Record-Breaking Global Forest Loss: Wildfires And Deforestation
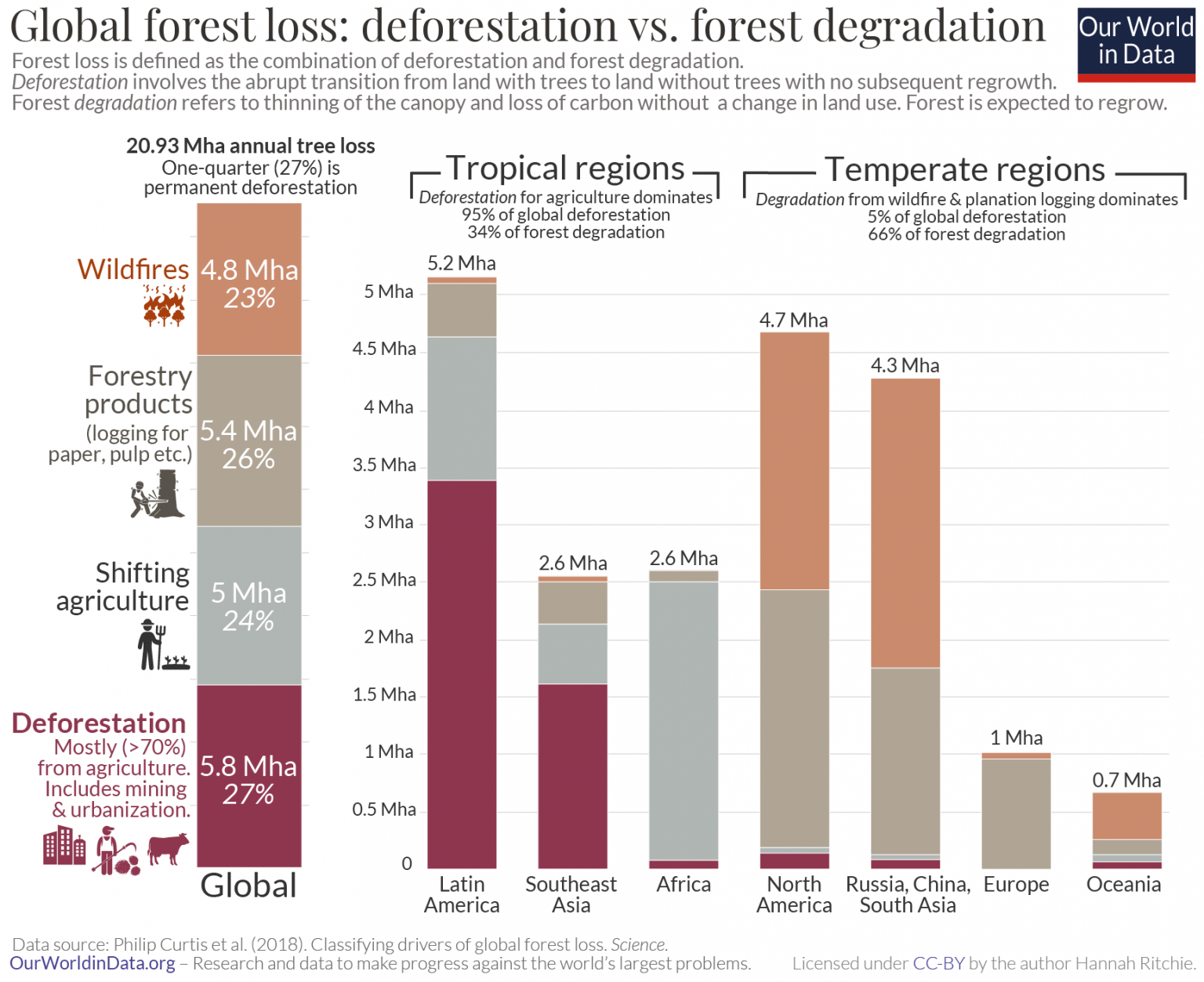
Table of Contents
The Dire Statistics of Global Forest Loss
The extent of global forest loss is staggering. Tracking this destruction requires sophisticated methods, primarily relying on satellite imagery and ground-based surveys that provide crucial data on deforestation rates and wildfire impacts. These tools allow scientists and environmental organizations to monitor changes in forest cover over time, revealing a grim picture.
Measuring the Extent of Deforestation
Global deforestation monitoring utilizes advanced technologies like Landsat and Sentinel satellites, providing high-resolution images that capture changes in forest cover. Ground surveys, often conducted in conjunction with satellite analysis, provide crucial ground-truthing data, confirming and refining satellite observations. These combined efforts provide a more accurate picture of the extent of deforestation.
- The Amazon Rainforest: Recent years have witnessed record levels of deforestation in the Amazon, with millions of hectares lost annually. This loss represents a significant blow to global biodiversity and carbon sequestration.
- The Congo Basin: Deforestation in the Congo Basin, the second-largest rainforest in the world, is also escalating rapidly, driven by logging, agricultural expansion, and mining activities.
- Southeast Asia: Vast areas of rainforest in Southeast Asia, particularly in Indonesia and Malaysia, have been cleared for palm oil plantations, leading to significant biodiversity loss and greenhouse gas emissions.
Wildfires as a Major Contributor
Wildfires are increasingly contributing to global forest loss, with their frequency and intensity amplified by climate change and human activities. These catastrophic events often consume vast areas of forest in a short period, releasing massive amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
- Australia 2019-2020: The devastating bushfires in Australia highlighted the catastrophic impact of extreme weather conditions exacerbated by climate change.
- Siberia, Russia: Increasingly frequent and severe wildfires in Siberia are causing significant damage to boreal forests, releasing huge quantities of carbon into the atmosphere.
- California Wildfires: Recurring and intense wildfires in California demonstrate the escalating impact of climate change and drought on forest ecosystems. Human negligence and arson also contribute significantly to the frequency of these devastating events.
Underlying Causes of Deforestation and Wildfires
The root causes of deforestation and wildfires are complex and interconnected, involving a multitude of factors related to unsustainable practices, economic pressures, and climate change.
Agricultural Expansion and Logging
Agricultural expansion, particularly cattle ranching and palm oil plantations, is a primary driver of deforestation. The insatiable global demand for these products fuels the conversion of vast tracts of forest into agricultural land. Unsustainable logging practices, often illegal, further contribute to forest loss, depleting timber resources and harming biodiversity.
- Cattle Ranching in the Amazon: Much of the deforestation in the Amazon is driven by the expansion of cattle ranches to meet the growing global demand for beef.
- Palm Oil Plantations in Southeast Asia: The production of palm oil, used in a wide range of products, has led to the destruction of vast areas of rainforest in Southeast Asia.
- Illegal Logging: Illegal logging operations often operate with impunity, exploiting valuable timber resources without regard for environmental sustainability.
Mining and Infrastructure Development
Mining operations and the development of infrastructure projects, such as roads and dams, contribute significantly to deforestation and habitat fragmentation. These activities often involve clearing large areas of forest, disrupting ecosystems, and increasing the risk of wildfires.
- Mining in the Congo Basin: Mining activities in the Congo Basin are contributing to deforestation and habitat loss, threatening biodiversity and impacting local communities.
- Road Construction in Amazonia: New roads built into the Amazon provide access for logging, agriculture, and settlement, leading to further deforestation.
Climate Change's Amplifying Effect
Climate change significantly exacerbates both deforestation and wildfires. Rising temperatures, prolonged droughts, and increased frequency of extreme weather events create ideal conditions for wildfires to spread rapidly and intensely. Deforestation, in turn, contributes to climate change by releasing vast amounts of stored carbon into the atmosphere. This creates a dangerous feedback loop.
- Increased temperatures and drought: Higher temperatures and prolonged droughts desiccate forests, increasing their vulnerability to wildfires.
- Extreme weather events: More frequent and intense heatwaves, storms, and lightning strikes increase the risk of wildfires.
The Devastating Consequences of Global Forest Loss
The consequences of global forest loss are far-reaching and devastating, impacting biodiversity, climate change, and human societies.
Biodiversity Loss and Extinction
Deforestation leads to massive biodiversity loss, as habitats are destroyed and species are forced to adapt or face extinction. Forests are critical for maintaining the intricate web of life, and their loss disrupts entire ecosystems.
- Endangered species: Many endangered species, including orangutans, tigers, and various bird species, are severely threatened by deforestation and habitat loss.
- Loss of ecosystem services: Forests provide essential ecosystem services, such as clean water, pollination, and climate regulation. Their loss diminishes these crucial services.
Climate Change Acceleration
Forests act as vital carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Deforestation releases this stored carbon, contributing significantly to greenhouse gas emissions and accelerating climate change.
- Carbon emissions: Deforestation is a major source of greenhouse gas emissions, accounting for a significant percentage of global CO2 emissions.
- Reduced carbon sequestration: The loss of forests reduces the planet's capacity to absorb CO2 from the atmosphere, exacerbating climate change.
Impacts on Human Communities
Deforestation has severe socioeconomic consequences for human communities, impacting livelihoods, water resources, and leading to displacement of indigenous populations who depend on forests for their survival.
- Loss of income: Many communities depend on forests for their livelihoods, through activities such as logging, farming, and gathering forest products. Deforestation threatens these livelihoods.
- Water security: Forests play a vital role in regulating water cycles. Deforestation can lead to reduced water availability and increased soil erosion.
Conclusion
Record-breaking global forest loss, driven by a combination of deforestation and wildfires, poses a grave threat to our planet. The underlying causes are complex, involving unsustainable practices, economic pressures, and the amplifying effect of climate change. The consequences are devastating, leading to biodiversity loss, climate change acceleration, and severe impacts on human communities. Urgent and concerted action is needed to address this crisis. We must support sustainable forestry practices, combat illegal logging, protect existing forests, and invest in reforestation efforts. Learn more about global forest loss and take action today. Support organizations like the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) and Greenpeace, who are working tirelessly to protect our planet's forests. The future of our planet depends on our collective action to combat global forest loss and secure a sustainable future.

Featured Posts
-
 Peter Laviolette Fired Impact On The New York Rangers
May 26, 2025
Peter Laviolette Fired Impact On The New York Rangers
May 26, 2025 -
 Klasemen Moto Gp Terbaru Marc Marquez Menang Sprint Race Argentina 2025
May 26, 2025
Klasemen Moto Gp Terbaru Marc Marquez Menang Sprint Race Argentina 2025
May 26, 2025 -
 Le Jeu De La Rtbf Gerez Votre Equipe Cycliste Au Tour De France
May 26, 2025
Le Jeu De La Rtbf Gerez Votre Equipe Cycliste Au Tour De France
May 26, 2025 -
 What Is A Flash Flood Emergency Preparedness And Response Strategies
May 26, 2025
What Is A Flash Flood Emergency Preparedness And Response Strategies
May 26, 2025 -
 Canada And Mexico Diversifying Trade To Counter Us Tariff Effects
May 26, 2025
Canada And Mexico Diversifying Trade To Counter Us Tariff Effects
May 26, 2025
