Shared Nuclear Power: France's European Initiative
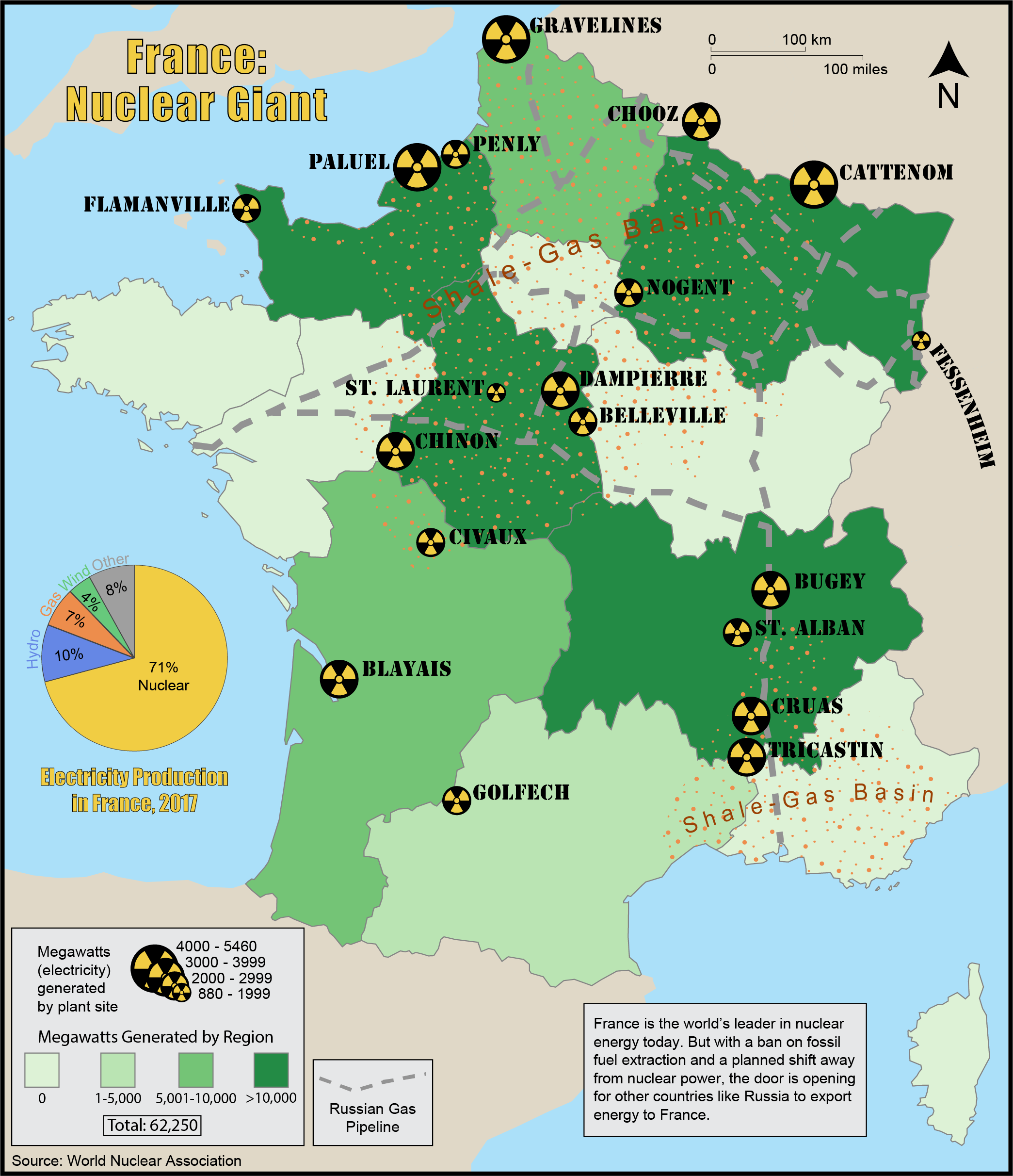
Table of Contents
France's Nuclear Expertise and Capacity
France boasts unparalleled experience in nuclear power generation, possessing a robust and sophisticated infrastructure built over decades. With over 50 operational reactors, France generates a significant portion of its electricity from nuclear energy, demonstrating its commitment to and mastery of this technology. This expertise extends to reactor design, construction, operation, and waste management, making it a prime candidate to lead a shared European nuclear power initiative. Key aspects of French nuclear prowess include:
- Advanced reactor designs: France has pioneered advanced reactor designs, such as the European Pressurized Reactor (EPR), which offer improved safety features, efficiency, and potentially lower costs compared to older generation reactors. These designs are attractive prospects for export and collaboration within a shared nuclear energy framework.
- Stringent safety regulations and oversight: France has a long-standing and rigorous regulatory framework for nuclear safety, ensuring the highest standards are maintained throughout the nuclear fuel cycle. This experience can be instrumental in developing shared safety protocols for a European initiative.
- Established nuclear fuel cycle capabilities: France possesses a complete nuclear fuel cycle, including uranium enrichment and spent fuel reprocessing capabilities. This self-sufficiency significantly enhances its energy independence and provides a foundation for supporting other European partners in a shared nuclear power program.
The Rationale Behind a Shared European Nuclear Power Initiative
A shared European nuclear power initiative offers compelling advantages across energy security, environmental sustainability, and economic growth. The benefits of shared nuclear energy extend beyond individual nations, creating a stronger, more resilient energy ecosystem for the entire continent.
-
Enhanced Energy Security: Reducing reliance on volatile fossil fuel markets and potentially unstable geopolitical regions is paramount for Europe's energy security. Shared nuclear power offers a pathway to diversification, bolstering energy independence and resilience.
-
Environmental Benefits: Nuclear power plants generate significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuel-based power plants, directly addressing climate change concerns and helping Europe meet its emission reduction targets. This is crucial for shared nuclear energy's long-term viability.
-
Economic Advantages: Sharing infrastructure costs, research and development efforts, and expertise can lead to significant economic benefits. Joint ventures and collaborative projects can unlock economies of scale, reducing the overall financial burden and promoting cost-effectiveness in shared nuclear energy projects.
-
Specific Advantages:
- Diversification of energy sources: Reducing dependence on a single energy source makes the entire European energy system more resistant to shocks.
- Geopolitical stability: Reduced dependence on volatile global energy markets strengthens Europe's geopolitical position.
- Job creation: The nuclear sector offers highly skilled jobs, boosting economic growth across participating countries.
Addressing Concerns and Challenges
While the potential benefits are substantial, a shared nuclear power initiative must also address public concerns and potential challenges:
-
Public perception of nuclear safety and waste disposal: Addressing public anxieties about nuclear safety and the long-term management of nuclear waste is crucial. Open communication, transparent procedures, and robust safety measures are essential to building public trust and support.
-
Regulatory hurdles and standardization: Harmonizing nuclear safety regulations and standards across different European countries will require significant diplomatic effort and collaborative regulatory frameworks.
-
Political and diplomatic challenges: Successfully navigating the complexities of cross-border collaborations, aligning national interests, and ensuring fair distribution of benefits require careful diplomatic management.
-
Solutions:
- Enhanced public engagement: Invest in transparent communication, emphasizing safety records and waste management solutions.
- International regulatory harmonization: Establish common standards and procedures for safety, licensing, and waste management.
- Collaborative waste management solutions: Develop joint strategies for long-term storage and disposal of nuclear waste.
Potential Participating Countries and Collaboration Models
Several European countries could benefit from participating in a shared nuclear power initiative. Those with existing nuclear programs or those considering developing them could find advantages in sharing resources and expertise. Collaboration models could include:
-
Joint ventures: Partnerships between countries to build and operate new nuclear power plants.
-
Technology transfer: France sharing its expertise and technology with partner nations.
-
Research partnerships: Joint research initiatives to advance nuclear technology and safety.
-
Potential Partners: Countries with existing nuclear programs or those planning to develop nuclear energy could be potential partners.
-
EU Facilitation: The European Union could play a vital role in coordinating and facilitating this initiative.
-
Risk and Profit Sharing: Clear mechanisms for sharing risks and distributing profits are crucial to ensuring equitable participation.
Conclusion
Shared nuclear power presents a compelling solution to Europe's energy challenges. Leveraging France's extensive experience and capacity in nuclear energy, a collaborative initiative can enhance energy security, reduce carbon emissions, and stimulate economic growth across the continent. While challenges remain, the potential benefits of shared nuclear energy far outweigh the risks, making it a critical area for further research, discussion, and ultimately, implementation. Let us actively pursue the exploration of shared nuclear power initiatives as a crucial step towards a more sustainable and secure energy future for Europe.

Featured Posts
-
 Mestarien Liiga Bayern Inter Ja Psg Seuraavalle Kierrokselle
May 09, 2025
Mestarien Liiga Bayern Inter Ja Psg Seuraavalle Kierrokselle
May 09, 2025 -
 Sensex Nifty
May 09, 2025
Sensex Nifty
May 09, 2025 -
 The Closure Of Anchor Brewing Company Reflecting On 127 Years
May 09, 2025
The Closure Of Anchor Brewing Company Reflecting On 127 Years
May 09, 2025 -
 Elizabeth Hurleys Maldives Bikini Vacation Photos And Details
May 09, 2025
Elizabeth Hurleys Maldives Bikini Vacation Photos And Details
May 09, 2025 -
 R5 2025
May 09, 2025
R5 2025
May 09, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 The Experiences Of Transgender People Under Trumps Executive Orders
May 10, 2025
The Experiences Of Transgender People Under Trumps Executive Orders
May 10, 2025 -
 Trumps Legacy The Transgender Communitys Perspective
May 10, 2025
Trumps Legacy The Transgender Communitys Perspective
May 10, 2025 -
 Bangkok Post Highlights Growing Movement For Transgender Equality
May 10, 2025
Bangkok Post Highlights Growing Movement For Transgender Equality
May 10, 2025 -
 The Impact Of Trumps Transgender Military Ban A Critical Analysis
May 10, 2025
The Impact Of Trumps Transgender Military Ban A Critical Analysis
May 10, 2025 -
 The Trump Presidency And Its Impact On The Transgender Community
May 10, 2025
The Trump Presidency And Its Impact On The Transgender Community
May 10, 2025
