Understanding Stock Market Valuations: BofA's Take
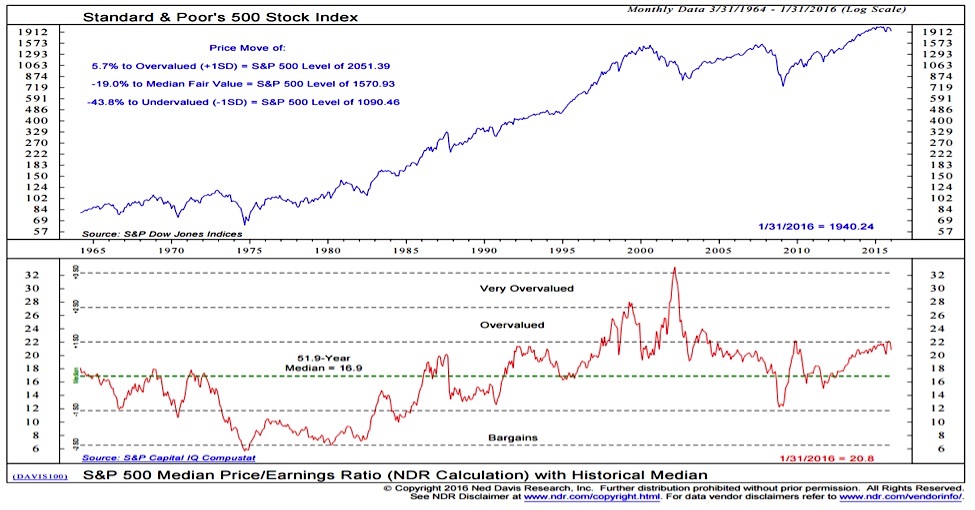
Table of Contents
Key Valuation Metrics: What BofA Analyzes
Understanding stock market valuations requires familiarity with various metrics. These metrics offer different perspectives on a company's intrinsic value, providing a more comprehensive picture than any single indicator. BofA, with its extensive research capabilities, utilizes a blend of these metrics to form its investment recommendations. Let's explore some key ones:
Price-to-Earnings Ratio (P/E):
The P/E ratio is arguably the most widely used valuation metric. It represents the market price per share divided by the earnings per share (EPS). A high P/E ratio suggests investors are willing to pay a premium for each dollar of earnings, often indicating high growth expectations or perceived strong future performance. Conversely, a low P/E ratio might suggest undervaluation or concerns about future earnings.
- BofA's Interpretation: BofA analysts likely consider the P/E ratio in relation to the company's industry peers and historical trends. A high P/E ratio in a rapidly growing tech company might be considered justified, whereas the same ratio in a mature utility company could signal overvaluation. For instance, BofA might highlight a tech company with a high P/E but strong revenue growth as a potential investment, while flagging a utility company with a high P/E and stagnant growth as a risk.
- Hypothetical Example: Imagine BofA reports that Company X (in the tech sector) has a P/E of 40, while its competitors average 30. BofA might justify this higher ratio by citing Company X's superior growth prospects, innovative technology, and strong market share.
- Limitations: The P/E ratio can be distorted by one-time events (like a large write-down) or accounting manipulations. It also doesn't account for a company's debt or asset base.
Price-to-Book Ratio (P/B):
The P/B ratio compares a company's market capitalization to its book value (assets minus liabilities). It's particularly useful for valuing asset-heavy companies, such as those in the financial or manufacturing sectors. A low P/B ratio might suggest undervaluation, while a high P/B ratio could indicate overvaluation.
- BofA's Usage: BofA likely incorporates the P/B ratio, especially when analyzing financial institutions. A low P/B for a bank might indicate that the market undervalues its assets, presenting a potential investment opportunity.
- Limitations: Book value doesn't always reflect a company's true market value, especially in industries with significant intangible assets (like technology).
Other Key Metrics:
BofA's comprehensive valuation analysis likely extends beyond P/E and P/B ratios. Other important metrics include:
- PEG ratio: Considers both P/E and growth rate, providing a more nuanced view of valuation.
- Dividend yield: Measures the annual dividend per share relative to the share price. Useful for income-oriented investors.
- Free cash flow analysis: Focuses on the cash generated by a company's operations, a key indicator of financial health and future investment capacity. BofA likely uses this to assess a company’s ability to sustain growth and dividend payments.
BofA's Approach to Valuation: Sector-Specific Insights
BofA's valuation approach isn't one-size-fits-all. Its analysts likely tailor their methods to each sector, recognizing the unique characteristics and drivers of value in different industries.
Technology Sector Valuation:
For technology companies, BofA's valuation likely emphasizes growth metrics such as revenue growth, user acquisition, and market share. Intangible assets, like brand reputation and intellectual property, also play a significant role. Future earnings potential, often projected through discounted cash flow models, is crucial.
Financial Sector Valuation:
In the financial sector, BofA's approach likely emphasizes tangible assets, capital adequacy ratios, and regulatory compliance. Profitability metrics, such as return on equity (ROE) and net interest margins, become critical indicators. Given BofA's presence in the sector, their expertise here is particularly insightful.
Other Sectors:
BofA's approach will vary depending on the industry. For example, in the consumer staples sector, valuation may focus heavily on factors such as brand strength, market share, and stable earnings, while in the energy sector, factors such as reserve life, production costs, and commodity prices play a key role.
Interpreting BofA's Valuation Signals: Identifying Opportunities and Risks
Understanding how to interpret BofA's analysis is key to utilizing their insights.
Undervalued Stocks:
Stocks identified by BofA as having significantly lower valuations than their intrinsic value, based on multiple valuation metrics and sector-specific analysis, represent potential opportunities. Looking for consistency across different metrics is crucial before making investment decisions.
Overvalued Stocks:
BofA's analysis may highlight stocks trading at premiums compared to their perceived intrinsic value. These stocks carry higher risk and investors should exercise caution. BofA's warnings on overvalued stocks shouldn't be ignored; they could indicate potential for future price corrections.
Considering Macroeconomic Factors:
It's crucial to remember that even the most detailed valuation analysis must consider broader macroeconomic factors. Interest rate changes, inflation, and geopolitical events can significantly influence stock prices regardless of a company's intrinsic value. BofA's analysis likely incorporates these broader economic trends.
Conclusion: Mastering Stock Market Valuations with BofA's Guidance
Understanding stock market valuations is essential for informed investment decisions. By utilizing key metrics like P/E and P/B ratios, and incorporating sector-specific insights from experts like BofA, investors can enhance their decision-making process. BofA's approach, which considers a variety of factors across different sectors, offers a valuable perspective. To further refine your understanding of stock market valuations, explore BofA's research reports and publications available on their website. Mastering stock market valuations takes time and effort, but with diligent research and the guidance of experts like BofA, you can significantly improve your investment strategy.

Featured Posts
-
 Hotgirl Cau Long Va Tham Vong Chinh Phuc Top 20 The Gioi Tai Dong Nam A
May 31, 2025
Hotgirl Cau Long Va Tham Vong Chinh Phuc Top 20 The Gioi Tai Dong Nam A
May 31, 2025 -
 Isabelle Autissier Ce Qui M Interesse C Est De Faire Avec Les Autres Analyse D Une Philosophie
May 31, 2025
Isabelle Autissier Ce Qui M Interesse C Est De Faire Avec Les Autres Analyse D Une Philosophie
May 31, 2025 -
 Is This The Good Life Evaluating Your Current Path And Making Changes
May 31, 2025
Is This The Good Life Evaluating Your Current Path And Making Changes
May 31, 2025 -
 Bernard Kerik Ex Nypd Commissioner Passes Away At Age 69
May 31, 2025
Bernard Kerik Ex Nypd Commissioner Passes Away At Age 69
May 31, 2025 -
 Today In History March 26 The Impact Of Princes Death
May 31, 2025
Today In History March 26 The Impact Of Princes Death
May 31, 2025
