The Scarcity Of Rare Earth Minerals: A 21st-Century Cold War
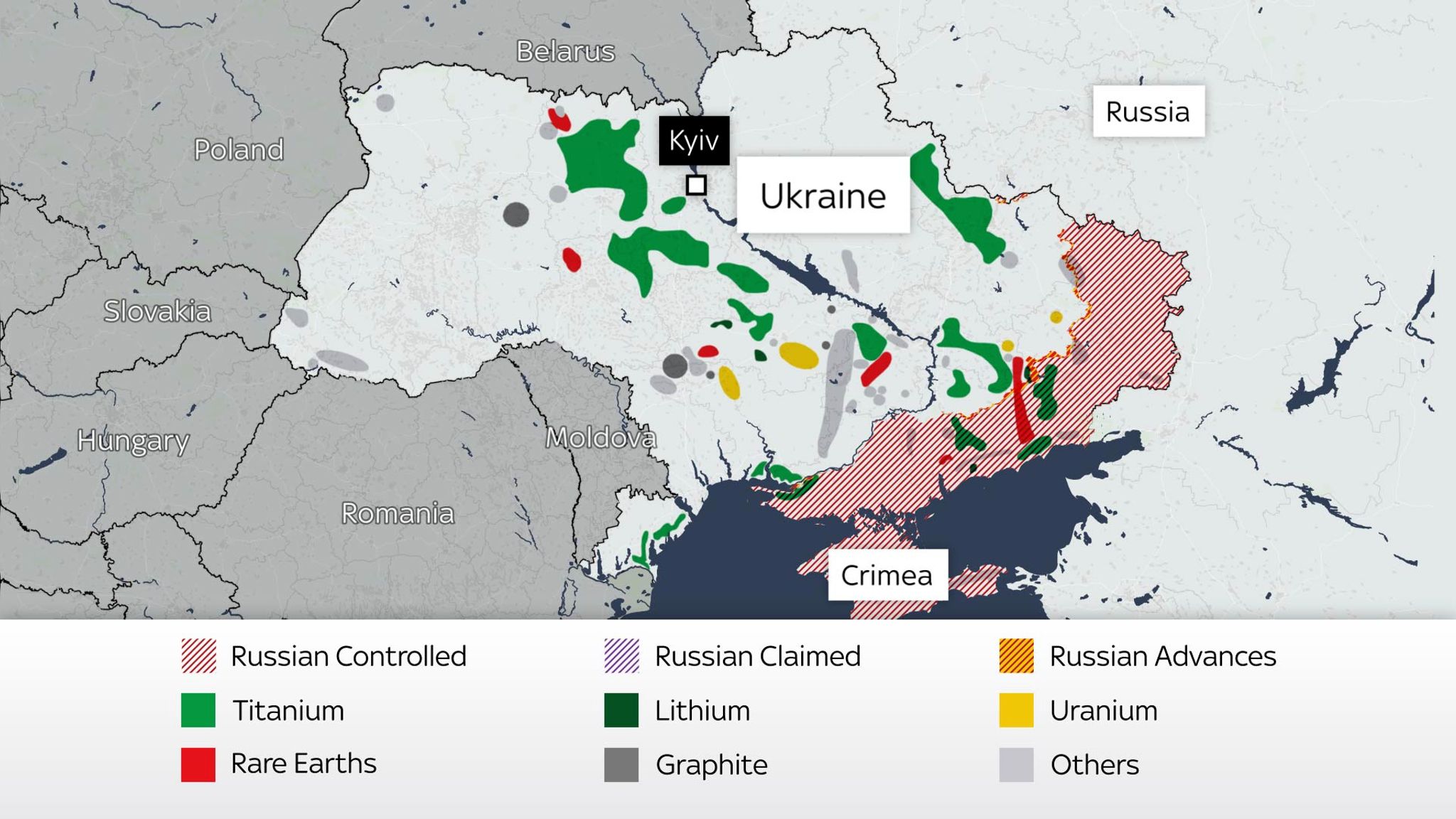
Table of Contents
What are Rare Earth Minerals and Why are They So Important?
Rare earth elements (REEs) are a group of 17 chemically similar elements: scandium, yttrium, and the 15 lanthanides. Their unique magnetic, luminescent, and catalytic properties are crucial for a vast array of modern technologies. While the term "rare earth" might suggest scarcity, these elements are actually relatively abundant in the Earth's crust. However, their dispersion and the difficulty and cost of extraction make them economically scarce.
This economic scarcity is what fuels the current geopolitical tensions. REEs are essential components in numerous technologies, including:
- Green technologies: Wind turbine generators rely heavily on neodymium and dysprosium magnets for their powerful motors. Electric vehicles (EVs) also utilize these same REEs extensively in their motors and batteries. Solar panels incorporate REEs for improved efficiency. The transition to a green economy is directly dependent on a stable and secure supply of these minerals.
- Consumer electronics: Smartphones, computers, and other consumer electronics use REEs in various components, including screens, magnets, and catalysts. Yttrium, for example, is a critical component in many smartphone screens. The ubiquitous nature of these devices further underscores the importance of REEs.
- Military applications: Guided missiles, radar systems, and other military technologies depend on the unique properties of REEs for their performance. This aspect adds another layer of strategic importance to the supply chain.
Specifically:
- Neodymium is crucial for high-strength permanent magnets in wind turbine generators and electric vehicle motors.
- Dysprosium is essential for magnets in electric vehicles and wind turbines, enhancing their performance at higher temperatures.
- Yttrium is used in various applications, including phosphors in smartphone and television screens.
The crucial role of these elements in modern technology makes their scarcity a serious concern.
The Geopolitical Landscape of Rare Earth Mineral Production
China currently dominates the global rare earth minerals market, holding a significant share of both mining and processing capacity. This dominance stems from decades of investment and development in the sector. However, this concentration of power presents significant geopolitical risks.
Other countries, such as Australia, the USA, Brazil, and several countries in Africa, also produce REEs. However, their production levels are significantly lower than China's, often hampered by environmental regulations, extraction costs, or a lack of investment.
This concentrated production leads to several strategic implications:
- Trade wars and sanctions: Disputes over REE supply can quickly escalate into trade wars, affecting global supply chains and economies.
- Resource nationalism: Countries rich in REEs may prioritize domestic use, limiting exports and creating shortages elsewhere.
- Supply chain vulnerabilities: Over-reliance on a single supplier creates significant vulnerabilities for various industries.
Geopolitical risks associated with rare earth minerals include:
- Trade disputes and sanctions could severely disrupt the supply of crucial REEs.
- Concerns over resource security and national dependency are driving efforts towards diversification.
- The potential for conflict over REE-rich territories adds another layer of complexity to this issue.
The Environmental Impact of Rare Earth Mining
The extraction and processing of rare earth minerals have significant environmental consequences. Mining activities often lead to:
- Water pollution: Acid mine drainage and the release of heavy metals contaminate water sources.
- Land degradation: Mining operations can cause significant habitat destruction and soil erosion.
- Air pollution: Dust and emissions from processing plants contribute to air pollution.
These environmental impacts are often more severe than those associated with other mining activities due to the complex chemical processes involved in REE extraction and purification.
The need for sustainable mining practices and responsible sourcing is paramount. This includes:
- Implementing stricter environmental regulations and monitoring.
- Developing and implementing cleaner extraction and processing technologies.
- Promoting responsible sourcing initiatives and certifications.
Specific examples of environmental damage include the contamination of water sources in China and the land degradation in other REE-producing regions. Technological advancements such as improved tailings management and the use of more efficient separation techniques are essential for mitigating these impacts.
Addressing the Scarcity of Rare Earth Minerals: Solutions and Strategies
Addressing the scarcity of rare earth minerals requires a multifaceted approach:
- Recycling and urban mining: Recovering REEs from electronic waste ("e-waste") is crucial. Urban mining offers a significant opportunity to reduce reliance on primary extraction.
- Exploration and development of new REE deposits: Geological surveys and the development of innovative mining techniques are necessary to secure new sources.
- Technological advancements: Finding substitutes for REEs in some applications and improving efficiency in REE utilization can reduce demand.
- International cooperation and policy: Collaborative efforts to secure sustainable REE supplies and promote responsible mining are vital.
Specific solutions include:
- Successful recycling programs in countries like Japan demonstrate the potential of recovering valuable REEs.
- Technological innovations such as improved hydrometallurgical processes are being explored to reduce environmental impact and improve extraction efficiency.
- International agreements on responsible sourcing and supply chain transparency are crucial for long-term sustainability.
Conclusion:
The scarcity of rare earth minerals poses a significant challenge to the global economy and geopolitical stability. China's dominance in the market creates vulnerabilities and risks, highlighting the urgent need for diversified sourcing, sustainable mining practices, and technological innovation. Addressing the scarcity of rare earth minerals requires a multifaceted approach involving international cooperation, technological advancements, and a commitment to responsible resource management. We must act decisively to mitigate the risks and secure a future where the demand for these critical resources is met sustainably. Further research into alternative materials and advancements in rare earth mineral recycling is crucial to alleviate the growing scarcity of rare earth minerals.

Featured Posts
-
 How To Get All Fortnite Tmnt Skins The Ultimate Guide
May 17, 2025
How To Get All Fortnite Tmnt Skins The Ultimate Guide
May 17, 2025 -
 Emirates Id Card New Fees For Newborn Babies In Uae March 2025 Update
May 17, 2025
Emirates Id Card New Fees For Newborn Babies In Uae March 2025 Update
May 17, 2025 -
 Should Jalen Brunson End His Podcast Perkins Weighs In
May 17, 2025
Should Jalen Brunson End His Podcast Perkins Weighs In
May 17, 2025 -
 Stem Scholarships Supporting Local Student Achievement
May 17, 2025
Stem Scholarships Supporting Local Student Achievement
May 17, 2025 -
 Ubers Double Digit April Jump Key Factors And Analysis
May 17, 2025
Ubers Double Digit April Jump Key Factors And Analysis
May 17, 2025
