The Future Of European Public Transit: Hydrogen Or Battery Buses?

Table of Contents
<meta name="description" content="Explore the ongoing debate: will hydrogen or battery power dominate Europe's public transport future? We weigh the pros and cons of each technology for cleaner, more efficient buses.">
The modernization of European public transit is underway, with a critical focus on reducing emissions and improving efficiency. A key component of this shift is the transition to electric buses, but the path forward remains uncertain: will hydrogen fuel cell buses or battery-electric buses ultimately prevail? This article analyzes the strengths and weaknesses of both technologies, examining their potential to shape the future of European public transport. The choice between these two power sources will significantly impact the environmental sustainability and economic viability of public transit systems across the continent for decades to come.
<h2>Battery-Electric Buses: The Current Frontrunner</h2>
Battery-electric buses (BEBs) are currently leading the charge in the transition to cleaner public transport across Europe. Their prevalence is largely due to readily available technology and a relatively mature supply chain.
<h3>Advantages of Battery-Electric Buses:</h3>
- Lower Upfront Cost: BEBs generally have a lower initial purchase price compared to hydrogen fuel cell buses (HFCBs), making them a more accessible option for many cities and transit authorities with tighter budgets.
- Established Charging Infrastructure: A growing network of charging stations is already in place across many European cities, simplifying integration and reducing operational complexities. This existing infrastructure reduces the upfront investment needed for deployment.
- Improved Energy Efficiency (Urban Settings): BEBs demonstrate higher energy efficiency in urban environments characterized by frequent stops and starts, maximizing battery life and minimizing energy consumption.
- Reduced Noise Pollution: The near-silent operation of BEBs significantly reduces noise pollution compared to traditional diesel buses, improving the quality of life for residents and passengers alike.
- Mature Supply Chain and Manufacturing: The established supply chain for BEBs ensures a reliable supply of components and facilitates mass production, contributing to cost reductions and faster deployment.
<h3>Disadvantages of Battery-Electric Buses:</h3>
- Limited Range: The range of BEBs is significantly restricted compared to HFCBs, particularly on longer routes or in areas with challenging terrain. This range limitation can necessitate frequent charging stops, potentially disrupting service schedules.
- Longer Charging Times: Charging BEBs takes considerably longer than refueling HFCBs, leading to downtime and potential service disruptions. Optimized charging strategies and fast-charging technologies are continually being developed to mitigate this issue.
- Environmental Concerns of Battery Production: The production of lithium-ion batteries raises concerns about resource extraction, manufacturing processes, and the environmental impact of battery disposal. Research into sustainable battery production and recycling is crucial.
- Dependence on Electricity Grid Infrastructure: The reliance on electricity grids for charging poses challenges, particularly if the grid relies heavily on fossil fuels. Integration with renewable energy sources is vital to minimizing the overall carbon footprint.
- Battery Weight: The substantial weight of battery packs can affect vehicle performance, maneuverability, and the lifespan of other vehicle components.
<h2>Hydrogen Fuel Cell Buses: A Promising Alternative</h2>
While BEBs currently dominate the market, hydrogen fuel cell buses (HFCBs) present a compelling alternative, particularly for longer routes and areas where extensive charging infrastructure is lacking.
<h3>Advantages of Hydrogen Fuel Cell Buses:</h3>
- Longer Range and Faster Refueling: HFCBs boast significantly longer ranges and much faster refueling times than BEBs, making them ideal for intercity routes and areas with sparse charging infrastructure. Refueling times are comparable to those of diesel buses.
- Potential for Carbon-Neutral Operation: If produced using renewable energy sources (green hydrogen), HFCBs offer the potential for truly carbon-neutral operation, emitting only water vapor.
- Reduced Reliance on Electricity Grid: HFCBs are less dependent on the electricity grid, offering a degree of energy independence and reducing strain on existing infrastructure.
- Suitable for Longer Routes and Intercity Travel: The extended range of HFCBs makes them particularly well-suited for longer routes and intercity transport, addressing a key limitation of BEBs.
- Minimal Tailpipe Emissions: HFCBs produce virtually zero tailpipe emissions, significantly reducing air pollution in urban and suburban environments.
<h3>Disadvantages of Hydrogen Fuel Cell Buses:</h3>
- Higher Initial Investment Costs: The initial cost of HFCBs is considerably higher than that of BEBs, presenting a significant barrier to adoption for many transit authorities.
- Limited Hydrogen Refueling Infrastructure: The lack of widespread hydrogen refueling infrastructure across Europe remains a major hurdle to the wider adoption of HFCBs. The development of a robust refueling network is crucial for their success.
- Energy Efficiency Losses: There are energy losses associated with hydrogen production, transportation, and storage, impacting the overall efficiency of the HFCB system. Improvements in hydrogen production and storage technologies are essential.
- Safety Concerns: Concerns about the safe storage and handling of hydrogen require stringent safety regulations and protocols to mitigate potential risks.
- Technological Immaturity: While rapidly advancing, hydrogen fuel cell technology is still relatively immature compared to battery-electric technology, leaving room for improvements in efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
<h2>The Role of Government Policy and Infrastructure</h2>
The successful deployment of both BEBs and HFCBs depends heavily on supportive government policies and the development of necessary infrastructure.
<h3>Government Incentives and Subsidies:</h3>
Government incentives, subsidies, and targeted funding programs are vital in driving the adoption of both BEBs and HFCBs. These incentives can help offset the higher upfront costs of HFCBs and encourage investment in the development of refueling infrastructure. Funding should also support research and development to improve the efficiency and reduce the cost of both technologies.
<h3>Infrastructure Development:</h3>
Expanding charging infrastructure for BEBs and establishing hydrogen refueling stations for HFCBs are crucial for the widespread adoption of both technologies. Strategic planning and collaboration between governments, private companies, and transit authorities are essential to ensure the efficient and effective deployment of these networks.
<h3>Regulatory Framework:</h3>
A clear and consistent regulatory framework is needed to ensure the safety and environmental compliance of both BEBs and HFCBs. This framework should encompass safety standards, emission regulations, and guidelines for the handling and storage of hydrogen.
<h2>Conclusion</h2>
The choice between hydrogen and battery-electric buses for the future of European public transit is complex and depends on various factors, including initial investment costs, operational efficiency, environmental impact, and the availability of supporting infrastructure. While battery-electric buses are currently the more established technology, hydrogen fuel cell buses offer compelling advantages for longer routes and areas where charging infrastructure is limited. Both technologies have a role to play in achieving cleaner and more sustainable public transportation in Europe. The optimal solution may involve a mixed fleet approach, utilizing both technologies strategically based on specific route requirements and local conditions.
Call to Action: The transition to sustainable public transport is crucial. Learn more about the ongoing advancements in both hydrogen and battery-electric bus technologies and how they are shaping the future of European public transit. Stay informed about the latest developments in hydrogen and battery bus technology to make informed decisions regarding the future of your city’s public transportation.

Featured Posts
-
 Celebrity Special On Who Wants To Be A Millionaire Behind The Scenes And Big Wins
May 07, 2025
Celebrity Special On Who Wants To Be A Millionaire Behind The Scenes And Big Wins
May 07, 2025 -
 The Strategic Importance Of Middle Managers Maximizing Company Potential And Employee Talent
May 07, 2025
The Strategic Importance Of Middle Managers Maximizing Company Potential And Employee Talent
May 07, 2025 -
 Hawkgirls Flight And Costume An Actors Perspective In Superman
May 07, 2025
Hawkgirls Flight And Costume An Actors Perspective In Superman
May 07, 2025 -
 The Truth Behind Jenna Ortegas Absence From Scream 7
May 07, 2025
The Truth Behind Jenna Ortegas Absence From Scream 7
May 07, 2025 -
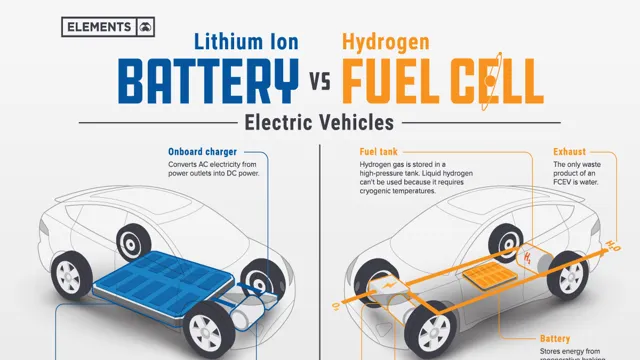 Hydrogen Fuel Cell Buses Vs Battery Electric Buses A European Perspective
May 07, 2025
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Buses Vs Battery Electric Buses A European Perspective
May 07, 2025
