Toxic Chemical Residue From Ohio Train Derailment: Extended Building Contamination
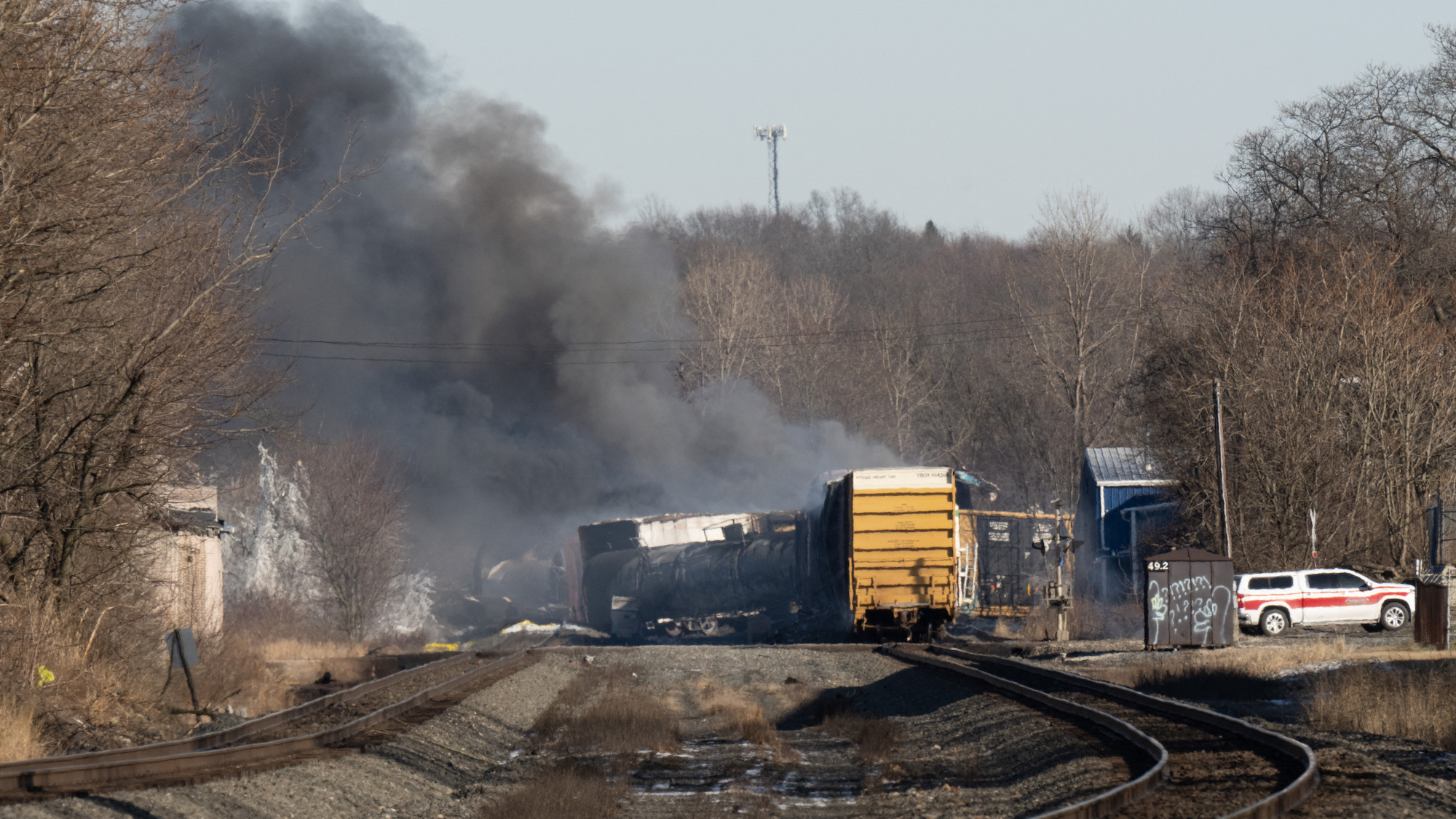

Table of Contents
Types of Toxic Chemicals and Their Impact on Buildings
The derailment released a cocktail of hazardous substances, most notably vinyl chloride, butyl acrylate, and ethylene glycol monobutyl ether. Understanding the properties of these chemicals is crucial to assessing their impact on buildings.
-
Vinyl Chloride: A known carcinogen, vinyl chloride is a colorless gas that can easily penetrate porous building materials like drywall and wood. Long-term exposure can lead to liver damage, angiosarcoma (a rare and aggressive cancer), and other serious health problems.
-
Butyl Acrylate: This colorless liquid with a characteristic pungent odor can also penetrate building materials. Exposure can cause respiratory irritation, skin and eye irritation, and potentially more severe health issues with prolonged contact.
-
Ethylene Glycol Monobutyl Ether: This solvent can leach into groundwater, potentially contaminating building foundations and causing structural damage over time. It's also a known irritant to the skin, eyes, and respiratory system.
These chemicals can:
- Penetrate porous surfaces like drywall, wood, and insulation, leading to persistent contamination.
- Cause long-term degradation of building materials, weakening structures and potentially leading to costly repairs or replacements.
- Leach into groundwater, compromising building foundations and the surrounding environment.
Assessing and Mitigating Building Contamination
Determining the extent of building contamination requires professional environmental testing. This involves a multi-pronged approach:
- Air Quality Testing: Measures the concentration of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) like vinyl chloride and butyl acrylate in the air.
- Water Testing: Analyzes water sources for the presence of contaminants that may have leached from the soil or building materials.
- Soil Testing: Assesses the level of contamination in the surrounding soil, providing a crucial understanding of the potential for further migration of toxins into buildings.
Remediation techniques vary depending on the severity and type of contamination, but may include:
- Removal of Contaminated Materials: This involves the careful extraction and disposal of affected building materials like drywall, insulation, or flooring.
- Specialized Cleaning: Employing specialized cleaning techniques and products to decontaminate surfaces and remove chemical residues.
Safety protocols are paramount during the remediation process. This includes:
- Proper Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Workers must use respirators, protective clothing, and other PPE to minimize their exposure to hazardous chemicals.
- Air Monitoring and Ventilation: Maintaining adequate ventilation and continuous air monitoring to ensure worker safety.
- Waste Disposal: Proper disposal of contaminated materials according to environmental regulations.
Long-term monitoring after remediation is essential to ensure the effectiveness of cleanup efforts and to detect any potential resurgence of contamination.
The Role of Building Materials in Chemical Absorption
Different building materials exhibit varying degrees of porosity and permeability, influencing their ability to absorb and retain chemicals.
- Porous Materials: Materials like wood, drywall, and some types of insulation readily absorb liquids and gases, making them highly susceptible to contamination.
- Non-Porous Materials: Materials like concrete and brick are less porous and therefore less likely to absorb chemicals, though they can still be affected by surface contamination.
Understanding absorption rates is crucial for determining the extent of contamination and developing appropriate remediation strategies. Building material testing, including analysis of samples for chemical residue, helps ascertain the level of penetration and informs the best course of action.
Long-Term Health Effects and Concerns
Exposure to the chemicals released in the Ohio train derailment poses significant long-term health risks.
- Vinyl Chloride Exposure: Can lead to liver damage, angiosarcoma, and other cancers.
- Butyl Acrylate Health Effects: Can cause respiratory problems, skin and eye irritation, and other health issues.
Early detection and intervention are crucial for managing health problems associated with chemical exposure. Ongoing medical monitoring is recommended for residents and workers in affected areas.
Legal and Regulatory Implications
The Ohio train derailment raises significant legal and regulatory questions:
- Liability: Determining the liability of the railroad company, contractors, and government agencies involved.
- Compensation Claims: Affected residents have the right to seek compensation for property damage, health problems, and other losses.
- Environmental Regulations: Compliance with environmental regulations, including those set by the EPA, is crucial for cleanup efforts and preventing future contamination.
Understanding your legal rights and responsibilities is essential in navigating the aftermath of this environmental disaster.
Conclusion
The Ohio train derailment's aftermath presents a significant and long-lasting challenge in the form of extended building contamination. Addressing the issue of toxic chemical residue requires comprehensive environmental testing, effective remediation strategies, and ongoing monitoring to protect public health and ensure the safety of building occupants. Ignoring the threat of lingering toxic chemical residue can lead to serious health problems and long-term financial burdens. Don't wait for the problem to worsen; take action today by contacting environmental specialists to assess your building for Ohio train derailment contamination. Proactive steps in addressing building contamination are crucial to mitigating the risks associated with this environmental disaster.

Featured Posts
-
 Le Depute Jacobelli Se Felicite De La Decision De Justice Concernant Le Rn En 2026
May 30, 2025
Le Depute Jacobelli Se Felicite De La Decision De Justice Concernant Le Rn En 2026
May 30, 2025 -
 The Killer Seaweed Threatening Australias Marine Life
May 30, 2025
The Killer Seaweed Threatening Australias Marine Life
May 30, 2025 -
 Caida De Ticketmaster Hoy 8 De Abril Ultimas Noticias De Grupo Milenio
May 30, 2025
Caida De Ticketmaster Hoy 8 De Abril Ultimas Noticias De Grupo Milenio
May 30, 2025 -
 Taylor Swift Ticketmaster Update Your Spot In Line
May 30, 2025
Taylor Swift Ticketmaster Update Your Spot In Line
May 30, 2025 -
 Understanding The Absence Of Excessive Heat Warnings In Weather Reports
May 30, 2025
Understanding The Absence Of Excessive Heat Warnings In Weather Reports
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Global Covid 19 Update Who Reports On Emerging Variant
May 31, 2025
Global Covid 19 Update Who Reports On Emerging Variant
May 31, 2025 -
 Indian Wells 2024 Swiatek Advances To Quarterfinals
May 31, 2025
Indian Wells 2024 Swiatek Advances To Quarterfinals
May 31, 2025 -
 Recent Rise In Covid 19 Cases Possibly Linked To New Variant According To Who
May 31, 2025
Recent Rise In Covid 19 Cases Possibly Linked To New Variant According To Who
May 31, 2025 -
 New Covid 19 Variant Who Links Rise In Cases To Emerging Strain
May 31, 2025
New Covid 19 Variant Who Links Rise In Cases To Emerging Strain
May 31, 2025 -
 Stefanos Tsitsipas And Goran Ivanisevic A New Coaching Partnership
May 31, 2025
Stefanos Tsitsipas And Goran Ivanisevic A New Coaching Partnership
May 31, 2025
