The New Workplace Reality: Are Employees Truly Replaceable?
Table of Contents
The Illusion of Replaceability: Skills and Experience Matter
The notion that employees are easily replaceable often overlooks the significant value of specialized skills and years of accumulated experience. While automation might handle routine tasks, certain roles require a level of expertise that's difficult, if not impossible, to replicate quickly.
Specialized Skills and Expertise
Highly specialized skills and deep expertise are crucial in many industries, making certain employees incredibly difficult to replace.
- Examples: A neurosurgeon's precision, a software architect's intricate understanding of complex systems, or a data scientist's ability to interpret vast datasets—these are not easily replicated.
- Cost and Time: Training a replacement for these highly skilled individuals often involves years of education, extensive on-the-job training, and significant financial investment. The cost of employee replacement far outweighs the perceived savings of automation in many cases.
- Institutional Knowledge: Beyond specific skills, experienced professionals possess valuable institutional knowledge—an understanding of company history, processes, and relationships crucial for efficient operations. Losing this knowledge can be detrimental to a business.
Years of Experience and Company Knowledge
Years of experience contribute to a depth of understanding and tacit knowledge that's hard to quantify but undeniably valuable. Experienced employees often contribute beyond their formal job descriptions.
- Beyond the Job Description: Experienced employees frequently mentor junior colleagues, identify and solve unexpected problems, and navigate complex organizational dynamics.
- Difficult to Replicate: The nuanced understanding of company culture, client relationships, and intricate processes accumulated over years cannot be easily replicated by a new hire, regardless of their qualifications.
- Impact on Productivity and Morale: The loss of experienced employees can significantly impact team productivity, morale, and overall company performance. Employee replacement in these scenarios is often costly and disruptive.
Beyond Technical Skills: The Human Factor
While technical skills are undeniably important, the human factor—soft skills and emotional intelligence—plays a crucial role in determining an employee's true value and replaceability.
Soft Skills and Emotional Intelligence
Soft skills, such as communication, teamwork, problem-solving, and adaptability, are increasingly valued in the modern workplace. Emotional intelligence, the ability to understand and manage one's own emotions and the emotions of others, is equally crucial.
- Team Performance and Company Culture: These soft skills contribute significantly to team cohesion, positive company culture, and overall workplace efficiency.
- Difficult to Quantify: Unlike technical skills, soft skills are harder to measure and quantify, yet their impact on productivity and workplace harmony is undeniable.
- Personality and Work Ethic: An employee's personality, work ethic, and commitment also contribute significantly to their overall value and are nearly impossible to replicate.
Employee Engagement and Loyalty
Employee engagement and loyalty are directly linked to productivity, innovation, and overall company success. Highly engaged and loyal employees are less likely to leave, reducing the cost and disruption associated with employee replacement.
- Cost of High Employee Turnover: High employee turnover is expensive, involving recruitment costs, training expenses, and the loss of productivity during the transition period.
- Positive Work Environment: Investing in a positive and supportive work environment fosters employee engagement and loyalty, making employees less likely to seek opportunities elsewhere.
- Employee Retention Strategies: Proactive employee retention strategies, such as offering competitive compensation, providing opportunities for professional development, and promoting work-life balance, are essential for reducing employee turnover.
The Impact of Automation and AI
Automation and AI are undeniably reshaping the workplace, but they don't render all employees replaceable. Instead, they are shifting job demands, requiring upskilling and reskilling initiatives.
Automation's Role in Shifting Job Demands
Automation and AI are automating routine and repetitive tasks, affecting certain jobs more than others.
- Jobs Affected by Automation: Many manufacturing, data entry, and customer service roles are experiencing automation.
- Upskilling and Reskilling: To remain competitive, employees need to adapt by acquiring new skills and embracing lifelong learning. Businesses must invest in upskilling and reskilling programs to support their workforce.
- Emergence of New Roles: Technological advancements are creating new roles and opportunities, requiring individuals with specialized skills in areas like AI development, data analytics, and cybersecurity.
Human Oversight and Collaboration with AI
Even in highly automated systems, human oversight and collaboration with AI remain crucial.
- Human Judgment and Critical Thinking: Many tasks require human judgment, critical thinking, creativity, and complex problem-solving skills—areas where AI currently falls short.
- Human-AI Collaboration: Effective human-AI collaboration can lead to significant innovation and efficiency gains, augmenting human capabilities rather than replacing them.
Conclusion: Redefining Replaceability in the Modern Workplace – A Call to Action
While automation and technological advancements are transforming the workplace, employees with specialized skills, significant experience, strong soft skills, and a commitment to their work remain invaluable and difficult to replace completely. Investing in employee development, fostering positive work environments, and adapting to the changing demands of the modern workplace are essential for organizational success. Are you prepared to address the question of employee replaceability in your organization? Investing in your employees is investing in the future – don't let the illusion of replaceability overshadow their true value.

Featured Posts
-
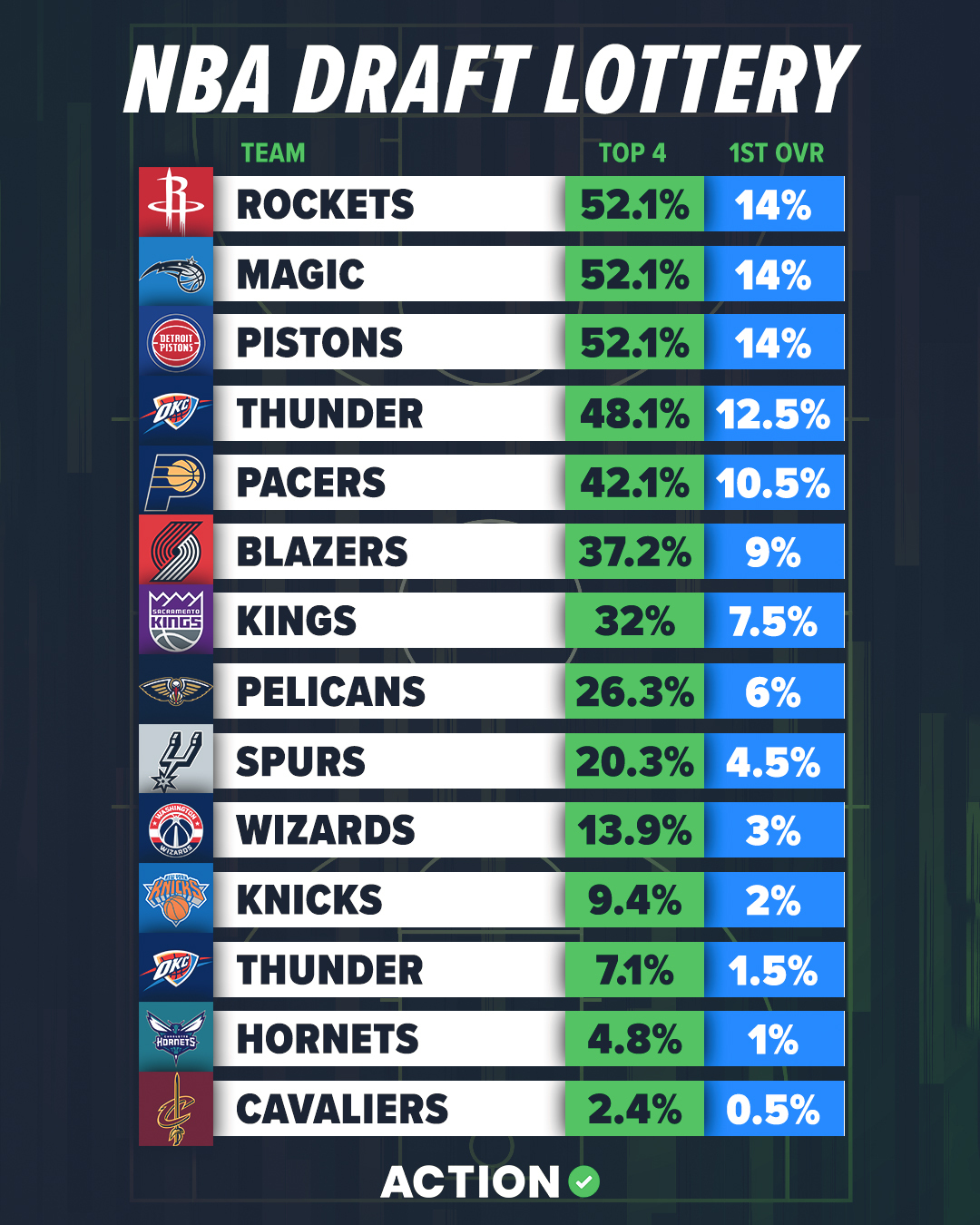 Sixers Chances To Win The Nba Draft Lottery A Complete Guide
May 13, 2025
Sixers Chances To Win The Nba Draft Lottery A Complete Guide
May 13, 2025 -
 Families Of Gaza Hostages Endure Lingering Nightmare
May 13, 2025
Families Of Gaza Hostages Endure Lingering Nightmare
May 13, 2025 -
 State Of The Union 2024 Local Protests And Their Significance
May 13, 2025
State Of The Union 2024 Local Protests And Their Significance
May 13, 2025 -
 Ali Larter On Angela Reverse Engineering A Trophy Wife In Season 2 Of She
May 13, 2025
Ali Larter On Angela Reverse Engineering A Trophy Wife In Season 2 Of She
May 13, 2025 -
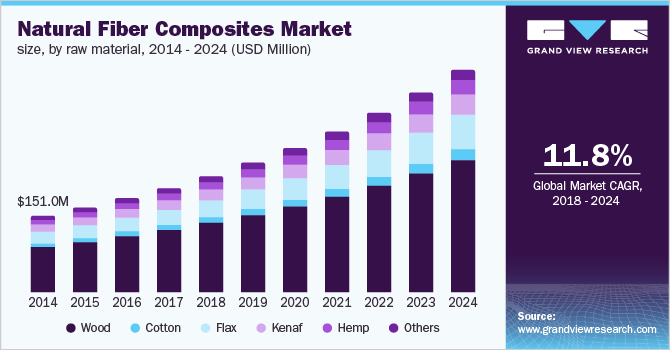 Global Natural Fiber Composites Market Outlook To 2029
May 13, 2025
Global Natural Fiber Composites Market Outlook To 2029
May 13, 2025
