Non-Xenomorph Alien Life On Earth: Prediction And Discovery

Table of Contents
The search for extraterrestrial intelligence (SETI) primarily focuses on detecting radio signals from advanced civilizations. However, the broader search for extraterrestrial life, often termed astrobiology, encompasses a far wider range of possibilities, including the potential for microbial life, vastly different from anything we've encountered before. This article centers on the exciting possibility of finding such life, not in the stars, but right here on our own planet.
Predicting Non-Xenomorph Life: Extremophiles and Beyond
Extremophiles as a Model
Extremophiles, organisms thriving in extreme environments, provide compelling evidence for life's incredible adaptability. Their existence suggests that life might flourish in conditions far beyond what was once considered habitable, paving the way for the discovery of non-xenomorph alien life on Earth.
- Thermophiles: These heat-loving organisms flourish in geothermal vents and hot springs, surviving temperatures that would kill most other life forms. Their unique enzymes and metabolic processes offer insights into how life might adapt to extreme heat, a condition found on many other planets and moons.
- Halophiles: These "salt-lovers" thrive in hypersaline environments like the Great Salt Lake, showcasing adaptations to extreme salinity. Their cellular mechanisms provide clues about how life might survive on planets with salty oceans or subsurface brine.
- Acidophiles: Flourishing in highly acidic environments, these organisms demonstrate life's resilience to extreme pH levels. Understanding their survival mechanisms is crucial in expanding the definition of habitable zones and the potential for non-xenomorph alien life on Earth.
These extremophiles demonstrate the potential for life to adapt to conditions drastically different from those on Earth's surface, strongly suggesting that life might exist in other extreme environments, both on Earth and elsewhere in the universe. This underlines the potential for finding non-xenomorph alien life on Earth.
Astrobiology and the Search for Biosignatures
Astrobiology employs various methods to search for life beyond Earth. These methods, however, can also be applied to the search for unique life on our planet. The search focuses on identifying biosignatures – chemical or physical indicators of past or present life.
- Biomarkers: These specific molecules (like certain amino acids or lipids) are often associated with living organisms and can be used to detect evidence of life.
- Isotopic ratios: Slight variations in the ratios of certain isotopes can indicate biological processes. For example, the presence of specific carbon isotope ratios could suggest the presence of life that uses photosynthesis or other metabolic pathways.
Discovering unusual isotopic ratios or biomarkers in extreme environments could signal the presence of non-xenomorph alien life on Earth.
Potential Habitats for Non-Xenomorph Life on Earth
Subsurface Environments
The Earth's deep subsurface, encompassing the deep biosphere, presents a vast and largely unexplored habitat for potential life. This environment includes:
- Hydrothermal vents: These deep-sea vents spew superheated water rich in chemicals, supporting thriving ecosystems of extremophiles. The possibility of discovering even more unique life forms in these environments, drastically different from surface life, is strong.
- Deep biosphere: Extending kilometers beneath the surface, the deep biosphere is home to a diverse array of microorganisms, many of which are yet to be discovered. These organisms may represent life forms that have evolved in complete isolation from surface life, making them potential candidates for non-xenomorph alien life on Earth.
Studying these environments presents significant challenges, requiring advanced drilling techniques and specialized equipment for sample collection and analysis. However, the potential rewards – the discovery of completely novel life forms – are immense.
Unusual Terrestrial Environments
Beyond the subsurface, several extreme terrestrial environments offer promising locations for discovering unique life forms:
- High-altitude lakes: The extreme conditions of high altitude, including low temperatures, high UV radiation, and low oxygen levels, may have selected for unique adaptations.
- Hypersaline lakes: Extremely salty lakes like the Dead Sea provide harsh environments where halophilic organisms have evolved, showcasing the potential for diverse adaptations to high salinity.
- Deep-sea trenches: The crushing pressures and perpetual darkness of deep-sea trenches present an environment distinct from any other on Earth, potentially harboring unique life forms.
These unique environments highlight the extraordinary diversity of life on Earth and the possibility that even more surprising organisms remain undiscovered.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations in Discovering Non-Xenomorph Life
Technological Limitations
Current technology presents several limitations in detecting and studying microscopic alien life:
- Sample collection: Accessing and collecting samples from extreme environments like the deep biosphere requires sophisticated and often expensive technologies.
- Analysis: Identifying and characterizing novel microorganisms requires specialized techniques and expertise, often pushing the boundaries of current scientific capabilities.
Overcoming these technological limitations is crucial for advancing our understanding of the potential for non-xenomorph alien life on Earth.
Ethical Implications of Discovery
The discovery of non-xenomorph life raises significant ethical questions:
- Planetary protection: Preventing contamination of these unique environments with terrestrial life is paramount.
- Bioethics: The ethical implications of interacting with these organisms and understanding their place in the Earth's ecosystem require careful consideration.
- Responsible science: Establishing robust research protocols that prioritize the protection and preservation of these unique ecosystems is vital.
Responsible research protocols and international collaborations will be crucial for navigating the ethical implications of discovering non-xenomorph alien life on Earth.
Conclusion
The possibility of finding non-xenomorph alien life on Earth is not science fiction; it's a realistic scientific pursuit. By studying extremophiles, utilizing advanced techniques in astrobiology, and exploring extreme environments, we can increase the likelihood of discovering unique life forms. While technological limitations and ethical considerations remain, the potential rewards—a revolutionary shift in our understanding of life itself—make the search for non-xenomorph alien life on Earth a vital and exciting endeavor. Let's continue to support research in astrobiology and extremophile studies to further the quest for discovering non-xenomorph life and unlock the mysteries of our planet's biodiversity.

Featured Posts
-
 Kai Cenat And Ninja Clash Asmongold Offers His Perspective
May 27, 2025
Kai Cenat And Ninja Clash Asmongold Offers His Perspective
May 27, 2025 -
 Nimechchina Ta 10 Krayin Nova Koalitsiya Reb Dlya Ukrayini
May 27, 2025
Nimechchina Ta 10 Krayin Nova Koalitsiya Reb Dlya Ukrayini
May 27, 2025 -
 How To Watch Mob Land Episode 6 Online A Complete Guide
May 27, 2025
How To Watch Mob Land Episode 6 Online A Complete Guide
May 27, 2025 -
 Almanacco Di Domenica 23 Marzo Cosa Accadde Oggi
May 27, 2025
Almanacco Di Domenica 23 Marzo Cosa Accadde Oggi
May 27, 2025 -
 Selena Gomez And Taylor Swift A Wake Up Call Over Blake Lively And The Justin Baldoni Lawsuit
May 27, 2025
Selena Gomez And Taylor Swift A Wake Up Call Over Blake Lively And The Justin Baldoni Lawsuit
May 27, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Analysis Of The Rapidly Expanding Vaccine Packaging Market
May 30, 2025
Analysis Of The Rapidly Expanding Vaccine Packaging Market
May 30, 2025 -
 Understanding The Explosive Growth Of The Vaccine Packaging Market
May 30, 2025
Understanding The Explosive Growth Of The Vaccine Packaging Market
May 30, 2025 -
 Canadas Measles Elimination Status At Risk Fall 2024 A Critical Point
May 30, 2025
Canadas Measles Elimination Status At Risk Fall 2024 A Critical Point
May 30, 2025 -
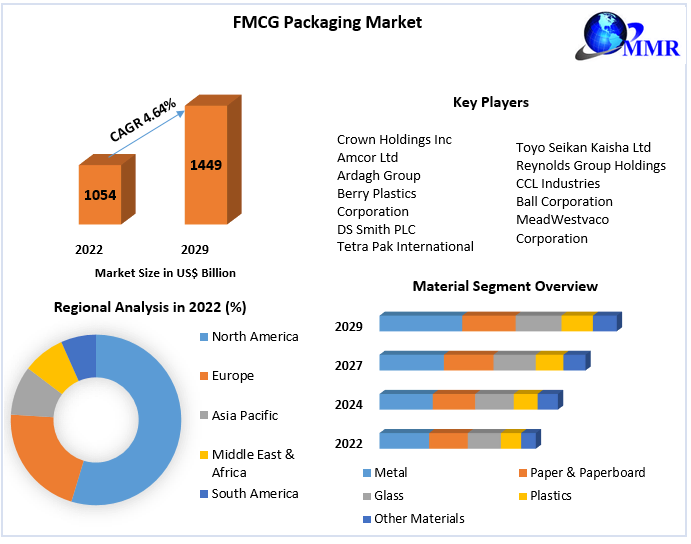 The Booming Vaccine Packaging Market Trends And Opportunities
May 30, 2025
The Booming Vaccine Packaging Market Trends And Opportunities
May 30, 2025 -
 Measles Cases In The Us A Slowdown Explained
May 30, 2025
Measles Cases In The Us A Slowdown Explained
May 30, 2025
