Uncertainty In The Economy: Inflation And Unemployment On The Rise
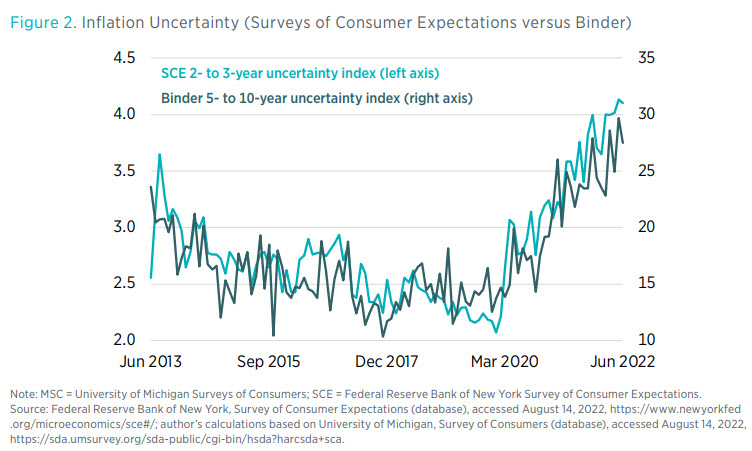
Table of Contents
The Inflationary Spiral: Understanding Rising Prices
The current inflationary pressures are squeezing household budgets and impacting global economic stability. This section will explore the causes, consequences, and potential government responses to this pervasive issue.
Causes of Inflation
Several factors contribute to the current inflationary surge. Supply chain disruptions caused by geopolitical events and the lingering effects of the pandemic have constrained the availability of goods, driving prices upward. Increased energy costs, fueled by global demand and geopolitical instability, significantly impact production and transportation costs, further exacerbating inflation. Simultaneously, increased consumer demand, coupled with robust government spending in some regions, has outpaced supply, creating upward pressure on prices.
- Rising Food Prices: Food costs have soared globally, impacting low-income households disproportionately.
- Energy Price Increases: The cost of gasoline, electricity, and heating fuels has skyrocketed, increasing the cost of living and impacting businesses.
- Housing Costs Surge: Rental and home prices have climbed sharply in many areas, reducing affordability and contributing to overall inflation.
Impact of Inflation on Consumers
Inflation erodes purchasing power, meaning that consumers can buy less with the same amount of money. This significantly impacts household budgets, particularly for low- and middle-income families. The rising cost of essential goods and services forces difficult choices, potentially leading to reduced consumption and decreased investment.
- Reduced Disposable Income: Inflation leaves less money for non-essential spending, impacting economic growth.
- Increased Poverty and Inequality: Inflation disproportionately affects vulnerable populations, widening the gap between rich and poor.
- Decreased Consumer Confidence: Uncertainty about future prices discourages spending and investment.
Government Responses to Inflation
Governments worldwide are implementing various policies to combat inflation. Central banks are often employing monetary policy tools such as interest rate hikes to curb spending and cool down the economy. Fiscal policy measures, including government spending cuts or tax increases, can also play a role in managing inflation. However, these measures often have potential drawbacks, potentially slowing economic growth and impacting employment.
- Interest Rate Hikes: Increasing interest rates makes borrowing more expensive, discouraging spending and investment.
- Fiscal Austerity Measures: Reducing government spending or increasing taxes can reduce demand-pull inflation.
- Supply-Side Policies: Governments may invest in infrastructure projects or address supply chain bottlenecks to boost supply and reduce inflationary pressures.
Rising Unemployment: A Looming Threat to Economic Stability
Simultaneously, rising unemployment poses a significant threat to economic stability, compounding the challenges presented by inflation. This section will analyze the factors contributing to job losses and their impact on individuals and society.
Factors Contributing to Unemployment
Several factors contribute to the increase in unemployment rates. Automation and technological advancements displace workers in certain industries. Economic slowdowns, often linked to inflation, reduce business activity and lead to job cuts. Furthermore, shifts in the job market, requiring workers to adapt to new skills and technologies, can create temporary unemployment gaps.
- Automation and Technological Displacement: Automation is eliminating jobs in manufacturing and other sectors.
- Economic Slowdowns: Recessions and economic uncertainty often lead to widespread job losses.
- Skills Mismatch: The demand for certain skills may outpace the supply, creating unemployment.
Impact of Unemployment on Individuals and Society
Unemployment carries severe social and economic consequences. Job loss leads to financial hardship, impacting individuals' ability to meet basic needs. Increased poverty, social unrest, and strain on social services are common outcomes. Beyond the financial strain, unemployment takes a significant toll on mental health and overall well-being.
- Increased Poverty and Homelessness: Job loss often leads to financial instability and homelessness.
- Strain on Social Services: Unemployment increases demand for social welfare programs.
- Mental Health Impacts: Job loss can lead to depression, anxiety, and other mental health issues.
Government Initiatives to Combat Unemployment
Governments employ various initiatives to alleviate unemployment. Job training programs help workers acquire in-demand skills, increasing their employability. Unemployment benefits provide financial support to those who have lost their jobs, helping them navigate challenging times. However, these initiatives often have limitations, and their effectiveness varies depending on the specific economic context.
- Job Training and Retraining Programs: Investing in education and training equips workers with relevant skills.
- Unemployment Insurance: Provides temporary financial support to unemployed individuals.
- Public Works Programs: Government-funded infrastructure projects create jobs.
The Interplay Between Inflation and Unemployment: The Phillips Curve
The Phillips curve illustrates the inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment. Traditionally, lower unemployment is associated with higher inflation, and vice versa. However, the relationship is not always straightforward, and the current economic climate presents a complex picture, with both inflation and unemployment rising simultaneously, challenging the traditional Phillips curve relationship. Understanding this complex relationship is crucial to formulating effective economic policies. Visual representations such as graphs and charts are crucial to illustrate this interplay.
Navigating Economic Uncertainty: Strategies for Individuals and Businesses
Economic uncertainty requires proactive strategies for both individuals and businesses to mitigate its impact.
Strategies for Individuals
Individuals can adopt several strategies to manage their finances during times of economic uncertainty. Creating and sticking to a detailed budget is essential to track expenses and identify areas for potential savings. Building an emergency fund provides a financial cushion to weather unexpected job losses or economic shocks. Diversifying investments helps to reduce risk and protect assets during volatile economic periods.
- Budgeting and Expense Reduction: Track expenses, identify areas for savings, and prioritize essential spending.
- Emergency Fund Creation: Build a savings account to cover 3-6 months of living expenses.
- Investment Diversification: Spread investments across different asset classes to reduce risk.
Strategies for Businesses
Businesses must also adapt to navigate economic uncertainty. Implementing cost-cutting measures, such as streamlining operations and negotiating with suppliers, can improve profitability. Diversifying products or services reduces dependence on single markets and mitigates economic shocks. Investing in innovation and technology helps businesses remain competitive and adapt to changing market conditions.
- Cost-Cutting Measures: Streamline operations, negotiate with suppliers, and reduce non-essential expenses.
- Product/Service Diversification: Expand offerings to reduce reliance on single markets.
- Innovation and Technological Advancement: Invest in new technologies to improve efficiency and competitiveness.
Conclusion
The current economic climate, characterized by rising inflation and unemployment, presents significant challenges. The interconnected nature of these two forces creates substantial economic uncertainty, impacting individuals, businesses, and governments. Understanding the causes, consequences, and potential solutions is critical to effectively navigating this complex economic landscape. Proactive strategies, both at the individual and business levels, are essential to mitigate the effects of this economic uncertainty. Staying informed about economic trends and adopting sound financial practices are vital for long-term success. To further enhance your understanding and preparedness, explore reputable resources on personal finance management, business strategy, and macroeconomic trends. Understanding and proactively managing economic uncertainty is key to securing your financial future.

Featured Posts
-
 Apple Reportedly Plans To Rename Its Entire Os Lineup
May 30, 2025
Apple Reportedly Plans To Rename Its Entire Os Lineup
May 30, 2025 -
 Air Jordan Drop List All June 2025 Releases
May 30, 2025
Air Jordan Drop List All June 2025 Releases
May 30, 2025 -
 Bts Disbandment Rumors And Jungkooks Activities What We Know Before 2025
May 30, 2025
Bts Disbandment Rumors And Jungkooks Activities What We Know Before 2025
May 30, 2025 -
 Rainfall In March Insufficient To Overcome Water Deficit
May 30, 2025
Rainfall In March Insufficient To Overcome Water Deficit
May 30, 2025 -
 Mongoliya Massovaya Vaktsinatsiya V Otvet Na Epidemiyu Kori
May 30, 2025
Mongoliya Massovaya Vaktsinatsiya V Otvet Na Epidemiyu Kori
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 World Health Organization New Covid 19 Variant May Be Responsible For Rising Case Numbers
May 31, 2025
World Health Organization New Covid 19 Variant May Be Responsible For Rising Case Numbers
May 31, 2025 -
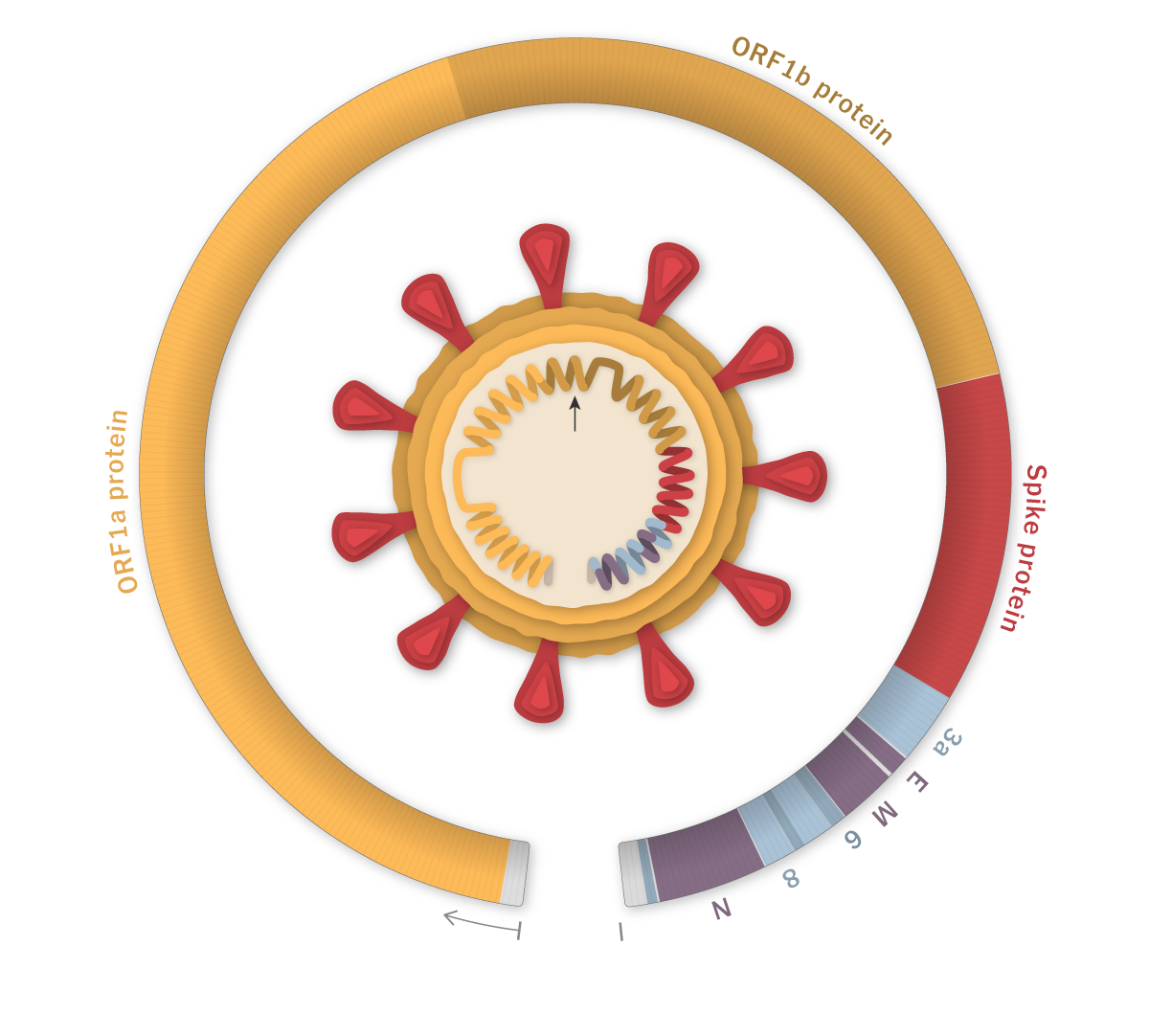 Emerging Covid 19 Variant Who Investigating Global Case Spike
May 31, 2025
Emerging Covid 19 Variant Who Investigating Global Case Spike
May 31, 2025 -
 Is A New Covid 19 Variant Behind The Recent Case Spike Who Investigation
May 31, 2025
Is A New Covid 19 Variant Behind The Recent Case Spike Who Investigation
May 31, 2025 -
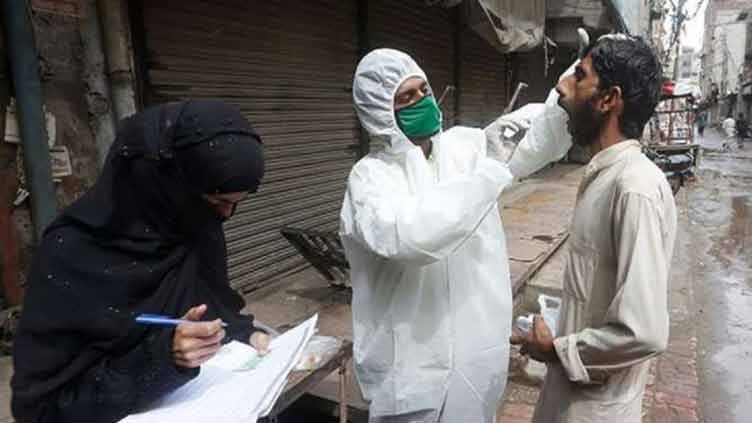 Who Reports Potential New Covid 19 Variant Linked To Rising Case Numbers
May 31, 2025
Who Reports Potential New Covid 19 Variant Linked To Rising Case Numbers
May 31, 2025 -
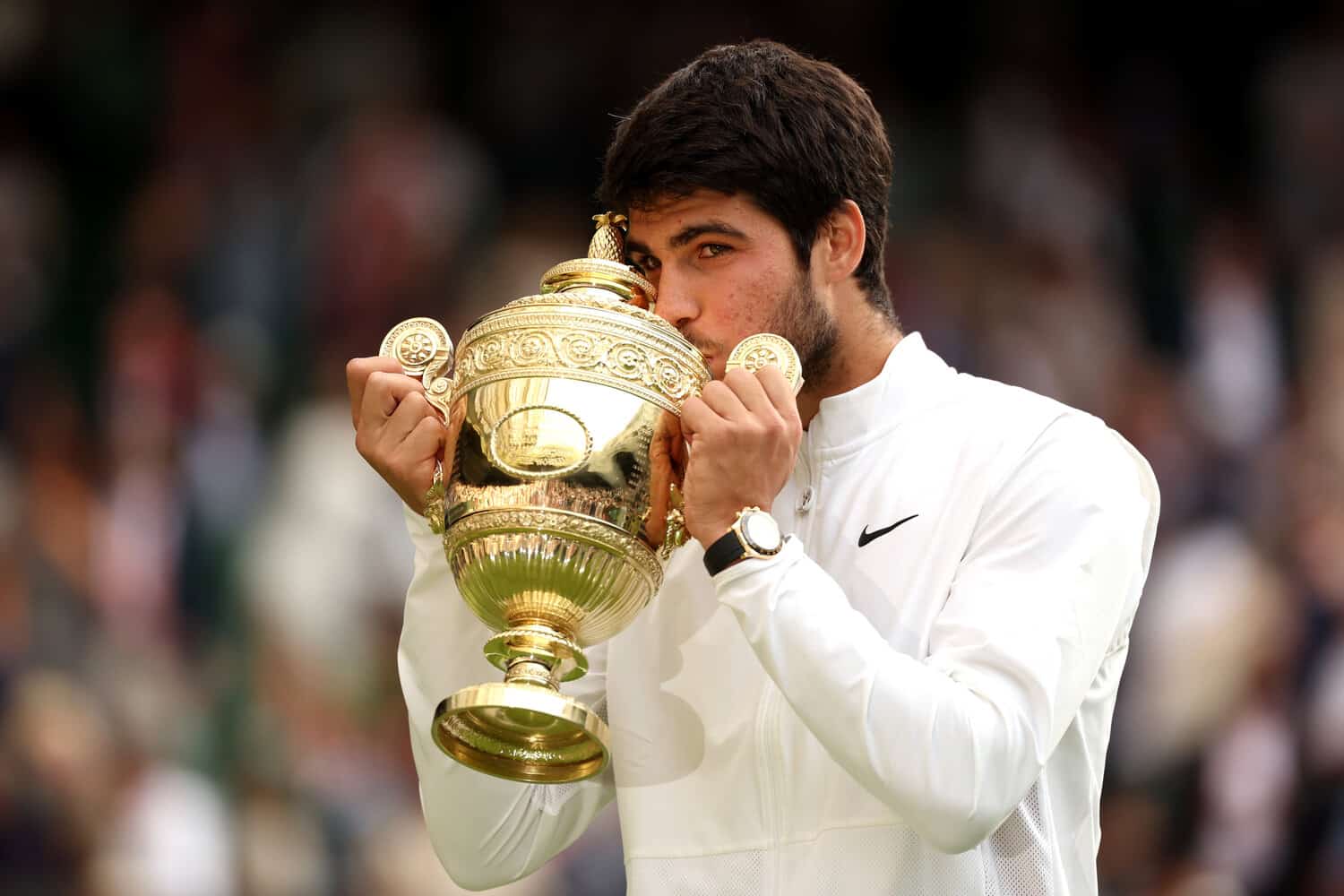 Rome Masters 2024 Alcaraz And Passaros Impact On The Italian International Tournament
May 31, 2025
Rome Masters 2024 Alcaraz And Passaros Impact On The Italian International Tournament
May 31, 2025
