This Is The Income Needed To Be Middle Class In Every US State

Table of Contents
Defining "Middle Class" in the US
Defining "middle class" in the US is surprisingly complex. There's no single, universally accepted definition. Unlike other countries with clearer socio-economic classifications, the US uses various methodologies, making comparisons challenging. Some common approaches include:
- Median household income: This represents the middle point of all household incomes, with half earning more and half earning less. Data for this is readily available from the U.S. Census Bureau.
- Percentile ranges: Defining the middle class as a specific percentile range (e.g., the 25th to 75th percentile of income earners) offers a broader perspective. This approach is frequently used by organizations like the Pew Research Center.
- Income brackets: Defining specific income brackets as representative of the middle class. However, these brackets are often arbitrary and need to be adjusted for inflation and cost of living.
The limitations of using income alone are significant. Other factors such as wealth (assets minus liabilities), education levels, occupation, and access to healthcare profoundly impact an individual's socio-economic standing. Simply focusing on income provides only a partial picture.
- Pew Research Center: Uses a multifaceted approach including income, education, and occupation.
- U.S. Census Bureau: Primarily relies on household income data to track poverty and income distribution.
Cost of Living Variations Across US States
The cost of living significantly impacts the income needed to maintain a middle-class lifestyle. A family earning $70,000 annually in Mississippi might live comfortably, while a similar family in California might struggle to make ends meet. Key cost-of-living factors include:
- Housing: This is often the largest expense for middle-class families, varying wildly across states.
- Transportation: Gas prices, public transportation costs, and car insurance all play a role.
- Healthcare: The cost of health insurance and medical care can be crippling, particularly without employer-sponsored coverage.
- Taxes: State and local taxes, including property taxes and sales taxes, vary considerably.
High cost of living states: California, New York, Hawaii, Massachusetts, and Washington often top the list, primarily due to high housing costs.
Low cost of living states: Mississippi, Arkansas, West Virginia, Oklahoma, and Alabama consistently rank lower due to lower housing, transportation, and healthcare costs.
Housing Costs and Middle Class Income
Housing costs disproportionately affect the middle class. In states like California, where home prices are astronomically high, a significant portion of middle-class income goes towards housing, leaving less for other necessities. Conversely, in states with lower housing costs, a larger percentage of income is available for other expenses, improving the quality of life. For example, a mortgage in San Francisco could easily consume 50% of a middle-class family's income, while the same income in a smaller city in the Midwest might cover housing and leave a substantial surplus.
Healthcare Costs and Middle Class Income
Healthcare expenses place an enormous burden on middle-class families across the US. The lack of affordable healthcare in many states forces families to make difficult choices, often delaying necessary care or sacrificing other essential expenses. States with higher healthcare costs often correlate with higher premiums and deductibles, further impacting the disposable income of middle-class families. For example, a family in Texas might face significantly lower healthcare costs compared to a family in New York.
State-by-State Analysis of Middle Class Income
(Note: A comprehensive table or interactive map with data sourced from the U.S. Census Bureau, Bureau of Economic Analysis, and other reputable sources would be inserted here. This data is dynamic and requires up-to-date figures.)
This data would highlight significant regional disparities, showing a clear correlation between cost of living and the income required to achieve middle-class status. Potential outliers would be discussed, highlighting specific economic factors contributing to unusual income thresholds.
- High income states: States with high costs of living would naturally require significantly higher incomes to maintain a similar lifestyle to lower-cost states.
- Low income states: States with lower costs of living would have lower income thresholds, allowing for a more comfortable lifestyle on a smaller income.
The Impact of Inflation on Middle Class Income
Inflation significantly erodes the purchasing power of middle-class income. Rising prices for essential goods and services, such as food, energy, and housing, reduce the real value of income, making it harder to maintain a middle-class lifestyle. Different states are affected differently based on their economic structures and local market conditions.
- Statistics on inflation rates: Data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics would illustrate the varying impact of inflation across states.
- Impact on middle-class families: The impact would be illustrated by showing how inflation affects spending power on essential items.
Future Outlook for Middle Class Income in the US
The future of middle-class income in the US is uncertain, influenced by several factors:
-
Automation and technological advancements: These advancements could lead to job displacement in some sectors while creating new opportunities in others.
-
Economic growth: Strong economic growth can boost income levels, while stagnation or recession can hinder progress.
-
Policy implications: Government policies on taxation, social safety nets, and minimum wage can significantly impact the well-being of middle-class families.
-
Predictions and potential scenarios: A discussion of potential future economic scenarios, considering optimistic and pessimistic forecasts.
This Is The Income Needed To Be Middle Class In Every US State – A Summary
This analysis has demonstrated the significant variations in the income needed to be considered middle class across the 50 US states. Factors such as cost of living, particularly housing and healthcare costs, play a crucial role in determining this threshold. The impact of inflation further complicates the picture, reducing the purchasing power of middle-class income. Understanding these complexities is crucial for effective financial planning and navigating the challenges and opportunities facing the middle class in the US. Use this guide to understand your state's middle-class income threshold and plan your finances accordingly. Learn how to navigate the complexities of middle-class living in your state using the information provided in this analysis of income needed to be middle class.

Featured Posts
-
 Understanding Beyonce And Jay Zs Approach To Sir Carters Privacy
Apr 30, 2025
Understanding Beyonce And Jay Zs Approach To Sir Carters Privacy
Apr 30, 2025 -
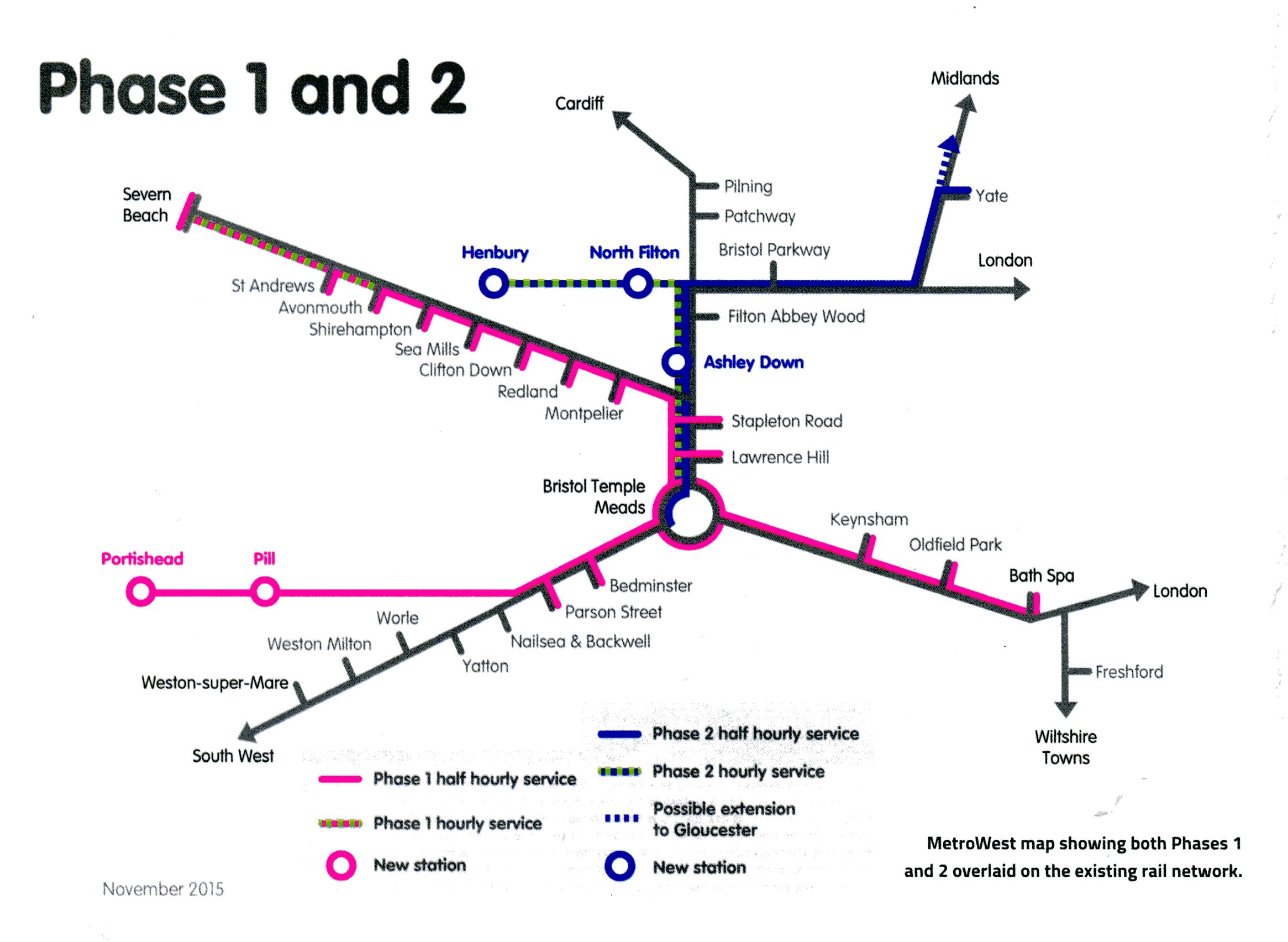 Yate To Bristol And Gloucester Train Services A Comprehensive Guide
Apr 30, 2025
Yate To Bristol And Gloucester Train Services A Comprehensive Guide
Apr 30, 2025 -
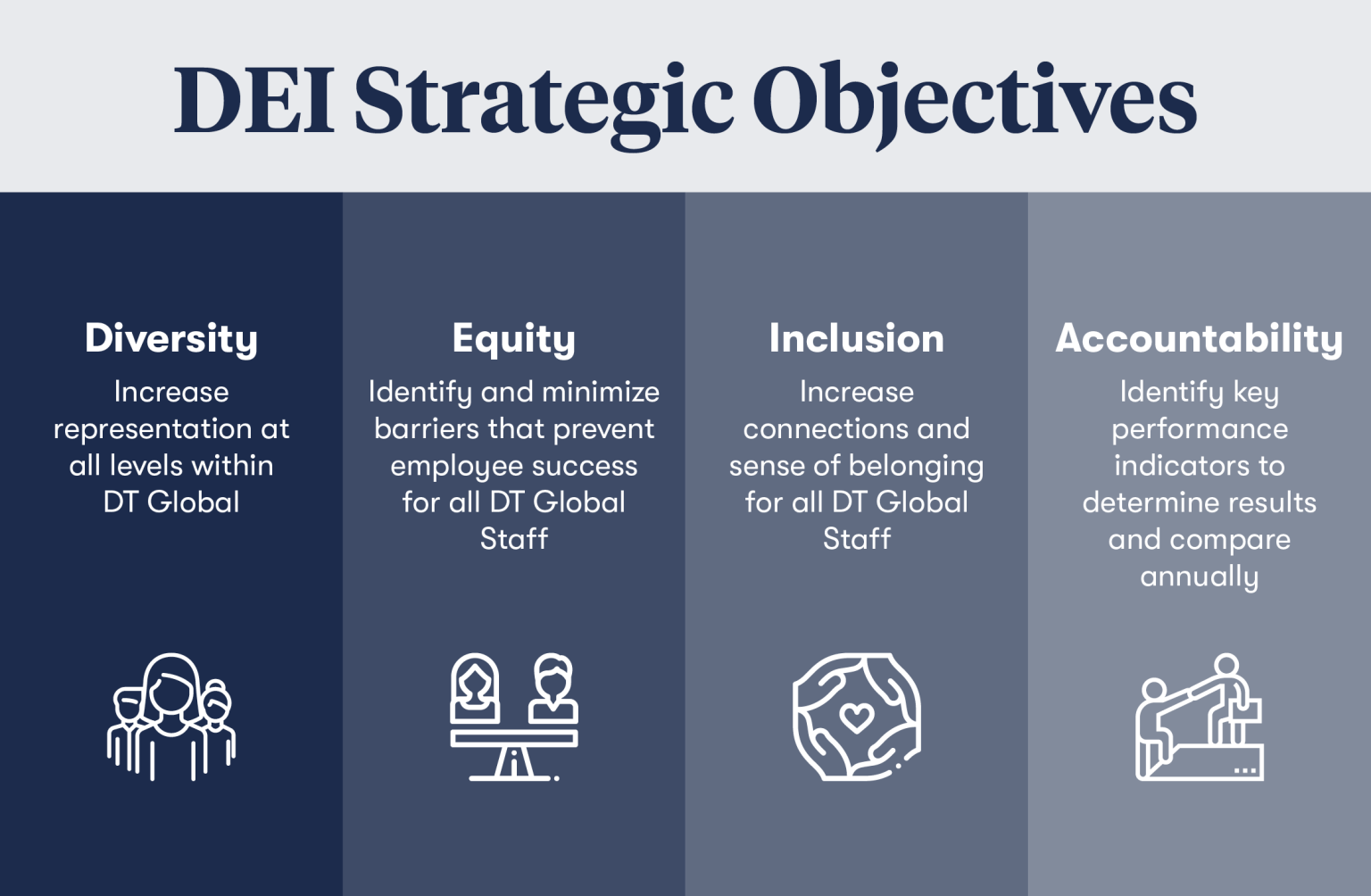 A Critical Look At Targets Evolving Dei Commitment
Apr 30, 2025
A Critical Look At Targets Evolving Dei Commitment
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Open Ai And Chat Gpt The Ftcs Investigation And Its Potential Impact
Apr 30, 2025
Open Ai And Chat Gpt The Ftcs Investigation And Its Potential Impact
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Istoriya Vorombe Issledovanie Samykh Krupnykh Ptits
Apr 30, 2025
Istoriya Vorombe Issledovanie Samykh Krupnykh Ptits
Apr 30, 2025
