The Drop In US Measles Cases: Factors And Analysis
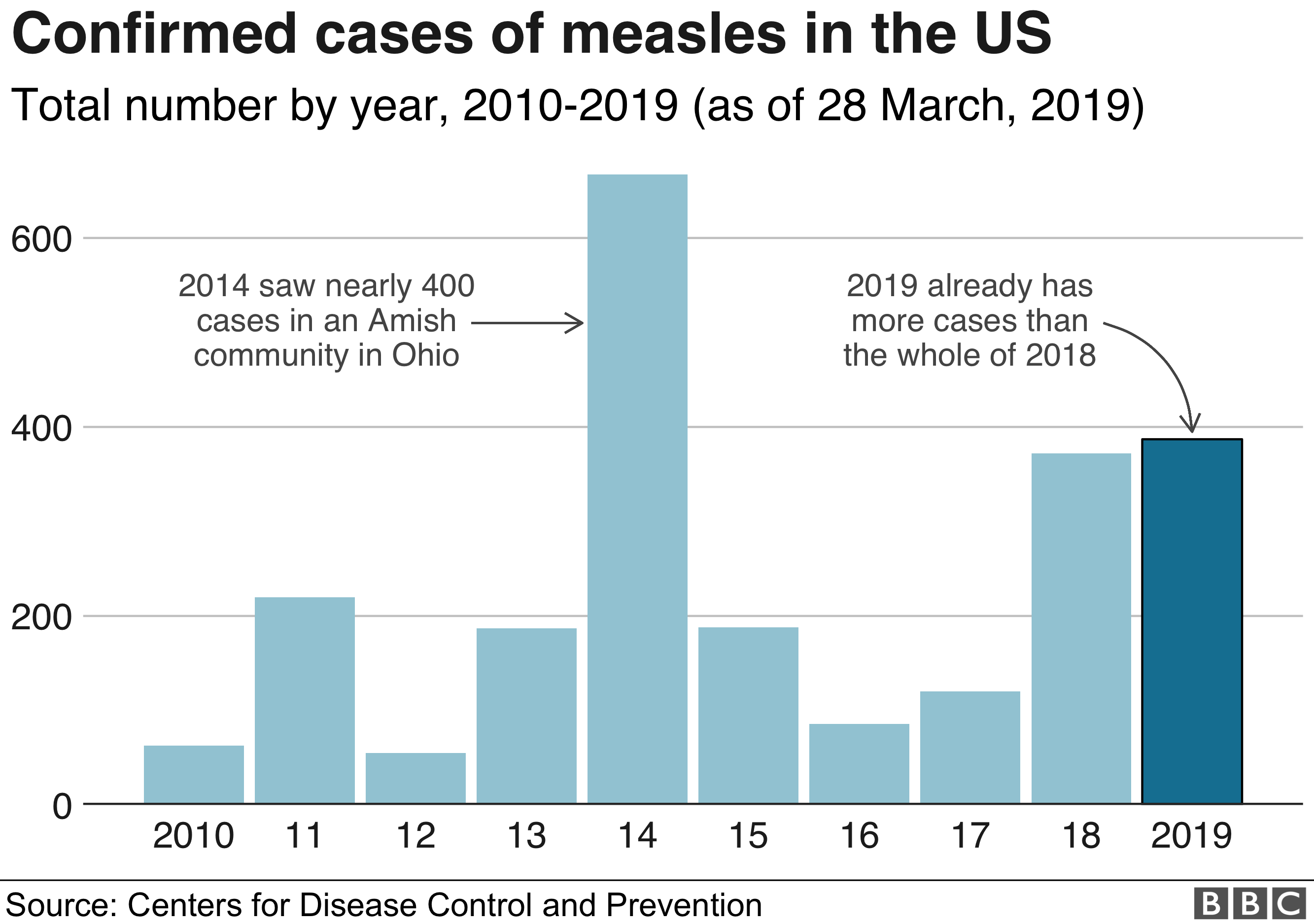
Table of Contents
The Effectiveness of the Measles, Mumps, and Rubella (MMR) Vaccine
The MMR vaccine stands as the cornerstone of measles prevention. Its high efficacy, typically exceeding 97%, makes it a powerful tool in combating the disease. Widespread vaccination campaigns, initiated decades ago, have dramatically altered the landscape of measles in the US. The success isn't solely about the vaccine's effectiveness; it's also about accessibility and uptake.
- Increased vaccination rates among children: Consistent, high vaccination rates amongst children, achieved through mandatory vaccination policies in most states and widespread public health education, have significantly reduced susceptibility to measles within the population. This "herd immunity" protects even those who cannot be vaccinated.
- Improved access to vaccination programs: Initiatives to increase vaccine access for underserved communities have played a crucial role. Programs offering free or low-cost vaccines have ensured that socioeconomic barriers don't hinder vaccination efforts.
- Government initiatives promoting MMR vaccination: Continued government support, including funding for vaccination programs and public awareness campaigns, has been essential in maintaining high vaccination rates.
- Educational campaigns raising awareness about vaccine safety and efficacy: Addressing vaccine hesitancy through robust educational programs and dispelling misinformation has been vital in ensuring widespread acceptance of the MMR vaccine. These campaigns have successfully countered false narratives linking vaccines to autism and other health problems.
Improved Public Health Surveillance and Response
Enhanced disease surveillance and rapid response mechanisms are crucial in preventing measles outbreaks. Early detection and swift action are paramount to limiting the spread of infection.
- Improved case reporting and tracking systems: Modern, sophisticated systems allow for the prompt identification and reporting of suspected measles cases, enabling a quicker response.
- Faster identification of outbreaks: Advanced data analysis tools help public health officials quickly identify clusters of cases and pinpoint the source of outbreaks, allowing for targeted interventions.
- Efficient contact tracing and quarantine measures: Contact tracing enables the identification and isolation of individuals who may have been exposed, effectively preventing further spread. Quarantine measures, when necessary, limit community transmission.
- Public health interventions targeted at high-risk populations: Public health officials focus on vulnerable populations, like those in overcrowded settings or with compromised immune systems, to ensure they receive timely vaccination and preventative measures.
Decreased International Importation of Measles
While domestic vaccination efforts are paramount, the global context also significantly impacts measles incidence in the US. Reduced importation of measles from other countries plays a vital role in maintaining low case numbers.
- Global vaccination initiatives reducing measles transmission worldwide: International collaborations to increase global vaccination coverage have lowered the overall prevalence of measles, making importation less likely.
- Improved border health screening and quarantine procedures: Stricter screening at points of entry, along with effective quarantine protocols for individuals exhibiting symptoms, minimizes the risk of measles entering the country.
- Reduced international travel from affected areas: Fluctuations in international travel patterns, influenced by factors such as global health crises, also affect the importation risk of measles.
Potential Contributing Factors and Limitations
While vaccination and public health measures are the primary drivers, other factors likely contribute to the drop in US measles cases. It’s also important to acknowledge limitations in data interpretation.
- Improved overall hygiene and sanitation practices: Improved hygiene and sanitation across the US contribute to lower rates of infectious diseases, including measles.
- Enhanced access to healthcare, leading to early diagnosis and treatment: Improved access to healthcare enables quicker diagnosis and treatment, minimizing severe complications and potential spread.
- Limitations in data accuracy due to underreporting or misclassification: Data on measles cases might not be completely accurate due to underreporting or misclassification of cases.
- Potential confounding factors influencing measles case numbers: Other variables, such as seasonal fluctuations or changes in diagnostic practices, might influence reported case numbers.
Conclusion: Maintaining the Decline in US Measles Cases – A Call to Action
The dramatic drop in US measles cases is a testament to the power of vaccination, robust public health surveillance, and global collaboration. The effectiveness of the MMR vaccine, combined with improved public health response and decreased international importation, has significantly contributed to this positive trend. However, maintaining these low measles case numbers requires sustained vigilance and effort. Continued high vaccination rates, robust public health infrastructure, and global cooperation are vital for preventing future outbreaks. Get vaccinated, support vaccination programs in your community, and stay informed about measles prevention. Together, we can continue to reduce measles cases and protect the health of our communities. For more information on measles and vaccination, visit the CDC website: [insert CDC link here].

Featured Posts
-
 Investigating The Death Bath Profiling A Serial Killer Through Six Victims
May 30, 2025
Investigating The Death Bath Profiling A Serial Killer Through Six Victims
May 30, 2025 -
 Sacramento County Wastewater Shows Measles Virus What You Need To Know
May 30, 2025
Sacramento County Wastewater Shows Measles Virus What You Need To Know
May 30, 2025 -
 Elevated Uncertainty The Growing Risks Of Inflation And Job Losses
May 30, 2025
Elevated Uncertainty The Growing Risks Of Inflation And Job Losses
May 30, 2025 -
 Kivalliq Hydro Fibre Link Manitoba And Nunavut Forge A New Energy And Economic Corridor
May 30, 2025
Kivalliq Hydro Fibre Link Manitoba And Nunavut Forge A New Energy And Economic Corridor
May 30, 2025 -
 Listen To Jayne Hintons Sundae Servings On Bolton Fm
May 30, 2025
Listen To Jayne Hintons Sundae Servings On Bolton Fm
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Grigor Dimitrov Vliyanieto Na Kontuziyata Vrkhu Karierata Mu
May 31, 2025
Grigor Dimitrov Vliyanieto Na Kontuziyata Vrkhu Karierata Mu
May 31, 2025 -
 Kontuziyata Na Grigor Dimitrov Aktualna Informatsiya I Analiz
May 31, 2025
Kontuziyata Na Grigor Dimitrov Aktualna Informatsiya I Analiz
May 31, 2025 -
 Trumps Uncertainty What Made Him Question Elon Musk
May 31, 2025
Trumps Uncertainty What Made Him Question Elon Musk
May 31, 2025 -
 Uncertainty And The End Trumps Doubts About Elon Before The Break
May 31, 2025
Uncertainty And The End Trumps Doubts About Elon Before The Break
May 31, 2025 -
 Everything Revealed In The Star Trek Strange New Worlds Season 3 Teaser
May 31, 2025
Everything Revealed In The Star Trek Strange New Worlds Season 3 Teaser
May 31, 2025
