Rare Earth Minerals And The Emerging Cold War Conflict
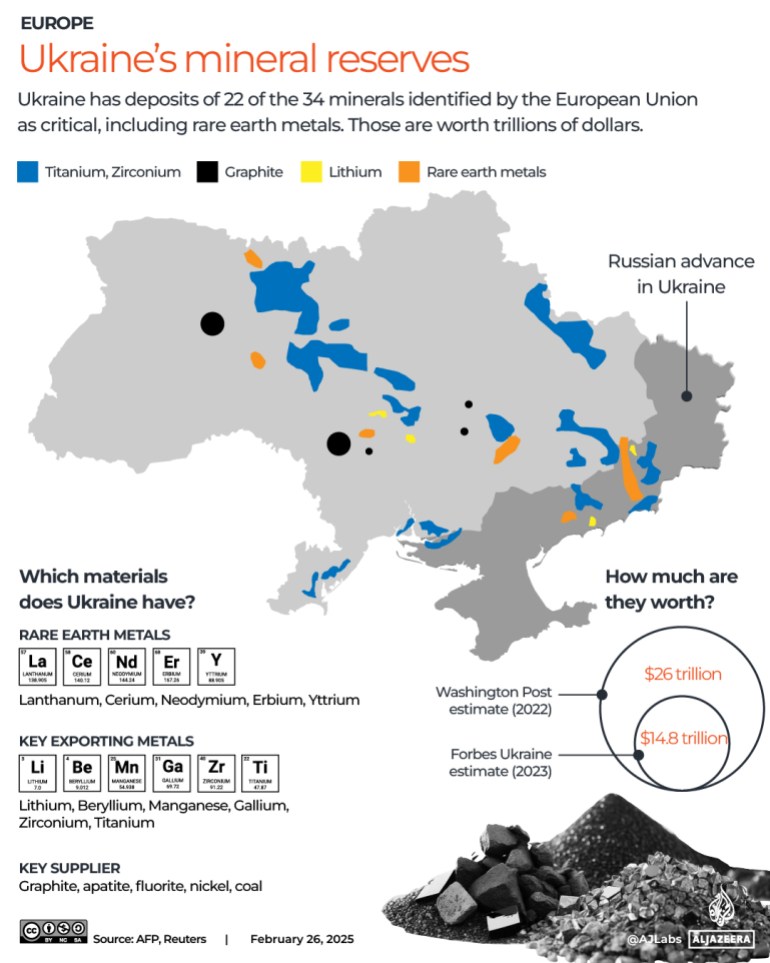
Table of Contents
The Strategic Importance of Rare Earth Minerals
Rare earth elements (REEs) are a group of 17 chemically similar elements crucial for a wide range of high-tech applications. Their unique magnetic, luminescent, and catalytic properties make them indispensable components in modern technology, creating a landscape of intense competition for their control.
Critical Applications in Modern Technology
REEs are fundamental to countless technologies shaping our daily lives and national security. Their applications span across multiple sectors:
- Consumer Electronics: Smartphones, laptops, and tablets rely heavily on REEs for their screens, magnets, and other components.
- Renewable Energy: Wind turbines, electric vehicles, and energy-efficient lighting systems all incorporate REEs in significant quantities. This makes them key to the global transition to renewable energy.
- Military Technology: REEs are essential for advanced military hardware, including guided missiles, radar systems, and night-vision equipment. Their use in military technology significantly elevates national defense capabilities.
- High-tech Manufacturing: From medical imaging equipment to advanced manufacturing processes, REEs play a critical role across numerous high-tech industries.
The dependence of developed nations on these minerals is substantial, making supply chain disruptions a significant threat to economic stability and technological advancement. Securing a reliable supply of REEs is, therefore, paramount for global power.
Geopolitical Concentration of REE Production
The global distribution of REEs is highly uneven, with China holding a dominant position in mining and processing. China's market share in REE production is overwhelmingly significant, giving it considerable leverage in the global market. This dominance is a major factor in the current geopolitical tensions. While other countries like Australia, the USA, and several nations in Africa also produce REEs, their capacity significantly lags behind China's, leading to concerns about resource security and potential supply chain vulnerabilities. This uneven distribution fuels "resource nationalism," with countries prioritizing domestic REE resources over global cooperation. The implications for global trade and technological development are profound, raising concerns about potential monopolies and price manipulation.
The Emerging Cold War and Competition for Rare Earths
The competition for rare earth minerals is a defining feature of the emerging Cold War, particularly between the US and China.
US-China Rivalry and the Race for REE Dominance
The strategic competition between the US and China over REEs is intense. China's dominance presents a significant challenge to the US and its allies, leading to initiatives aimed at diversifying REE supply chains and reducing dependence on China. This involves various strategies, including:
- Technological Decoupling: Efforts to reduce reliance on Chinese technology and expertise in REE processing and manufacturing.
- Supply Chain Diversification: Investing in and fostering the development of REE production and processing capabilities in other countries, building alliances with partners like Australia and Canada.
- Geopolitical Rivalry: The competition extends beyond economic strategies, encompassing political and diplomatic pressure aimed at shifting the global REE landscape.
These efforts are coupled with significant government policies and investments aimed at boosting domestic REE production within the US and its allies.
The Role of Other Global Actors
Beyond the US and China, other global actors are actively engaged in the REE market. Australia, Canada, and the EU, for example, are developing their own strategies to secure REE supplies and participate more meaningfully in the global REE market. This includes exploring new mining opportunities, investing in advanced processing technologies, and forming strategic partnerships to enhance resource security and reduce reliance on single sources. Potential alliances and collaborations among these nations could emerge as a counterbalance to China’s dominance, shaping the future of the global REE landscape through international cooperation.
The Environmental and Ethical Considerations
The pursuit of REEs carries significant environmental and ethical implications.
Environmental Impact of REE Mining
The extraction and processing of REEs have substantial environmental consequences. Mining operations often lead to water pollution, land degradation, and habitat destruction. The environmental impact of REE mining necessitates a focus on:
- Sustainable Mining Practices: Implementing environmentally friendly extraction methods to minimize pollution and habitat disruption.
- Environmental Regulations: Strengthening environmental regulations to ensure responsible mining operations and mitigation of negative environmental impacts.
- Responsible Sourcing: Prioritizing REEs sourced from operations adhering to stringent environmental standards.
Addressing these environmental challenges is vital for sustainable development and minimizing the ecological footprint of REE production.
Ethical Concerns in the REE Supply Chain
Ethical concerns in the REE supply chain are significant, particularly regarding labor practices and human rights in some mining operations. Issues include:
- Ethical Sourcing: Ensuring that REEs are sourced from operations that respect human rights, provide safe working conditions, and pay fair wages.
- Human Rights: Addressing human rights violations in REE mining, including child labor and exploitative working conditions.
- Corporate Social Responsibility: Promoting corporate social responsibility throughout the REE supply chain to improve working conditions and human rights standards.
Addressing these ethical challenges is essential for creating a just and equitable REE industry.
Rare Earth Minerals and the Future of Geopolitical Stability
In conclusion, the strategic importance of rare earth minerals, the intensifying geopolitical competition, and the significant environmental and ethical challenges associated with their extraction and processing are inextricably linked. Access to rare earth minerals is becoming increasingly intertwined with national security, technological advancement, and economic growth. The future of geopolitical stability depends in part on the ability of nations to collaborate and implement responsible sourcing, sustainable practices, and international cooperation to mitigate the risks and ensure a secure and equitable future.
To learn more about the complex issues surrounding Rare Earth Minerals and the Emerging Cold War Conflict, explore resources from reputable organizations focusing on mineral resource management, geopolitical analysis, and sustainable development. Understanding this critical issue is vital for informed engagement with the future of global technology and security.

Featured Posts
-
 Reese Cuts Short Question About Clark What Happened
May 17, 2025
Reese Cuts Short Question About Clark What Happened
May 17, 2025 -
 Wnba Lockout Angel Reeses Stance On Player Demands
May 17, 2025
Wnba Lockout Angel Reeses Stance On Player Demands
May 17, 2025 -
 The Jim Morrison Maintenance Man Theory Fact Or Fiction
May 17, 2025
The Jim Morrison Maintenance Man Theory Fact Or Fiction
May 17, 2025 -
 Is Reddit Down Thousands Report Issues Globally
May 17, 2025
Is Reddit Down Thousands Report Issues Globally
May 17, 2025 -
 Analyzing Ralph Laurens Fall 2025 Riser Collection
May 17, 2025
Analyzing Ralph Laurens Fall 2025 Riser Collection
May 17, 2025
