The Connection Between National Debt And Your Mortgage Payment
Table of Contents
How Government Borrowing Impacts Interest Rates
Government borrowing to finance the national debt significantly influences interest rates across the board, including mortgage rates. When the government needs to borrow more money, it increases the demand for loanable funds. This increased demand, in a system of finite resources, drives up interest rates. Think of it like supply and demand for any other commodity: higher demand equals higher prices.
- Increased demand for loanable funds drives up interest rates: The government competes with businesses and individuals for available capital, pushing interest rates higher.
- The Federal Reserve's response to national debt can influence interest rate policies: To manage inflation potentially fueled by high national debt, the Federal Reserve may raise interest rates, further increasing mortgage rates.
- Inflation, often linked to high national debt, also impacts interest rates: High national debt can lead to inflation, forcing lenders to increase interest rates to compensate for the decreased value of money.
This means a higher national debt could directly translate to higher mortgage rates, increasing your monthly payments and potentially impacting your ability to afford a home.
Inflation's Role in Mortgage Affordability
Inflation, frequently a consequence of high national debt, erodes purchasing power, impacting your ability to afford a mortgage. As prices for goods and services rise, your budget is stretched thinner, leaving less room for a substantial mortgage payment.
- Rising prices of goods and services directly impact the cost of living: From groceries to gasoline, inflation increases the cost of everything, reducing your disposable income.
- Increased inflation makes it harder to afford a mortgage: Even if your income increases, it may not keep pace with inflation, making your mortgage payments feel increasingly burdensome.
- Higher inflation can lead to increased mortgage rates as lenders adjust for inflation risk: Lenders factor inflation into their calculations, passing the increased risk onto borrowers through higher interest rates.
Inflation affects not just your initial mortgage payment but also the overall affordability of homeownership. It can make saving for a down payment more difficult and potentially limit your ability to buy a home altogether.
The Impact of Government Policies on the Housing Market
Government policies implemented to address the national debt can indirectly, but significantly, impact the housing market and your mortgage. Austerity measures, tax increases, and other economic policy shifts all have ripple effects.
- Reduced government spending can impact construction and housing supply: Cuts in government funding for infrastructure projects can slow down housing construction, reducing the supply of homes and potentially driving up prices.
- Changes in tax policies can influence homebuyer demand and affordability: Tax increases or changes to mortgage interest deductions can influence the demand for homes and make homeownership less accessible.
- Government initiatives aimed at stimulating the economy could have indirect effects on housing: Conversely, government programs designed to boost economic activity can sometimes indirectly increase demand and prices in the housing market.
These indirect effects can influence mortgage rates and the overall accessibility of homeownership, making it crucial to understand the interplay between national debt management and housing policy.
Long-Term Economic Uncertainty and Its Effect on Mortgages
High national debt contributes to long-term economic uncertainty, making lenders more risk-averse. This increased risk translates into changes in mortgage lending practices.
- Economic instability can lead to tighter lending standards: Lenders become more cautious, requiring higher credit scores, larger down payments, and more stringent financial documentation.
- Increased risk can result in higher mortgage rates: To compensate for the perceived increased risk, lenders charge higher interest rates on mortgages.
- Uncertainty can affect job security, reducing people's ability to afford a mortgage: Economic uncertainty often leads to job losses or reduced income, making it harder for individuals to qualify for or afford a mortgage.
This uncertainty can translate into higher mortgage payments, more stringent lending requirements, or difficulty securing a mortgage altogether.
Conclusion: Understanding the National Debt's Influence on Your Mortgage
In summary, high national debt influences interest rates, fuels inflation, impacts government policies affecting the housing market, and creates economic uncertainty – all factors that ultimately influence your mortgage payment. Understanding the connection between national debt and individual financial decisions, like securing a mortgage, is paramount. Staying informed about national debt levels and their potential impact on personal finance allows you to make more informed financial decisions. Further research into interest rate forecasts and economic policies will help you navigate this complex relationship and make the best choices for your future. Understanding "The Connection Between National Debt and Your Mortgage Payment" is key to securing your financial well-being.

Featured Posts
-
 Tampoy Kai Apokalypseis Mia Analysi Ton Akraion Synthikon
May 19, 2025
Tampoy Kai Apokalypseis Mia Analysi Ton Akraion Synthikon
May 19, 2025 -
 Michael Morales Winning Streak Continues Another Bonus At Ufc Vegas 106
May 19, 2025
Michael Morales Winning Streak Continues Another Bonus At Ufc Vegas 106
May 19, 2025 -
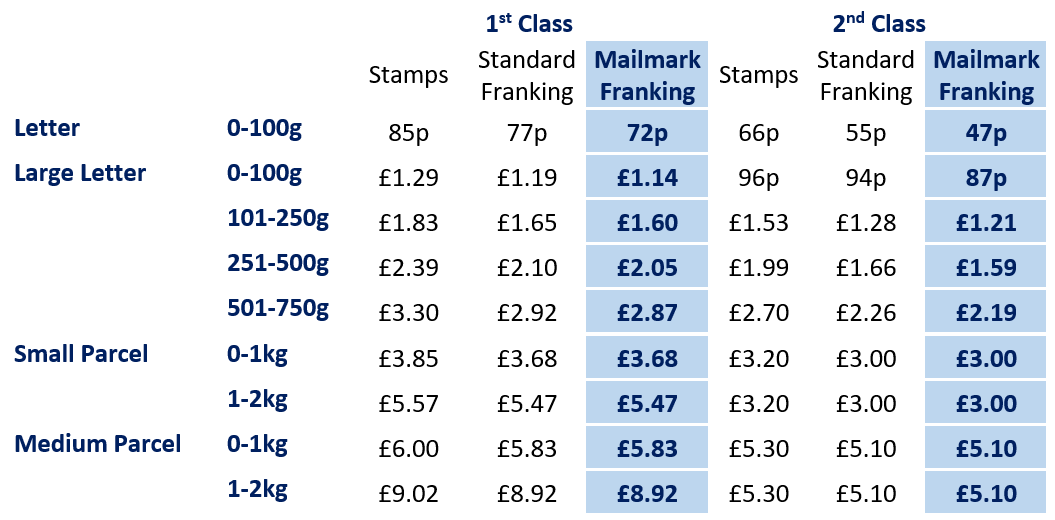 Royal Mail Stamp Price Hikes A 76p Increase In Five Years Sparks Outrage
May 19, 2025
Royal Mail Stamp Price Hikes A 76p Increase In Five Years Sparks Outrage
May 19, 2025 -
 Dimereis Sxeseis Kyproy Oyggarias Sigiarto Kompos Syzitoyn Kypriako And Proedria Ee
May 19, 2025
Dimereis Sxeseis Kyproy Oyggarias Sigiarto Kompos Syzitoyn Kypriako And Proedria Ee
May 19, 2025 -
 Cne Seis Pruebas Que Demuestran El Apagon De Su Sitio Web
May 19, 2025
Cne Seis Pruebas Que Demuestran El Apagon De Su Sitio Web
May 19, 2025
