The Impact Of Wildfires: Driving Record Levels Of Global Forest Loss
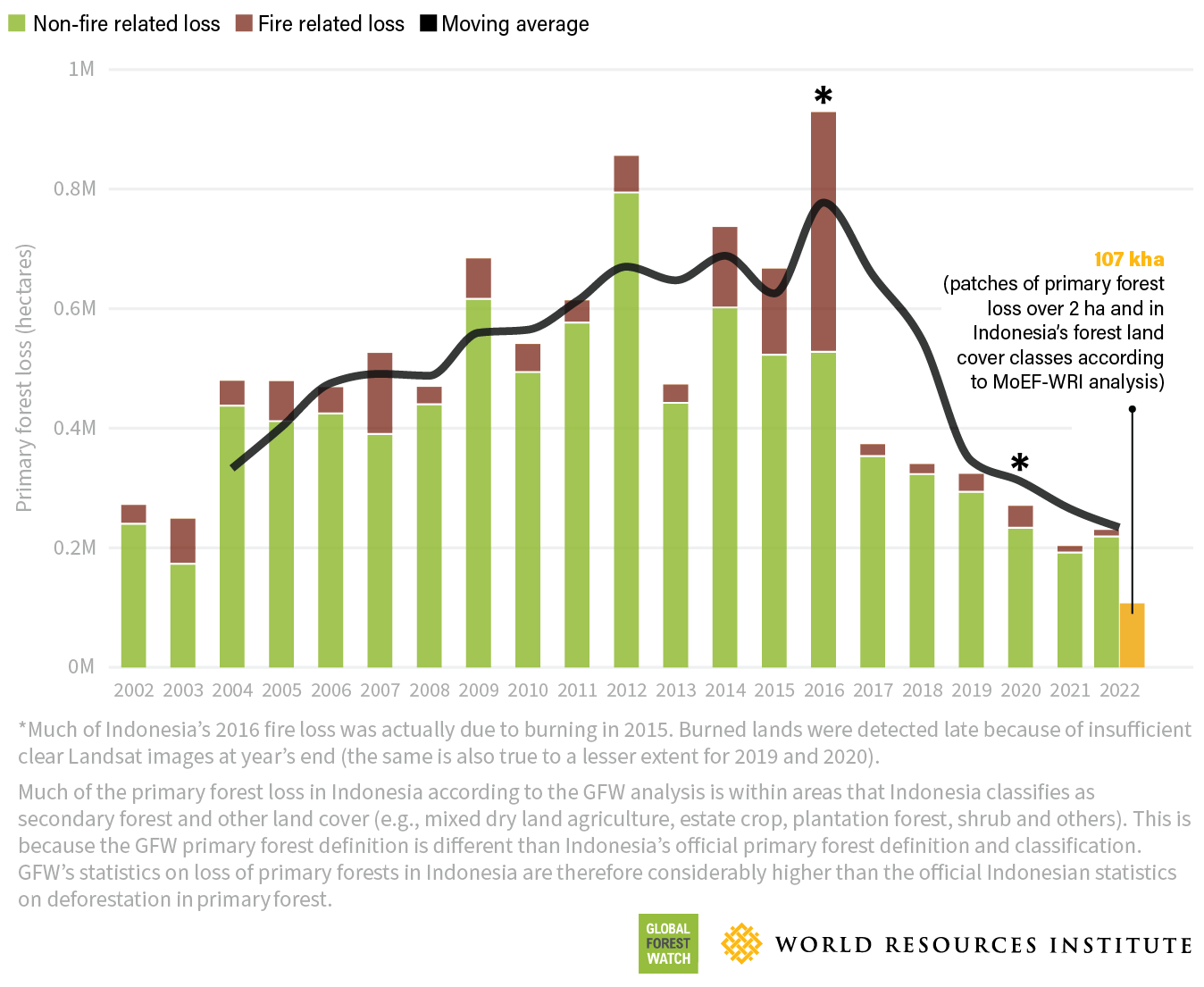
Table of Contents
Devastating Effects of Wildfires on Forest Ecosystems
Wildfires unleash a cascade of devastating effects on forest ecosystems, impacting every aspect of their delicate balance. The consequences extend far beyond the immediate destruction, with long-term repercussions for biodiversity, soil health, and the global climate.
Biodiversity Loss
Wildfires cause widespread habitat destruction, leading to significant biodiversity loss. The intense heat and flames obliterate vegetation, leaving behind barren landscapes unsuitable for many species.
- Examples of endangered species affected: The koala in Australia, the California condor, and various amphibian populations have suffered severe losses due to wildfires.
- Disruption of food chains: The loss of plant life directly impacts herbivores, leading to cascading effects throughout the food web. Predators lose their prey, and the entire ecosystem is thrown into disarray.
- Loss of genetic diversity: Wildfires can eliminate entire populations of plants and animals, reducing genetic diversity and making species more vulnerable to future threats. This loss is particularly devastating for already endangered or threatened species. The impact on biodiversity loss from wildfires is a significant threat to global ecosystems.
Soil Degradation
The impact of wildfires extends far beyond the immediate destruction of vegetation. Wildfires severely degrade soil health, leading to long-term consequences for forest regeneration.
- Increased vulnerability to landslides: The loss of vegetation exposes soil to erosion, increasing the risk of landslides and mudslides, especially on steep slopes.
- Reduced water retention: Burned soil loses its ability to absorb and retain water, leading to increased runoff and decreased water availability for plant growth.
- Impact on soil microorganisms: Wildfires kill beneficial soil microorganisms, reducing soil fertility and hindering nutrient cycling, making forest regeneration a slow and challenging process. The effects of wildfire on soil degradation can persist for decades, hindering the ability of forests to recover.
Carbon Emissions and Climate Change
Wildfires are a significant source of carbon emissions, releasing massive amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. This exacerbates climate change, creating a dangerous feedback loop.
- Quantifiable data on carbon emissions from wildfires: Recent studies have shown that wildfires release billions of tons of CO2 annually, significantly contributing to global greenhouse gas emissions.
- The feedback loop between climate change and increased wildfire risk: Climate change, with its rising temperatures and increased drought frequency, creates conditions that are more favorable for wildfires, leading to a vicious cycle of escalating wildfire severity and climate change impacts. Wildfires' contribution to climate change is a significant factor driving global forest loss.
Contributing Factors to Increased Wildfire Severity and Frequency
The increased severity and frequency of wildfires are not solely due to natural causes. Several factors, including climate change and human activities, contribute to this escalating crisis.
Climate Change
Climate change is a major driver of increased wildfire risk. Rising global temperatures, prolonged droughts, and altered precipitation patterns create ideal conditions for wildfires to ignite and spread rapidly.
- Specific examples of how climate change fuels wildfires: Drier vegetation acts as readily available fuel, longer fire seasons extend the period of risk, and extreme heat waves can quickly ignite dry brush.
- Increased frequency and intensity of heatwaves: More frequent and intense heat waves desiccate vegetation, making it extremely flammable and increasing the likelihood of wildfires.
Human Activities
Human activities play a significant role in both starting and spreading wildfires. Deforestation, poor land management practices, and infrastructure development all increase wildfire risk.
- Examples of human-caused wildfires: Many wildfires are ignited by human negligence, such as discarded cigarettes, campfires left unattended, and power lines sparking in dry vegetation.
- Impact of urbanization on wildfire risk: Urban sprawl encroaches on wildlands, increasing the interface between human settlements and flammable vegetation, raising the risk of wildfires impacting homes and communities.
- Inadequate forest management: Poorly managed forests, with excessive fuel loads and a lack of controlled burns, are more susceptible to intense and widespread wildfires.
Invasive Species
Invasive plant species can significantly alter forest ecosystems, making them more susceptible to wildfires. These species often have different flammability characteristics than native vegetation, increasing fuel loads and the intensity of fires.
- Examples of invasive species that increase wildfire risk: Certain grasses and shrubs can create dense, highly flammable underbrush, increasing the risk of rapid fire spread.
- Their impact on fuel loads: Invasive species can significantly increase fuel loads, providing more readily available fuel for wildfires, and changing the fire regime of an ecosystem.
Mitigating the Impact of Wildfires and Preventing Global Forest Loss
Combating the devastating impact of wildfires requires a multifaceted approach that combines improved forest management, climate change mitigation, and international cooperation.
Improved Forest Management
Sustainable forestry practices are crucial for reducing wildfire risk. Techniques such as controlled burns and forest thinning can significantly reduce fuel loads and create firebreaks.
- Benefits of controlled burns: Controlled burns reduce the amount of flammable material available for wildfires, creating a mosaic of vegetation that is less susceptible to large, intense fires.
- Effective forest management strategies: This includes thinning dense forests to reduce fuel loads, creating firebreaks, and using prescribed burning to manage underbrush.
- Importance of community involvement: Engaging local communities in forest management efforts is vital for successful implementation and long-term sustainability.
Climate Change Mitigation
Addressing climate change is paramount to mitigating wildfire risk. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions is crucial to slowing down global warming and reducing the frequency and severity of extreme weather events that contribute to wildfires.
- Actions individuals and governments can take to reduce emissions: Transitioning to renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and adopting sustainable transportation are vital steps in reducing carbon emissions.
- Importance of renewable energy: Investing in renewable energy sources like solar and wind power is essential to decrease our reliance on fossil fuels and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
International Cooperation
The challenge of wildfires and global forest loss requires global collaboration. International initiatives are needed to share best practices, coordinate efforts, and leverage technological advancements for effective wildfire prevention and forest conservation.
- Examples of international initiatives focused on forest conservation: International agreements and collaborative research efforts are essential to address this global challenge effectively.
- Importance of data sharing and technological advancements: Sharing data on wildfire patterns, using advanced satellite technology for early detection and monitoring, and developing innovative firefighting techniques are essential tools in the fight against wildfires.
Conclusion
The devastating impact of wildfires on global forest loss is undeniable. Climate change, human activities, and invasive species are all contributing factors to the increasing frequency and severity of these catastrophic events. To protect our forests and mitigate the devastating effects of wildfires, we must adopt a comprehensive strategy that includes improved forest management, aggressive climate change mitigation, and robust international cooperation. Understanding the impact of wildfires on global forest loss is crucial for taking effective action. Let's work together to protect our forests and mitigate the devastating effects of wildfires.

Featured Posts
-
 Princess Road Closed Emergency Response Following Pedestrian Accident
May 25, 2025
Princess Road Closed Emergency Response Following Pedestrian Accident
May 25, 2025 -
 Melanie Thierry Et Raphael Surmonter Les Defis D Une Famille Recomposee Ou Nombreuse
May 25, 2025
Melanie Thierry Et Raphael Surmonter Les Defis D Une Famille Recomposee Ou Nombreuse
May 25, 2025 -
 Italian Open Chief Credits Top Players For Chinese Tennis Culture Growth
May 25, 2025
Italian Open Chief Credits Top Players For Chinese Tennis Culture Growth
May 25, 2025 -
 7 Plunge For Amsterdam Stocks As Trade War Anxiety Mounts
May 25, 2025
7 Plunge For Amsterdam Stocks As Trade War Anxiety Mounts
May 25, 2025 -
 Ohnotheydidnts Hunger Games Live Journal A Comprehensive Archive
May 25, 2025
Ohnotheydidnts Hunger Games Live Journal A Comprehensive Archive
May 25, 2025
