Ozempic And Beyond: The Growing Applications Of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists In Medicine
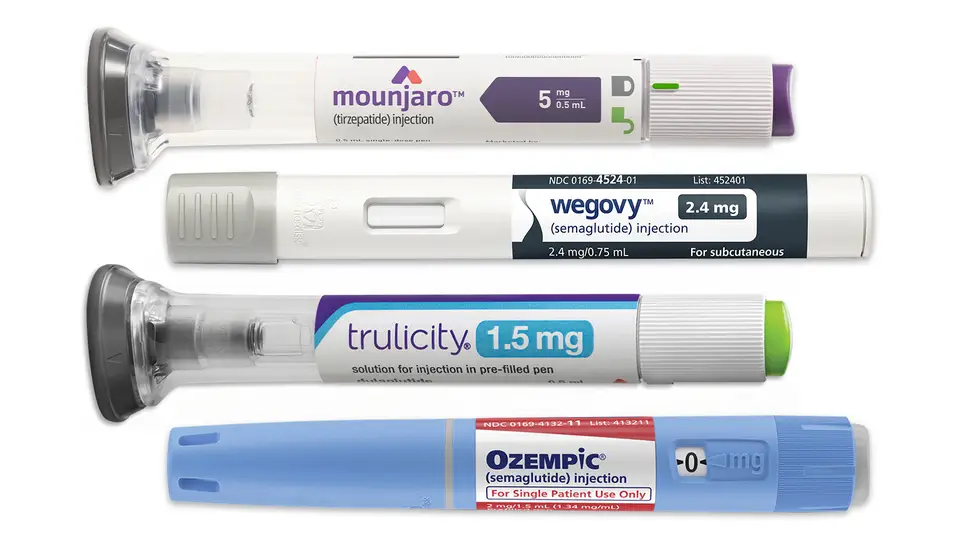
Table of Contents
GLP-1 receptor agonists, exemplified by the widely known Ozempic (semaglutide), have revolutionized the treatment of type 2 diabetes. However, their therapeutic applications extend far beyond blood sugar control, offering promising avenues in weight management, cardiovascular health, and even certain neurological conditions. This article explores the expanding horizons of GLP-1 receptor agonists and their significant impact on modern medicine.
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: A Deep Dive into Mechanism of Action
How GLP-1 Receptor Agonists Work:
GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) mimic the effects of glucagon-like peptide-1, an incretin hormone naturally produced in the gut in response to food intake. These medications work through several key mechanisms:
- Glucose-dependent Insulin Secretion: GLP-1 RAs stimulate the pancreas to release insulin, but only when blood glucose levels are elevated. This avoids hypoglycemia, a common side effect of other diabetes medications. This is a crucial aspect of their action in managing insulin resistance.
- Glucagon Suppression: They suppress the release of glucagon, a hormone that raises blood sugar levels. This dual action (increasing insulin, decreasing glucagon) contributes to better blood sugar control.
- Gastric Emptying Delay: GLP-1 RAs slow down the rate at which food leaves the stomach. This leads to increased satiety and helps regulate appetite.
- Appetite Regulation: By acting on areas of the brain involved in appetite control, GLP-1 RAs promote feelings of fullness and reduce food intake, contributing significantly to appetite suppression. This effect is vital for their efficacy in weight management.
Ozempic and Other GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: A Comparison of Available Medications
Semaglutide (Ozempic, Wegovy):
Semaglutide, the active ingredient in Ozempic (for type 2 diabetes) and Wegovy (for chronic weight management), is a highly effective GLP-1 RA. It's available in both injectable pen and, more recently, an oral form.
- Dosage Variations: Ozempic is typically administered once weekly, while Wegovy's dosage is also once weekly, but the starting dose and titration schedule differs based on the patient's needs.
- Administration Methods: Both are administered via subcutaneous injection. The ease of once-weekly administration is a significant advantage over older daily GLP-1 RAs.
- Potential Benefits: Improved glycemic control (HbA1c reduction), significant weight loss, and potential cardiovascular benefits.
- Drawbacks: Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation.
Liraglutide (Victoza, Saxenda):
Liraglutide is another widely used GLP-1 RA available in two formulations: Victoza (for type 2 diabetes) and Saxenda (for weight management). Unlike semaglutide, it’s administered daily.
- Dosage Forms: Both Victoza and Saxenda are administered via daily subcutaneous injection.
- Approved Indications: Victoza is approved for type 2 diabetes, while Saxenda is approved for chronic weight management.
- Side Effect Profile: Similar to semaglutide, common side effects include gastrointestinal issues.
Other GLP-1 Receptor Agonists:
Several other GLP-1 RAs are available, each with its own unique characteristics:
- Dulaglutide (Trulicity): Once-weekly injection, approved for type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular risk reduction.
- Exenatide (Byetta, Bydureon): Available in both twice-daily and once-weekly formulations for type 2 diabetes.
- Albiglutide (Tanzeum): Once-weekly injection, approved for type 2 diabetes.
Beyond Diabetes: Expanding Applications of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
Weight Management:
GLP-1 RAs have demonstrated remarkable efficacy in promoting weight loss, even in individuals without diabetes. They achieve this primarily through appetite suppression and increased satiety.
- Studies Demonstrating Weight Loss: Numerous clinical trials have shown substantial weight loss with GLP-1 RAs, often exceeding 10% of body weight.
- Impact on BMI: Significant reductions in BMI have been observed, indicating a positive impact on overall body composition.
- Long-term Effects: While longer-term studies are ongoing, early data suggest sustained weight loss with continued use.
Cardiovascular Benefits:
Several studies suggest that GLP-1 RAs may offer cardiovascular protection.
- Relevant Clinical Trials: Large-scale clinical trials have shown a reduction in major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) such as heart attack, stroke, and cardiovascular death in patients with type 2 diabetes.
- Cardiovascular Risk Reduction: This suggests a broader therapeutic role beyond glycemic control.
- GLP-1 and Heart Failure: Research is ongoing to explore the potential benefits of GLP-1 RAs in the management of heart failure.
Emerging Applications:
Research is exploring the potential of GLP-1 RAs in other areas:
- Neuroprotective Effects: Preclinical studies suggest potential neuroprotective effects, prompting research into their use in conditions like Alzheimer's disease.
- Alzheimer's Treatment: Early clinical trials are evaluating the potential of GLP-1 RAs to slow cognitive decline in Alzheimer's patients.
- GLP-1 Research: Ongoing research is exploring further potential applications in various neurological and metabolic disorders.
Potential Side Effects and Considerations
Common Side Effects:
The most common side effects of GLP-1 RAs are gastrointestinal, including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. These are usually mild and often resolve with continued use or dose adjustment.
- Strategies for Managing Side Effects: Starting with a low dose and gradually increasing it can help minimize side effects.
Contraindications and Precautions:
GLP-1 RAs are generally well-tolerated, but there are some contraindications:
- Personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC).
- Severe kidney disease.
- Pancreatitis.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Monitoring and Patient Management:
Regular monitoring of blood glucose, weight, and other relevant parameters is crucial during treatment with GLP-1 RAs.
Conclusion:
GLP-1 receptor agonists, including Ozempic and other medications, represent a significant advancement in the treatment of type 2 diabetes and are emerging as effective tools for weight management and possibly other health conditions. While side effects exist, their overall benefits warrant further exploration and research. Understanding the diverse applications and potential benefits of GLP-1 receptor agonists is crucial for both healthcare professionals and patients seeking effective treatment options. Consult with your doctor to determine if a GLP-1 receptor agonist is the right choice for managing your diabetes or weight. Learn more about the potential of GLP-1 receptor agonists and their role in improving your health.

Featured Posts
-
 Baldonis Legal Team Vows Accountability In Lively Lawsuit
May 28, 2025
Baldonis Legal Team Vows Accountability In Lively Lawsuit
May 28, 2025 -
 World Class Strikers Liverpool Interest Jeopardizes Arsenals Plans
May 28, 2025
World Class Strikers Liverpool Interest Jeopardizes Arsenals Plans
May 28, 2025 -
 Bon Plan Smartphone Samsung Galaxy S25 512 Go A 985 56 E
May 28, 2025
Bon Plan Smartphone Samsung Galaxy S25 512 Go A 985 56 E
May 28, 2025 -
 French Open 2024 Sinners Top Half Placement
May 28, 2025
French Open 2024 Sinners Top Half Placement
May 28, 2025 -
 2025 Marlins Opening Day Roster Projected Lineup And Key Battles
May 28, 2025
2025 Marlins Opening Day Roster Projected Lineup And Key Battles
May 28, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Elon Musks Daughters New Career A Closer Look
May 30, 2025
Elon Musks Daughters New Career A Closer Look
May 30, 2025 -
 From Silicon Valley To Runway Vivian Musks Journey
May 30, 2025
From Silicon Valley To Runway Vivian Musks Journey
May 30, 2025 -
 Analysis Of Vivian Jenna Wilsons Modeling Debut And Family Life
May 30, 2025
Analysis Of Vivian Jenna Wilsons Modeling Debut And Family Life
May 30, 2025 -
 A Public Feud Bill Gates Serious Allegations Against Elon Musk And The Response
May 30, 2025
A Public Feud Bill Gates Serious Allegations Against Elon Musk And The Response
May 30, 2025 -
 The Musk Gates Dispute Accusations Of Negligence And Child Mortality
May 30, 2025
The Musk Gates Dispute Accusations Of Negligence And Child Mortality
May 30, 2025
