Missing Excessive Heat Warnings: An Explanation

Table of Contents
Technological Limitations in Predicting and Disseminating Excessive Heat Warnings
Predicting and disseminating effective heat warnings requires a robust technological infrastructure. Unfortunately, significant limitations exist in several key areas.
Inadequate Weather Monitoring Networks
Accurate heat prediction relies on a dense network of weather stations providing real-time data. However, gaps in coverage are widespread, particularly in remote or underserved areas. This lack of comprehensive data hampers the accuracy of heatwave forecasts and the timely issuance of heat warnings.
- Lack of sensors: Many regions, especially in developing countries, lack sufficient weather sensors to capture localized temperature variations.
- Insufficient data resolution: Existing data may lack the spatial and temporal resolution to accurately pinpoint areas at highest risk.
- Reliance on outdated technology: Outmoded equipment and limited data processing capabilities further hinder accurate predictions.
Many developing nations lack the dense network of weather stations required for precise localized heat predictions, resulting in delayed or absent heat warnings, leaving vulnerable populations at increased risk of heatstroke and other heat-related illnesses.
Challenges in Forecasting Extreme Heat Events
Accurately predicting the intensity and duration of heatwaves is inherently complex. Current meteorological models, while improving, still struggle to capture the nuances of extreme heat events.
- Influence of climate change on heatwave prediction: The increasing frequency and intensity of heatwaves due to climate change pose significant challenges for accurate forecasting.
- Unpredictable weather patterns: The chaotic nature of atmospheric systems makes precise long-range heatwave forecasting difficult.
- Difficulty in predicting localized heat pockets: Urban heat islands, for instance, can experience significantly higher temperatures than surrounding areas, requiring hyperlocal forecasting capabilities.
The unpredictable nature of heatwaves, particularly their intensity and duration, makes accurate forecasting a significant challenge, sometimes leading to underestimation of risk and a failure to issue warnings.
Inefficient Warning Dissemination Systems
Even with accurate predictions, effective communication is crucial. However, challenges remain in reaching all at-risk populations.
- Digital divide: Reliance on digital platforms for disseminating heat warnings excludes individuals without internet access.
- Lack of multilingual warnings: Warnings may not be available in the languages spoken by all residents of a region.
- Reliance on outdated technologies: Traditional warning systems like sirens may not be universally understood or accessible.
- Difficulties reaching homeless populations: Individuals without stable housing are particularly vulnerable and difficult to reach.
Elderly individuals or those without internet access may be particularly vulnerable to missing crucial heat warnings distributed primarily through digital platforms. Effective dissemination strategies must consider the diverse needs of all community members.
Data Deficiencies and Resource Constraints
The ability to issue timely and accurate excessive heat warnings is also hampered by data deficiencies and limited resources.
Lack of Historical Heat Data
Building robust predictive models requires comprehensive historical temperature data. However, many regions suffer from incomplete or inconsistent data records.
- Insufficient data in certain geographic areas: Data sparsity makes it difficult to establish baseline temperatures and identify trends.
- Inconsistent data collection methods over time: Changes in data collection techniques can lead to inconsistencies and inaccuracies.
Accurate forecasting depends on robust historical data. However, many regions lack sufficient historical temperature data, hindering the development of reliable heatwave prediction models.
Underfunding of Meteorological Services
Many meteorological services are underfunded, limiting their capacity to monitor, predict, and disseminate heat warnings effectively.
- Lack of personnel: Insufficient staffing hinders data analysis, model development, and warning dissemination.
- Insufficient investment in technology upgrades: Outdated equipment restricts data collection and processing capabilities.
- Inadequate training: A lack of proper training limits the expertise available for accurate forecasting and communication.
Underfunded meteorological services often struggle to maintain and update their equipment, limiting their ability to provide timely and accurate excessive heat warnings.
Communication Barriers and Public Awareness
Effective communication and public awareness are vital for mitigating the risks associated with extreme heat.
Effective Communication Strategies
Clear, accessible, and timely communication is paramount for effective heat warnings.
- Utilizing multiple communication channels: Employing diverse methods (e.g., radio, television, social media, text alerts) ensures wider reach.
- Translating warnings into multiple languages: Ensuring warnings are accessible to all language groups is crucial.
- Employing visual aids: Using maps, charts, and other visual aids can improve comprehension.
- Focusing on actionable steps individuals can take: Warnings should clearly outline steps to protect oneself from extreme heat.
Using simple language, incorporating visuals, and providing clear instructions on heat safety precautions in warnings is crucial for effective communication.
Public Understanding of Heat-Related Risks
Increasing public awareness of heatstroke and other heat-related illnesses is critical.
- Educating the public about the symptoms of heatstroke: Early recognition of symptoms is key to prompt intervention.
- Promoting proactive heat safety measures: Educating the public on preventive measures can significantly reduce risks.
- Targeting vulnerable populations with tailored information: Specific messaging should address the unique needs of at-risk groups (elderly, children, individuals with chronic illnesses).
Public education campaigns should emphasize the seriousness of heat-related illnesses and promote preparedness measures to mitigate risks.
Conclusion: Addressing the Gap in Excessive Heat Warnings
Missing or inadequate excessive heat warnings result from a combination of technological limitations, data deficiencies, and communication barriers. Addressing these issues requires a multifaceted approach. Improved weather monitoring networks, increased investment in meteorological services, and enhanced communication strategies are all crucial. By demanding better funding for meteorological services and promoting improved communication strategies, we can collectively reduce the number of preventable heat-related illnesses and deaths caused by missing excessive heat warnings. Let's work together to ensure everyone receives the critical warnings they need to stay safe during heatwaves. Let's advocate for better heat warnings and a safer future.

Featured Posts
-
 Marine Le Pen Une Question De Justice Selon Jacobelli
May 30, 2025
Marine Le Pen Une Question De Justice Selon Jacobelli
May 30, 2025 -
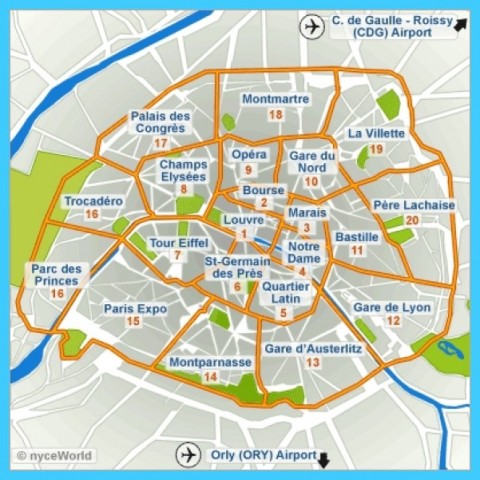 Exploring Paris A Guide To Its Best Neighborhoods
May 30, 2025
Exploring Paris A Guide To Its Best Neighborhoods
May 30, 2025 -
 Limited Time Offer R45 000 Discount On Kawasaki Ninja Bikes
May 30, 2025
Limited Time Offer R45 000 Discount On Kawasaki Ninja Bikes
May 30, 2025 -
 New Iowa Law Limits Cell Phones In Schools Impact On Students And Teachers
May 30, 2025
New Iowa Law Limits Cell Phones In Schools Impact On Students And Teachers
May 30, 2025 -
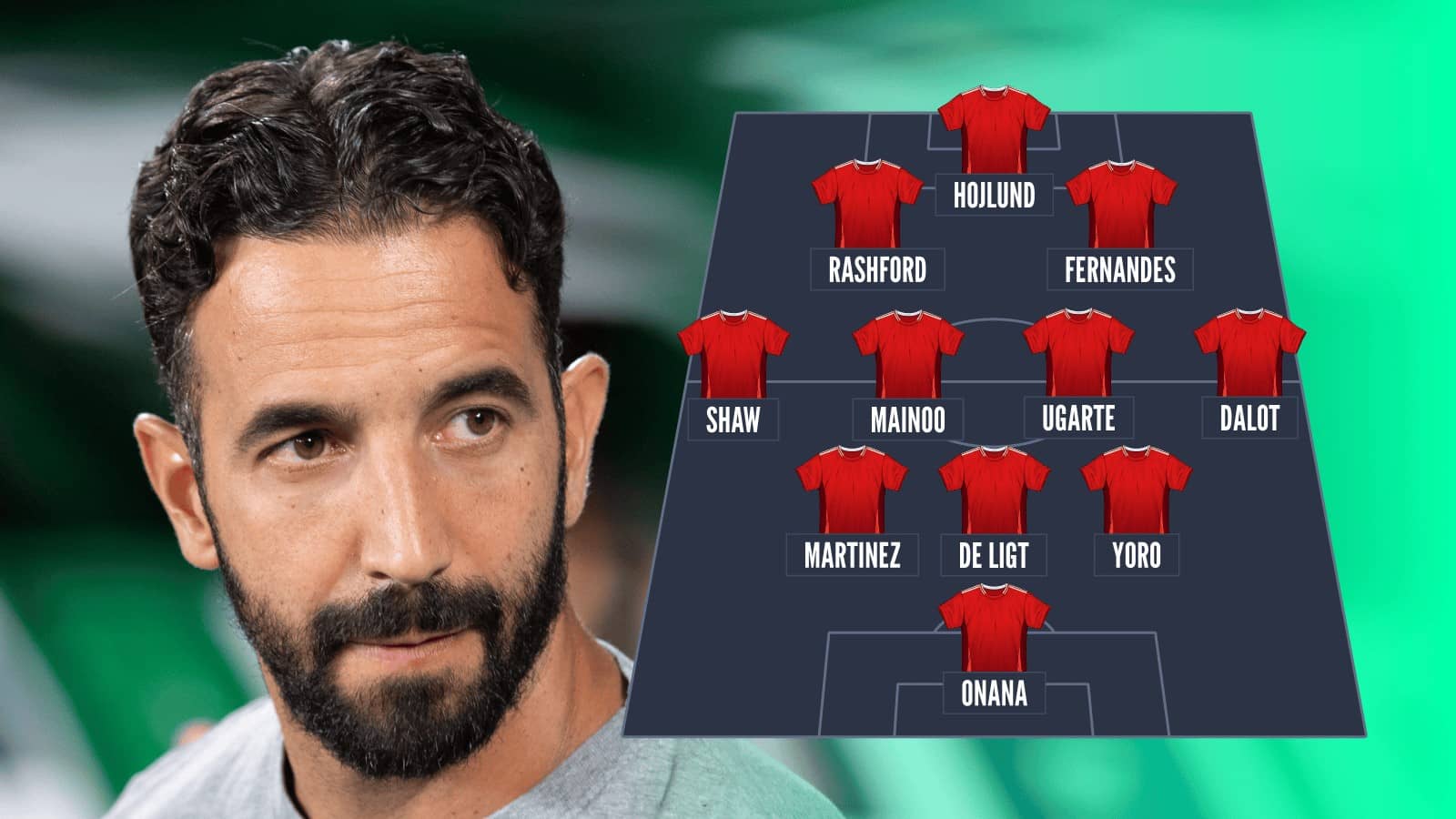 Sporting Cps Amorim Set To Reject Man Uniteds Transfer Offer
May 30, 2025
Sporting Cps Amorim Set To Reject Man Uniteds Transfer Offer
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Grigor Dimitrov Vliyanieto Na Kontuziyata Vrkhu Karierata Mu
May 31, 2025
Grigor Dimitrov Vliyanieto Na Kontuziyata Vrkhu Karierata Mu
May 31, 2025 -
 Kontuziyata Na Grigor Dimitrov Aktualna Informatsiya I Analiz
May 31, 2025
Kontuziyata Na Grigor Dimitrov Aktualna Informatsiya I Analiz
May 31, 2025 -
 Trumps Uncertainty What Made Him Question Elon Musk
May 31, 2025
Trumps Uncertainty What Made Him Question Elon Musk
May 31, 2025 -
 Uncertainty And The End Trumps Doubts About Elon Before The Break
May 31, 2025
Uncertainty And The End Trumps Doubts About Elon Before The Break
May 31, 2025 -
 Everything Revealed In The Star Trek Strange New Worlds Season 3 Teaser
May 31, 2025
Everything Revealed In The Star Trek Strange New Worlds Season 3 Teaser
May 31, 2025
