New COVID-19 Variant Driving Up Cases In Some Regions, Warns WHO
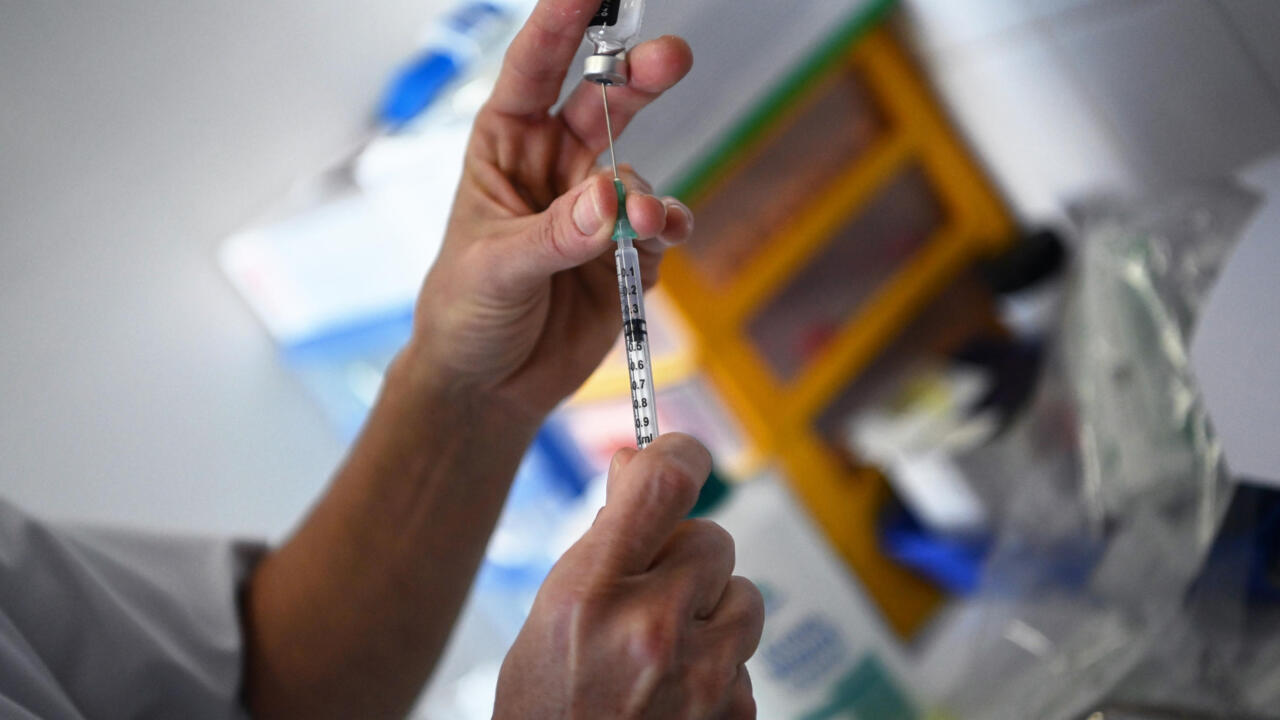
Table of Contents
Identification and Characteristics of the New COVID-19 Variant
The WHO has identified a new variant of concern, tentatively named XBB.1.5 (replace with the actual name if different). This new COVID variant carries several key mutations that are of significant interest to scientists and public health officials. These mutations are suspected to influence its transmissibility and perhaps even its severity.
- Specific mutations and their potential impact: The XBB.1.5 variant possesses mutations in the spike protein, the part of the virus that binds to human cells. These mutations (list specific mutations if known, e.g., F486P, S494P) are believed to increase its ability to evade existing immunity from prior infection or vaccination. Preliminary data suggests this could lead to increased re-infections.
- Comparison to previous variants: Compared to previous Omicron subvariants, XBB.1.5 shows a potentially higher transmissibility rate, meaning it spreads more easily. While initial data suggests the severity might be similar, further investigation is ongoing.
- Observed symptoms and their severity: Symptoms reported so far are consistent with previous COVID-19 variants, including fever, cough, fatigue, loss of taste or smell, and shortness of breath. The severity seems to vary between individuals, ranging from mild to severe, though more data is needed for a definitive assessment.
- Geographic regions most affected: Currently, XBB.1.5 appears to be predominantly affecting (list specific regions, e.g., North America, Europe), but global monitoring is crucial to track its spread.
Impact on Case Numbers and Hospitalizations
The emergence of this new COVID-19 variant is already being felt in increased case numbers and hospitalizations. The strain on healthcare systems is a growing concern.
- Specific data on case increases in affected regions: Preliminary reports (cite sources like the WHO or CDC) indicate a significant increase in COVID-19 cases in (specific regions), with daily case counts rising by (percentage or specific numbers) in recent weeks.
- Percentage increase in hospitalizations and ICU admissions: Hospital admissions and ICU occupancy rates are also rising in these areas, although the increase may not be directly proportional to the increase in overall cases, depending on vaccination rates and the severity of the new variant.
- Analysis of the impact on healthcare resources: The increasing number of patients requires more hospital beds, medical staff, and resources, potentially overwhelming some healthcare systems and delaying care for other conditions.
- Mention any reports of increased mortality: While early data suggests that mortality rates might not be significantly higher than previous variants, close monitoring is essential to understand the long-term implications.
Effectiveness of Existing Vaccines and Treatments
The effectiveness of existing vaccines and treatments against this new COVID-19 variant is a critical question.
- Data on vaccine effectiveness against infection and severe disease: While current vaccines may offer reduced protection against infection with XBB.1.5, they are likely still effective in reducing the severity of illness, hospitalization, and death. More research is needed to fully assess the extent of this protection.
- Effectiveness of available antiviral treatments: Current antiviral medications (e.g., Paxlovid, molnupiravir) are likely to remain effective against XBB.1.5, but their effectiveness might vary based on individual factors and the timing of treatment.
- Recommendations for booster shots or updated vaccines: Boosters, particularly those targeting Omicron subvariants, are strongly recommended to enhance protection against this new COVID variant. The development and rollout of updated vaccines tailored to XBB.1.5 or similar variants might become necessary.
WHO Recommendations and Public Health Measures
The WHO and other global health organizations are urging the implementation of several public health measures to mitigate the spread of this new COVID-19 variant.
- Specific recommendations from the WHO: The WHO recommends vaccination, booster doses for eligible populations, and continued surveillance to monitor the virus’s evolution.
- Recommended public health measures: Depending on local circumstances, measures like mask-wearing in indoor settings, improved ventilation, social distancing, and increased testing might be reintroduced.
- Importance of personal hygiene and vaccination: Simple practices like frequent hand washing, covering coughs and sneezes, and staying home when sick remain crucial in preventing the spread. Vaccination remains a critical defense against severe illness.
- Importance of monitoring symptoms and seeking testing if needed: Individuals should remain vigilant, monitor themselves for symptoms, and seek testing if they feel unwell.
Conclusion
The emergence of a new COVID-19 variant, such as XBB.1.5, highlights the ongoing need for vigilance and proactive public health measures. The increase in cases and potential strain on healthcare systems underscore the importance of vaccination, boosters, and adherence to recommended guidelines. Staying informed about this new COVID-19 variant and taking necessary precautions are vital for protecting ourselves and our communities. Consult the WHO and your local health authority for the most up-to-date information and guidelines. Stay informed about this new COVID-19 variant and take appropriate action to protect yourself and others.

Featured Posts
-
 Eastern Manitoba Wildfires A Devastating Fight Against Nature
May 31, 2025
Eastern Manitoba Wildfires A Devastating Fight Against Nature
May 31, 2025 -
 This Springs Echo Of 1968 Predicting Summer Drought
May 31, 2025
This Springs Echo Of 1968 Predicting Summer Drought
May 31, 2025 -
 France Far Left Reaction To Muslim Mans Death Highlights Islamophobia Concerns
May 31, 2025
France Far Left Reaction To Muslim Mans Death Highlights Islamophobia Concerns
May 31, 2025 -
 The Pursuit Of The Good Life Strategies For Lasting Well Being
May 31, 2025
The Pursuit Of The Good Life Strategies For Lasting Well Being
May 31, 2025 -
 Entrepreneurs Dragon Den Success Turns Sour Lawsuit Over Puppy Toilet Innovation
May 31, 2025
Entrepreneurs Dragon Den Success Turns Sour Lawsuit Over Puppy Toilet Innovation
May 31, 2025
