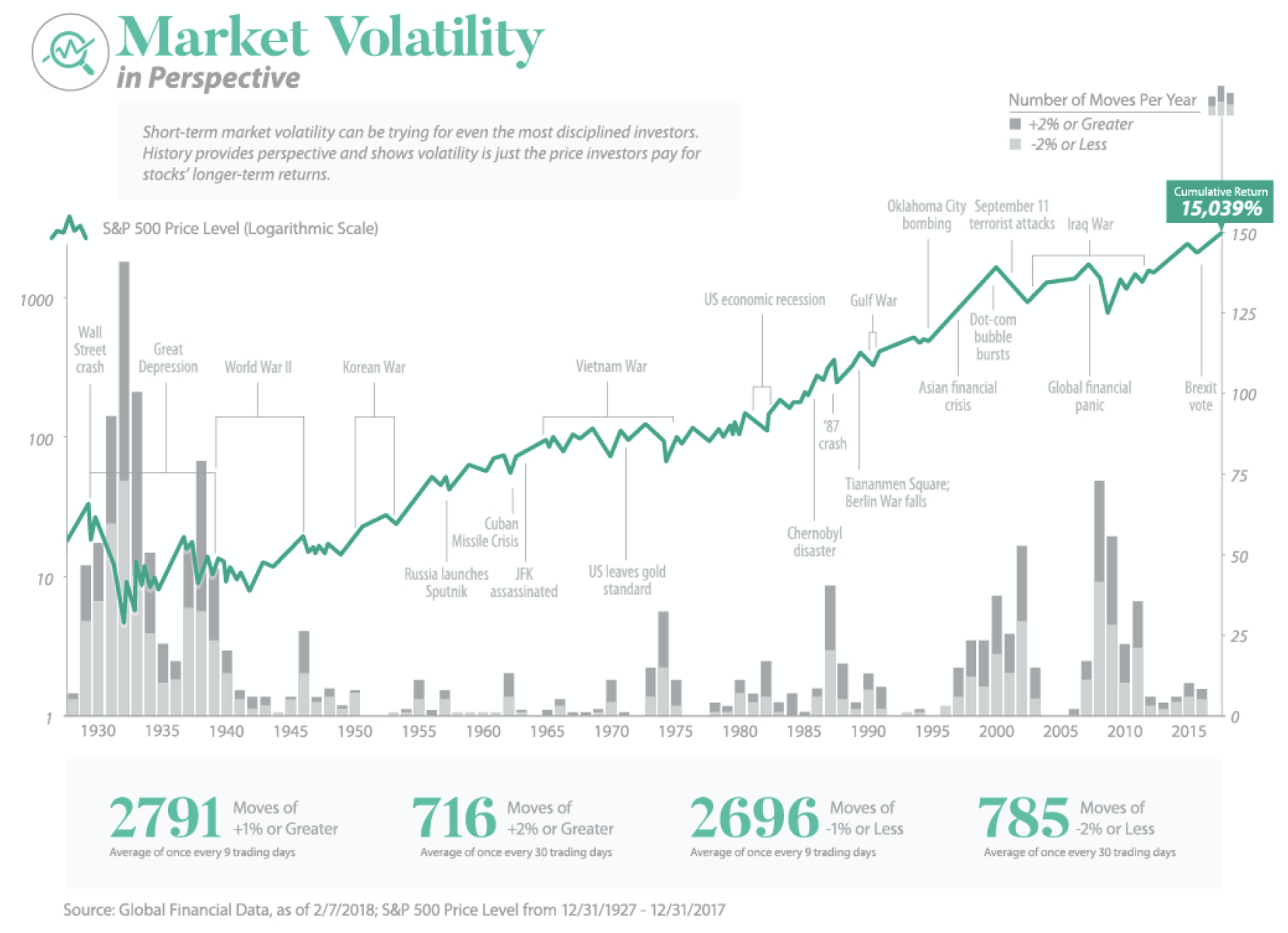
Table of Contents
Professional Investor Behavior During Market Volatility
Risk Management Strategies Employed by Professionals
Professional investors employ sophisticated risk mitigation techniques to navigate market volatility. Their strategies often include:
- Diversification: Spreading investments across various asset classes (stocks, bonds, real estate, etc.) and geographies to reduce the impact of any single market downturn.
- Hedging: Using financial instruments like options or futures contracts to offset potential losses in other investments.
- Options Strategies: Employing complex options trading strategies to manage risk and generate income, regardless of market direction.
- Stop-Loss Orders: Setting predetermined price points at which to automatically sell an asset to limit potential losses.
Professionals also have access to advanced analytical tools and market data, providing insights unavailable to the average individual investor. This allows for more informed decision-making and precise risk assessment. Furthermore, stress testing and scenario planning are integral parts of their portfolio construction, allowing them to anticipate and prepare for various market conditions.
Emotional Detachment and Long-Term Perspective
A key differentiator between professionals and individuals is emotional detachment. Professionals are trained to make rational, data-driven decisions, minimizing emotional responses to short-term market fluctuations. They understand that market volatility is inherent and focus on long-term investment horizons and strategic asset allocation. This contrasts sharply with the emotional decision-making often seen in individual investors, who may panic sell during downturns or chase short-term gains during rallies. A long-term perspective is paramount in their strategies, allowing them to weather market storms and capitalize on long-term growth opportunities.
The Role of Institutional Regulations and Compliance
Institutional regulations significantly influence professional investor behavior. Fiduciary duty, for example, legally obligates professionals to act in the best interests of their clients. Risk disclosure requirements ensure transparency and protect investors. Compliance requirements, while adding complexity, ultimately aim to promote responsible investment practices and prevent excessive risk-taking. These regulations, though burdensome, contribute to a more stable and predictable investment landscape compared to the unregulated realm of individual investing.
Individual Investor Behavior During Market Volatility
The Influence of Fear and Greed
Fear and greed are powerful emotions that significantly impact individual investor behavior during market volatility. Panic selling during downturns and chasing short-term gains during rallies are common outcomes of these emotional responses. Behavioral biases such as:
- Herd behavior: Following the crowd without independent analysis.
- Confirmation bias: Seeking information that confirms pre-existing beliefs.
exacerbate these issues. Media coverage and market sentiment further influence investor confidence, often leading to amplified emotional reactions.
Limited Access to Resources and Information
Individual investors often face challenges in accessing sophisticated analytical tools and market data. Unlike professionals, they may lack the specialized knowledge and resources for in-depth market analysis. Reliance on readily available (and potentially unreliable) information sources can lead to poor investment decisions, especially during periods of heightened market volatility. This information asymmetry creates a significant disadvantage for individual investors.
The Impact of Cognitive Biases on Investment Decisions
Cognitive biases significantly impact individual investor behavior. Examples include:
- Overconfidence: Overestimating one's ability to predict market movements.
- Anchoring bias: Over-relying on initial information, even if outdated.
- Disposition effect: Selling winning investments too early and holding onto losing investments for too long.
These biases can lead to suboptimal investment decisions and hinder long-term portfolio performance, particularly during volatile market conditions.
Key Differences and Strategies for Success
Comparing Professional and Individual Approaches
| Feature | Professional Investors | Individual Investors |
|---|---|---|
| Risk Management | Sophisticated strategies, diversification, hedging | Often limited, reactive, prone to emotional decisions |
| Emotional Response | Detached, data-driven | Prone to fear and greed, influenced by emotions |
| Information Access | Extensive data and analytical tools | Limited access, reliance on readily available information |
| Investment Horizon | Long-term perspective | Often short-term focused |
| Regulations | Subject to strict regulations and compliance standards | Largely unregulated |
Strategies for Individual Investors to Navigate Volatility
Individual investors can mitigate the impact of market volatility by:
- Diversifying their portfolios: Spreading investments across different asset classes to reduce risk.
- Adopting a long-term investment plan: Focusing on long-term goals and ignoring short-term market fluctuations.
- Seeking professional financial advice: Consulting with a financial advisor for personalized guidance and portfolio management.
- Employing volatility mitigation strategies: Using strategies like dollar-cost averaging to reduce the impact of market timing.
- Focusing on risk-adjusted returns: Prioritizing investments that offer acceptable returns relative to their level of risk.
- Engaging in long-term investment planning: Developing a clear financial plan with realistic goals and time horizons.
These strategies can significantly improve the chances of achieving long-term financial success, even in turbulent markets.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences in Market Volatility and Investor Behavior between professionals and individuals is critical for successful investing. Professionals leverage sophisticated tools, a long-term perspective, and emotional detachment to navigate volatility. Individuals, however, are often susceptible to emotional decision-making and cognitive biases, which can negatively impact their portfolio performance. Key takeaways include the importance of acknowledging the influence of emotions and cognitive biases, adopting a long-term investment strategy, and diversifying investments. To effectively manage your portfolio during periods of uncertainty, develop a comprehensive understanding of market volatility and investor behavior and consider seeking professional financial advice. Further reading on behavioral finance and risk management can significantly enhance your investment knowledge and help you make more informed decisions.

Featured Posts
-
 Harvard Researchers Deportation Hearing In Louisiana Awaiting Judges Decision
Apr 28, 2025
Harvard Researchers Deportation Hearing In Louisiana Awaiting Judges Decision
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Canadian Trade Mission To Southeast Asia Unlocking Energy Potential
Apr 28, 2025
Canadian Trade Mission To Southeast Asia Unlocking Energy Potential
Apr 28, 2025 -
 2000 Yankees Season Posadas Crucial Home Run Against The Royals
Apr 28, 2025
2000 Yankees Season Posadas Crucial Home Run Against The Royals
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Car Dealerships Step Up Fight Against Electric Vehicle Regulations
Apr 28, 2025
Car Dealerships Step Up Fight Against Electric Vehicle Regulations
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Ev Mandate Backlash Car Dealerships Renew Resistance
Apr 28, 2025
Ev Mandate Backlash Car Dealerships Renew Resistance
Apr 28, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Updated Injury List Rays Vs Yankees Series April 17 20
May 12, 2025
Updated Injury List Rays Vs Yankees Series April 17 20
May 12, 2025 -
 Jurickson Profars 80 Game Suspension The Full Story
May 12, 2025
Jurickson Profars 80 Game Suspension The Full Story
May 12, 2025 -
 Early Season Contrast Aaron Judges Dominance And Atlantas Slow Pace
May 12, 2025
Early Season Contrast Aaron Judges Dominance And Atlantas Slow Pace
May 12, 2025 -
 Injury Report Rays Vs Yankees April 17 20
May 12, 2025
Injury Report Rays Vs Yankees April 17 20
May 12, 2025 -
 Reaction And Fallout From Jurickson Profars 80 Game Ped Ban
May 12, 2025
Reaction And Fallout From Jurickson Profars 80 Game Ped Ban
May 12, 2025
