New York's 3°C Temperature Drop: Canadian Wildfire Smoke And Air Pollution Impacts
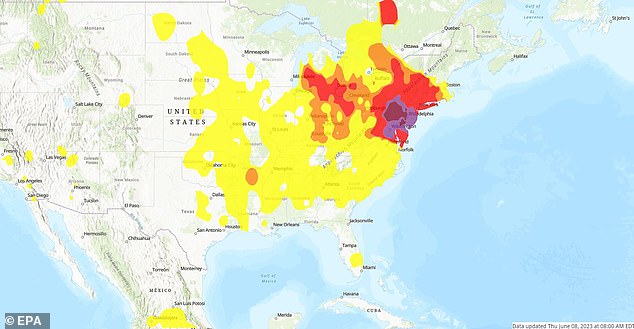
Table of Contents
The Canadian Wildfire Crisis and its Spread
The 2023 Canadian wildfire season has been unprecedented in its scale and severity. Thousands of wildfires have raged across the country, burning millions of acres of forest and releasing massive plumes of smoke into the atmosphere. The sheer magnitude of these fires, fueled by dry conditions and strong winds, is staggering. Provinces like British Columbia, Alberta, Ontario, and Quebec have been particularly hard hit. Weather patterns, specifically a persistent southward shift in prevailing winds, played a crucial role in transporting these smoke plumes hundreds, even thousands of miles, directly to New York City.
- Affected Regions: British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan, Ontario, Quebec.
- Area Burned: Millions of acres (precise figures vary depending on the constantly evolving situation).
- Weather Systems: High-pressure systems and jet stream patterns contributed to the southward movement of smoke.
[Insert image or map illustrating the smoke's movement from Canada to New York]
Air Quality Degradation in New York City
The wildfire smoke significantly degraded air quality in New York City, leading to hazardous levels of various air pollutants. The smoke contained high concentrations of fine particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), ozone, and other harmful substances. These pollutants pose significant health risks, particularly to vulnerable populations such as children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing respiratory or cardiovascular conditions. Exposure to these pollutants can exacerbate asthma, bronchitis, and other respiratory illnesses, and increase the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
During the period of the temperature drop, the Air Quality Index (AQI) in NYC reached hazardous levels.
- AQI Readings: Specific readings should be included here, sourced from official AQI reporting agencies. (e.g., "The AQI reached over 200, indicating hazardous conditions.")
- Air Quality Alerts: Mention any official warnings or advisories issued by the New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene or the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
- Hospital Admissions: Data on increased hospital admissions due to respiratory issues during this period would strengthen this section.
The Mechanism Behind the Temperature Drop
The noticeable temperature decrease in New York City is a direct consequence of the wildfire smoke. The smoke and aerosols present in the smoke plume block sunlight, reducing the amount of solar radiation reaching the Earth's surface. This phenomenon, known as radiative forcing, leads to a decrease in surface temperatures. This is not a seasonal change; it's a temporary, localized cooling effect caused by the smoke's impact on the atmosphere. Similar temperature drops have been observed in other locations following large-scale wildfire events or volcanic eruptions.
- Radiative Forcing: A detailed explanation of how aerosols in the atmosphere scatter and absorb incoming solar radiation should be included.
- Temperature Comparison: If data is available, comparing temperatures before and during the smoke event would be beneficial.
- Supporting Studies: Cite relevant scientific studies or research papers that support this explanation.
Long-Term Impacts and Mitigation Strategies
The long-term consequences of the Canadian wildfires and the resultant air pollution extend beyond the immediate temperature drop. Increased respiratory illnesses in vulnerable populations are likely, along with potential long-term effects on cardiovascular health. The environmental impact is also significant, with potential damage to ecosystems and long-term air quality concerns. Mitigating the effects of future wildfire smoke events requires a multi-pronged approach.
- Increased Respiratory Illnesses: Highlight the potential burden on healthcare systems.
- Improved Monitoring Systems: Advocating for improved air quality monitoring and early warning systems is crucial.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Emphasize the link between climate change, the increased frequency and intensity of wildfires, and the need for global action.
Conclusion
The connection between the devastating Canadian wildfires, the subsequent air pollution impacting New York City, and the unusual 3°C temperature drop is clear. This event underscores the severity of the wildfire crisis and the far-reaching consequences of wildfire smoke on air quality and even local weather patterns. Understanding the effects of Canadian wildfire smoke and air pollution on New York is crucial. Stay informed about air quality updates and take steps to protect your health, especially if you are in a vulnerable group. Learn more about how you can contribute to climate change mitigation efforts to help prevent future events like this, reducing the risk of similar impacts from Canadian wildfire smoke and air pollution in New York and beyond.

Featured Posts
-
 Covid 19 Variants Ba 1 And Lf 7 Insacog Report And Public Health Concerns In India
May 31, 2025
Covid 19 Variants Ba 1 And Lf 7 Insacog Report And Public Health Concerns In India
May 31, 2025 -
 La Foire Au Jambon De Bayonne 2025 Une Gestion Financiere A Revoir
May 31, 2025
La Foire Au Jambon De Bayonne 2025 Une Gestion Financiere A Revoir
May 31, 2025 -
 Assessing The Decline Of American Military Power Relative To Chinas Growth
May 31, 2025
Assessing The Decline Of American Military Power Relative To Chinas Growth
May 31, 2025 -
 Vancouvers Epic Banksy Exhibit Details And Tickets
May 31, 2025
Vancouvers Epic Banksy Exhibit Details And Tickets
May 31, 2025 -
 Wildfires Prompt Evacuation Of Hudbay Minerals Staff In Flin Flon Manitoba
May 31, 2025
Wildfires Prompt Evacuation Of Hudbay Minerals Staff In Flin Flon Manitoba
May 31, 2025
