The Economic Impact Of The US-China Trade War: Beijing's Perspective
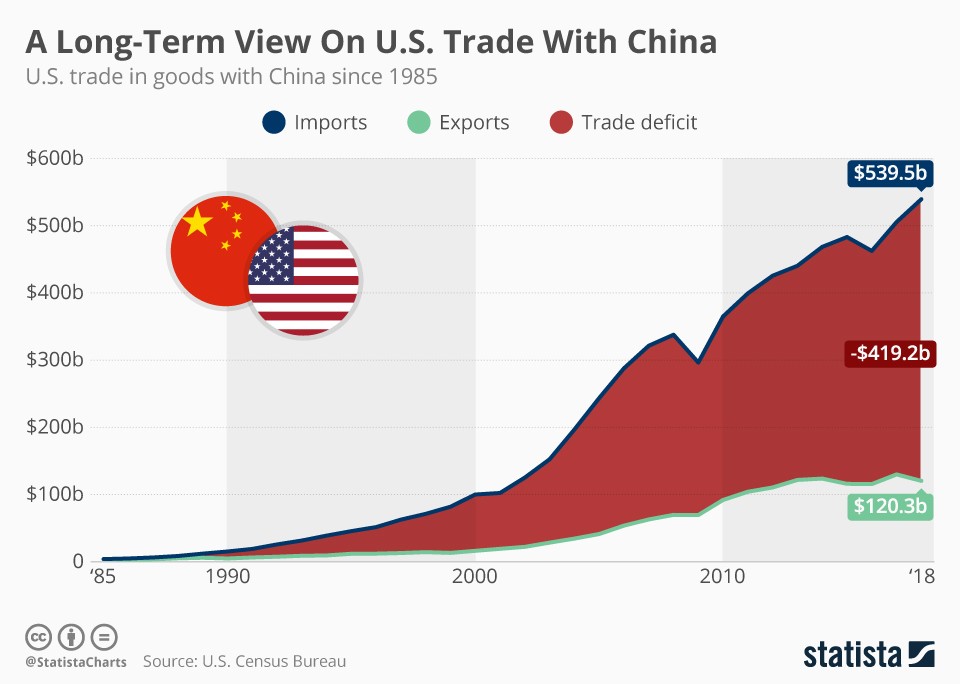
Table of Contents
Disruption to Chinese Exports and Global Supply Chains
The US-China trade war dramatically disrupted Chinese exports and global supply chains. The imposition of tariffs on numerous Chinese goods by the US led to a significant decrease in export volume and revenue for various sectors. This wasn't merely a reduction in trade; it triggered a fundamental reshaping of global manufacturing and logistics.
-
Impact on Manufacturing Sectors: Industries like textiles, electronics, and furniture experienced substantial setbacks. The increased costs associated with tariffs made Chinese products less competitive in the US market, forcing businesses to adapt or face decline.
-
Increased Costs for Chinese Businesses: Tariffs didn't just affect exporters; they increased the cost of inputs for many Chinese businesses, impacting their profitability and competitiveness even within the domestic market.
-
Diversification of Export Markets: Facing challenges in the US market, China actively sought to diversify its export destinations, strengthening trade relationships with countries in Asia, Africa, and Latin America. This strategy, while successful to some extent, didn't fully compensate for the losses incurred from the reduced US trade.
-
The Role of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): While FDI inflow to China slowed during the trade war, existing investments and strategic partnerships played a crucial role in helping some Chinese businesses weather the storm. This highlighted the importance of long-term international collaborations in mitigating trade risks.
Impact on Chinese Domestic Investment and Economic Growth
The US-China trade war significantly impacted Chinese domestic investment and economic growth. The slowdown in GDP growth during this period was partly attributed to the trade tensions. While China's economy remained resilient, the uncertainty created by the trade war dampened investor confidence, both domestically and internationally.
-
Decrease in Foreign Investment: The trade war created uncertainty, leading to a decrease in foreign direct investment in China, particularly in sectors directly affected by the tariffs.
-
Government Stimulus Packages and Their Effectiveness: The Chinese government implemented several stimulus packages to mitigate the economic slowdown. These included infrastructure projects, tax cuts, and measures to support businesses. While these measures helped stabilize the economy, their long-term effectiveness is still being debated.
-
Impact on Specific Sectors: Sectors such as real estate and technology experienced varying degrees of impact. The real estate sector faced headwinds due to decreased foreign investment and broader economic uncertainty, while the technology sector, although impacted, also saw increased government support for domestic innovation.
-
Long-Term Effects on Chinese Economic Growth Projections: The long-term effects of the trade war on Chinese economic growth projections remain a subject of ongoing analysis. While China continues to be a major global economic player, the trade war undoubtedly introduced significant short-term volatility and longer-term structural adjustments to the economy.
Strategic Responses from Beijing
In response to the US-China trade war, Beijing adopted a multi-pronged strategy emphasizing self-reliance and technological innovation. This included retaliatory tariffs and a broader push for economic independence.
-
Examples of Chinese Retaliatory Tariffs: China imposed retaliatory tariffs on US goods, impacting various sectors and escalating the trade conflict. These actions were part of Beijing's strategy to defend its economic interests and leverage its growing economic power.
-
Development of Domestic Supply Chains and Technologies: The trade war accelerated China's efforts to develop more self-reliant and resilient domestic supply chains. This included increased investment in research and development, fostering domestic technological innovation, and reducing reliance on foreign technology.
-
Increased Investment in Domestic Infrastructure and Innovation: Significant investments were made in domestic infrastructure projects and technological innovation, aiming to reduce dependence on foreign technologies and boost domestic consumption.
-
The Strategic Implications of the BRI: The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), a massive infrastructure project connecting Asia, Africa, and Europe, gained added significance in the context of the trade war. It was seen as a way to secure alternative trade routes and deepen economic ties with partner countries, lessening dependence on Western markets.
The Long-Term Implications for the Chinese Economy
The US-China trade war spurred significant long-term structural changes in the Chinese economy. While the immediate impact involved adjustments to trade flows and investment patterns, the longer-term consequences are far-reaching.
-
Restructuring of Chinese Industries and Sectors: The trade war forced a restructuring of several Chinese industries and sectors, pushing them to enhance efficiency, innovation, and competitiveness. This led to consolidation in some sectors and the rise of new players focused on domestic markets.
-
Increased Focus on Technological Self-Reliance: The experience solidified China's commitment to technological self-reliance, fostering domestic innovation and reducing reliance on foreign technology in strategic sectors.
-
Potential for Greater Regional Economic Integration (e.g., RCEP): The trade war prompted China to further strengthen regional economic integration efforts, such as the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), to create alternative trade routes and reduce dependence on the US market.
-
Shift in China's Global Economic Influence: The US-China trade war reshaped the global economic order, accelerating a shift in China's global economic influence and solidifying its role as a major economic player beyond its bilateral relationship with the United States.
Conclusion: Understanding the Lasting Effects of the US-China Trade War on Beijing's Economy
The US-China trade war had a profound and multifaceted impact on the Chinese economy. While Beijing successfully implemented strategies to mitigate the immediate negative effects, the long-term consequences are still unfolding. The strategic responses adopted by Beijing, including retaliatory tariffs, investment in domestic infrastructure and technology, and a push for greater regional economic integration, reveal a determined effort to reshape its economic trajectory and reduce its vulnerability to future trade conflicts. Understanding the complexities of the US-China trade war requires further exploration of the economic, political, and technological dimensions. To gain a deeper understanding of its global impact and Beijing’s perspective on the issue, consider exploring resources like reports from the World Trade Organization (WTO), the International Monetary Fund (IMF), and academic journals focusing on international economics and trade policy. Continued research into the US-China trade war and its enduring consequences is essential.

Featured Posts
-
 Justice Department Concludes Louisiana School Desegregation Case
May 02, 2025
Justice Department Concludes Louisiana School Desegregation Case
May 02, 2025 -
 To Ypoyrgiko Symvoylio Egkrinei Stratigiki P Syxikis Ygeias Simantikes Ekselikseis
May 02, 2025
To Ypoyrgiko Symvoylio Egkrinei Stratigiki P Syxikis Ygeias Simantikes Ekselikseis
May 02, 2025 -
 Republika Ceke Sulm Me Thike Ne Qender Tregtare Bilanci Dy Te Vdekur
May 02, 2025
Republika Ceke Sulm Me Thike Ne Qender Tregtare Bilanci Dy Te Vdekur
May 02, 2025 -
 The Roberts Court And Religious Freedom Examining The Blurring Of Church And State Lines
May 02, 2025
The Roberts Court And Religious Freedom Examining The Blurring Of Church And State Lines
May 02, 2025 -
 Bbc Faces Unprecedented Challenges Following 1bn Income Drop
May 02, 2025
Bbc Faces Unprecedented Challenges Following 1bn Income Drop
May 02, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Lynk Lee Sau Chuyen Gioi Nhan Sac Xinh Dep Va Cau Chuyen Tinh Yeu Day Cam Hung
May 10, 2025
Lynk Lee Sau Chuyen Gioi Nhan Sac Xinh Dep Va Cau Chuyen Tinh Yeu Day Cam Hung
May 10, 2025 -
 Lynk Lee Chuyen Gioi Hanh Trinh Lot Xac Ngoan Muc Va Tinh Yeu Tron Ven
May 10, 2025
Lynk Lee Chuyen Gioi Hanh Trinh Lot Xac Ngoan Muc Va Tinh Yeu Tron Ven
May 10, 2025 -
 The 10 Best Film Noir Movies Ever Made
May 10, 2025
The 10 Best Film Noir Movies Ever Made
May 10, 2025 -
 The Kreischers Marriage And The Netflix Stand Up Routine
May 10, 2025
The Kreischers Marriage And The Netflix Stand Up Routine
May 10, 2025 -
 Top 10 Must See Film Noir Movies
May 10, 2025
Top 10 Must See Film Noir Movies
May 10, 2025
