Southeast Asian Solar Imports Face Massive US Tariffs: A 3,521% Duty Increase

Table of Contents
The 3,521% Tariff: A Deep Dive into the Investigation and its Rationale
The astronomical tariff increase stems from a US Department of Commerce investigation into allegations of circumvention of existing anti-dumping and countervailing duties on solar cells and modules from China. Companies based in Cambodia, Malaysia, Thailand, and Vietnam – major exporters of solar panels to the US – were implicated. The investigation alleged that these Southeast Asian manufacturers were circumventing existing tariffs by importing components from China, assembling them, and then exporting the finished products to the US.
- Companies Involved: While the investigation named several companies, the impact extends across the entire Southeast Asian solar manufacturing landscape. Specific company details can be found in the official Department of Commerce documents [link to relevant document].
- Alleged Violations: The core allegation is that these companies are engaging in "circumvention" by utilizing Chinese components, thus undermining previous anti-dumping measures aimed at Chinese manufacturers.
- Legal Basis: The investigation was conducted under Section 731 of the Tariff Act of 1930, which empowers the government to impose anti-dumping and countervailing duties on imports deemed to be unfairly traded. The justification hinges on the determination that the circumventing practices cause material injury to the US domestic industry.
Impact on Southeast Asian Solar Manufacturers
The 3,521% tariff has dealt a devastating blow to Southeast Asian solar manufacturers. The immediate consequences are severe:
- Job Losses: Thousands of jobs are at risk across the affected factories and supply chains.
- Factory Closures: Some manufacturers are already facing financial distress and potential factory closures.
- Financial Distress: The sharply reduced demand from the US market is causing significant financial strain, hindering investment and expansion plans.
The long-term implications are equally worrying:
- Decreased Investment: The substantial increase in US solar tariffs discourages future investment in solar manufacturing capabilities within Southeast Asia.
- Hindered Renewable Energy Goals: The region’s ambitious renewable energy targets may be jeopardized by this setback.
- Relocation of Manufacturing: Many manufacturers might seek alternative locations outside of Southeast Asia to access the US market, potentially shifting production to other regions with more favorable trade policies.
Implications for the US Solar Industry and Consumers
The tariffs are not only affecting Southeast Asian manufacturers but also having a profound impact on the US solar industry and consumers:
- Higher Prices: The cost of solar panels in the US is expected to rise dramatically, making solar energy less accessible and affordable.
- Project Delays: Solar projects across the country may face delays or cancellations due to increased costs and supply chain disruptions.
- Reduced Consumer Adoption: Higher prices could significantly hinder consumer adoption of solar energy, slowing the growth of the US renewable energy sector.
The implications for the US's transition to cleaner energy are significant:
- Hindered Renewable Energy Transition: The tariffs risk undermining the US's climate change goals and efforts to transition to a cleaner energy future.
- Political Fallout: The decision is likely to trigger political backlash, with opposition from environmental groups and consumer advocates.
Potential Responses and Mitigation Strategies
Several potential responses and mitigation strategies are emerging:
- Southeast Asian Government Responses: Southeast Asian governments may engage in trade negotiations, diplomatic pressure, and even retaliatory tariffs to protect their solar industries.
- US Solar Company Strategies: US solar companies might diversify their supply chains, invest in domestic manufacturing, lobby for tariff reductions, and potentially engage in legal challenges.
- Role of International Organizations: The World Trade Organization (WTO) could potentially play a role in mediating the dispute, although the process is often lengthy and complex.
Conclusion: Navigating the Challenges of Southeast Asian Solar Imports and US Tariffs
The 3,521% tariff increase on Southeast Asian solar imports represents a significant challenge for the global solar industry and the transition to renewable energy. The impacts on Southeast Asian manufacturers, the US solar market, and consumers are substantial and far-reaching. The long-term consequences could include decreased investment in solar energy, slower adoption rates, and heightened geopolitical tensions. To alleviate this situation, a multi-faceted approach is needed, involving diplomatic efforts, trade negotiations, and a reevaluation of the current trade policies regarding Southeast Asian solar imports. We urge you to learn more about this critical issue by visiting the websites of relevant organizations [insert links] and contacting your representatives to advocate for sustainable energy policies and fair trade practices. The future of clean energy depends on finding a solution to this conflict surrounding Southeast Asia solar tariffs and US trade policies.

Featured Posts
-
 Guillermo Del Toro Documentary Sangre Del Toro Premieres At Cannes
May 30, 2025
Guillermo Del Toro Documentary Sangre Del Toro Premieres At Cannes
May 30, 2025 -
 Elon Musk Fathered Amber Heards Twins Examining The Evidence
May 30, 2025
Elon Musk Fathered Amber Heards Twins Examining The Evidence
May 30, 2025 -
 Alcaraz Vs Musetti Rolex Monte Carlo Masters 2025 Final Preview
May 30, 2025
Alcaraz Vs Musetti Rolex Monte Carlo Masters 2025 Final Preview
May 30, 2025 -
 Des Moines Police Respond To Single Vehicle Rollover Crash
May 30, 2025
Des Moines Police Respond To Single Vehicle Rollover Crash
May 30, 2025 -
 Mqawmt Aljdar Walastytan Altwse Alastytany Fy 13 Hya Flstynya
May 30, 2025
Mqawmt Aljdar Walastytan Altwse Alastytany Fy 13 Hya Flstynya
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Padel Court Development Update Bannatyne Health Club Ingleby Barwick
May 31, 2025
Padel Court Development Update Bannatyne Health Club Ingleby Barwick
May 31, 2025 -
 Post Dragons Den Entrepreneurs 40 Profit Growth
May 31, 2025
Post Dragons Den Entrepreneurs 40 Profit Growth
May 31, 2025 -
 Chafford Hundred Health Club Secures Investment For Padel Courts
May 31, 2025
Chafford Hundred Health Club Secures Investment For Padel Courts
May 31, 2025 -
 40 Profit Jump For Dragons Den Business Owner
May 31, 2025
40 Profit Jump For Dragons Den Business Owner
May 31, 2025 -
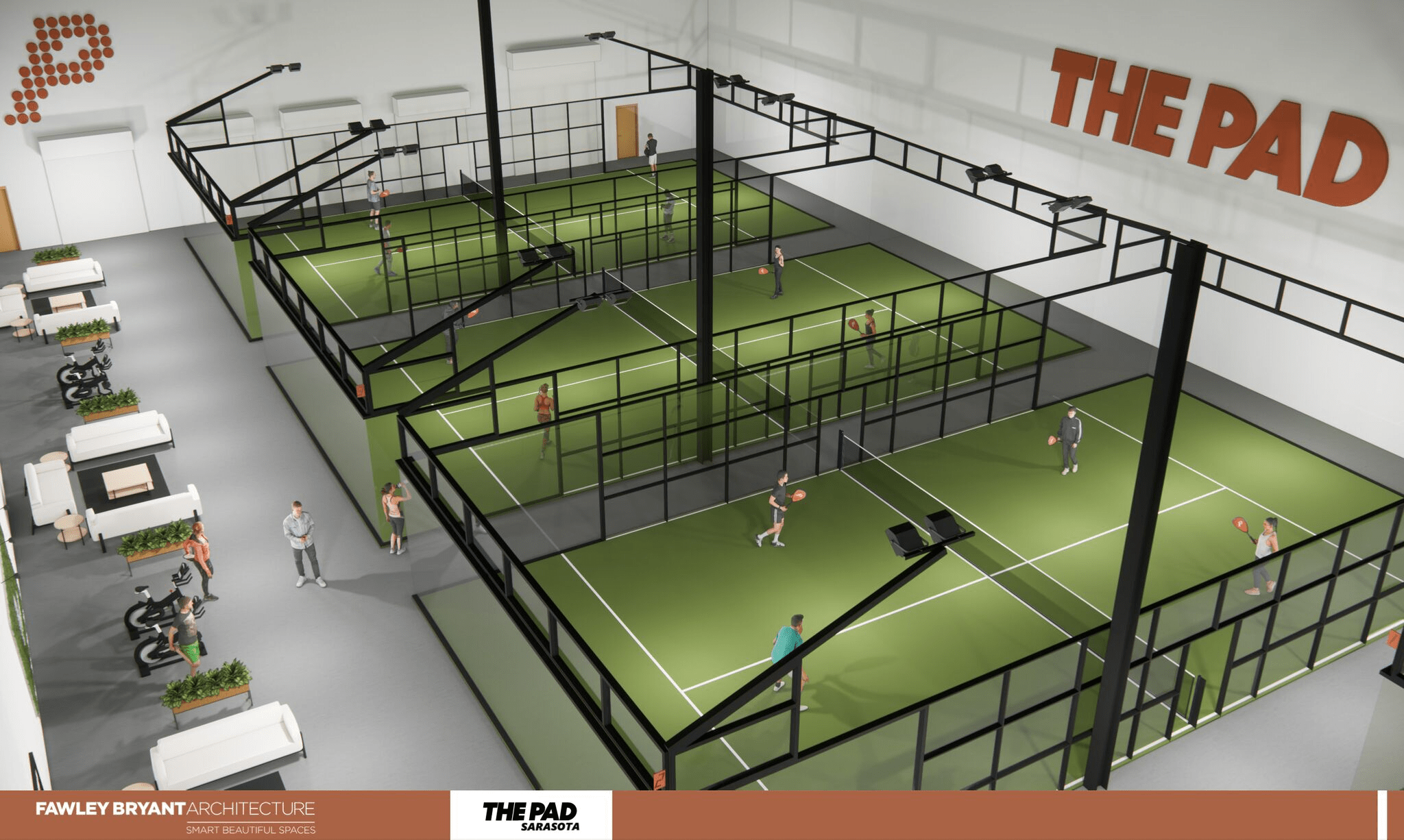 Dragon Dens Interest In New Chafford Hundred Padel Facility
May 31, 2025
Dragon Dens Interest In New Chafford Hundred Padel Facility
May 31, 2025
