Toxic Chemicals From Ohio Derailment: Months-Long Building Contamination
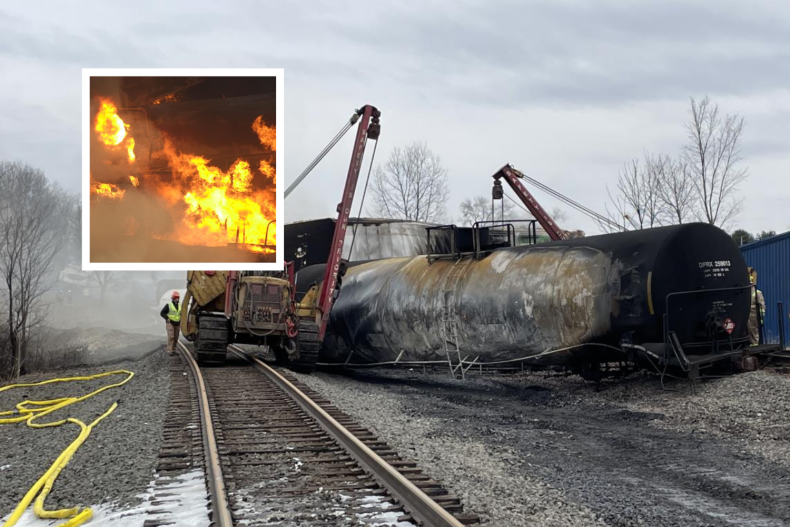

Table of Contents
The Scope of the Contamination: Beyond Immediate Impact
The immediate aftermath of the derailment focused on the immediate dangers of airborne toxins and water contamination. However, the less visible threat of building contamination remains a significant concern. Various toxic chemicals, including vinyl chloride, butyl acrylate, and ethylene glycol monobutyl ether, were released, and their residues may persist in building materials for a considerable time.
Persistent Chemical Residues
These chemicals can penetrate and adhere to building materials such as wood, drywall, and insulation. Their persistence depends on several factors:
- Chemical properties: Vinyl chloride, for example, is volatile and can evaporate relatively quickly, but it can also seep into porous materials. Butyl acrylate and ethylene glycol monobutyl ether have different properties, affecting their persistence and potential for long-term contamination. Specific studies on the half-life of these chemicals in various building materials are needed for a comprehensive understanding.
- Material porosity: Porous materials like wood and insulation absorb chemicals more readily than non-porous materials like glass or metal, making detection and remediation more challenging. The degree of porosity significantly impacts the extent and duration of building contamination.
- Detection difficulties: Identifying low levels of these chemicals in building materials requires sophisticated laboratory analysis. The complex chemical composition of building materials can complicate detection efforts, requiring specialized techniques and experienced professionals.
Contamination Pathways
The entry of toxic chemicals into buildings can occur through various pathways:
- Air infiltration: Airborne chemicals can penetrate building envelopes, especially in older structures with less-efficient sealing. Ventilation systems can inadvertently circulate contaminated air, increasing the risk of Ohio derailment toxic chemical building contamination.
- Water ingress: Contaminated groundwater can seep into basements and crawl spaces, leading to water contamination and subsequent building contamination. Rainwater runoff can also carry chemicals into buildings, especially if the chemicals have leached into the soil.
- Direct contact: Soil contaminated with chemicals can be tracked into buildings on shoes, clothing, and equipment. This is particularly relevant for residential buildings in close proximity to the derailment site. The type of building construction (e.g., presence of basements, crawl spaces) can affect vulnerability.
Health Risks Associated with Long-Term Exposure
Exposure to the toxic chemicals released in the derailment presents significant health risks, both acutely and chronically.
Acute and Chronic Effects
The health consequences of exposure to these chemicals vary depending on the chemical, the level of exposure, and the duration of exposure.
- Vinyl chloride: Acute exposure can cause dizziness, headaches, and nausea. Chronic exposure is linked to liver cancer and other serious health problems. [Link to CDC resource on vinyl chloride]
- Butyl acrylate: Can cause eye, skin, and respiratory irritation. Long-term effects are less well-understood but may include respiratory problems. [Link to relevant EPA resource]
- Ethylene glycol monobutyl ether: Can affect the nervous system, causing headaches, dizziness, and fatigue. Long-term exposure might lead to kidney and liver damage. [Link to authoritative source]
These are just a few examples; a comprehensive assessment of health risks requires ongoing monitoring and research.
Vulnerable Populations
Certain populations are more vulnerable to the health risks associated with this building contamination:
- Children: Children are particularly susceptible due to their developing organ systems and higher respiratory rates.
- Elderly individuals: The elderly often have pre-existing health conditions that make them more vulnerable to the effects of toxic chemical exposure.
- Individuals with pre-existing respiratory or cardiovascular conditions: Exposure to these chemicals can exacerbate existing respiratory or cardiovascular issues, leading to serious health complications.
The long-term health impacts on these groups require specialized monitoring and support.
Challenges in Detection and Remediation of Building Contamination
Addressing the problem of building contamination from the Ohio derailment poses significant challenges.
Testing and Monitoring Difficulties
Detecting low levels of these chemicals in various building materials is technically complex and expensive.
- Limitations of current testing methods: Current testing methods may not be sensitive enough to detect low levels of contamination in all types of building materials.
- Comprehensive testing is crucial: A thorough assessment requires comprehensive testing of various building materials to accurately determine the extent of contamination. This involves specialized sampling and laboratory analysis, which is time-consuming and costly.
- Cost and time involved: The cost of comprehensive testing can be prohibitive, particularly for homeowners. The time needed for results also impacts the speed of remediation efforts.
Remediation Strategies and Costs
Decontamination of buildings requires various remediation strategies:
- Air scrubbing: Specialized air filtration systems can remove airborne chemicals from the indoor environment.
- Surface cleaning: Surface cleaning can remove some chemical residues from building materials, but it is not always effective in removing contamination from porous materials.
- Material replacement: In severe cases, contaminated materials may need to be completely replaced. This is the most expensive and disruptive remediation approach.
The financial burden of remediation falls on homeowners, insurance companies, and potentially the government, adding another layer of complexity to this ongoing crisis.
Conclusion
The Ohio train derailment's impact extends far beyond the immediate aftermath. The lingering threat of building contamination from toxic chemicals poses a significant and long-term public health challenge, demanding comprehensive testing, effective remediation strategies, and ongoing monitoring. The long-term consequences of this environmental disaster are still unfolding, and proactive measures are crucial to mitigate the potential health risks associated with Ohio derailment toxic chemical building contamination.
Call to Action: Demand accountability and transparency regarding the ongoing investigation and remediation efforts related to the Ohio derailment toxic chemical building contamination. Stay informed about the latest updates, support affected communities, and advocate for stricter safety regulations to prevent future disasters. Learn more about the long-term health risks associated with toxic chemical exposure and how to protect yourself and your family.

Featured Posts
-
 Play Station Beta Program Sonys Latest Announcement Explained
May 02, 2025
Play Station Beta Program Sonys Latest Announcement Explained
May 02, 2025 -
 Lotto Draw Results Wednesday 30 April 2025
May 02, 2025
Lotto Draw Results Wednesday 30 April 2025
May 02, 2025 -
 6 Key Factors Determining The Success Of A Harry Potter Remake
May 02, 2025
6 Key Factors Determining The Success Of A Harry Potter Remake
May 02, 2025 -
 Tbs Safety And Nebofleet Partnership Automates Workboat Safety
May 02, 2025
Tbs Safety And Nebofleet Partnership Automates Workboat Safety
May 02, 2025 -
 Is This Xrps Big Moment Etf Approvals Sec Developments And Market Impact
May 02, 2025
Is This Xrps Big Moment Etf Approvals Sec Developments And Market Impact
May 02, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 The 10 Best Film Noir Movies Ever Made
May 10, 2025
The 10 Best Film Noir Movies Ever Made
May 10, 2025 -
 The Kreischers Marriage And The Netflix Stand Up Routine
May 10, 2025
The Kreischers Marriage And The Netflix Stand Up Routine
May 10, 2025 -
 Top 10 Must See Film Noir Movies
May 10, 2025
Top 10 Must See Film Noir Movies
May 10, 2025 -
 Bert Kreischers Netflix Specials A Look At His Wifes Perspective On His Jokes
May 10, 2025
Bert Kreischers Netflix Specials A Look At His Wifes Perspective On His Jokes
May 10, 2025 -
 10 Essential Film Noir Movies To Watch
May 10, 2025
10 Essential Film Noir Movies To Watch
May 10, 2025
