Understanding The Risks: Japan's Steep Bond Curve And Its Economic Impact
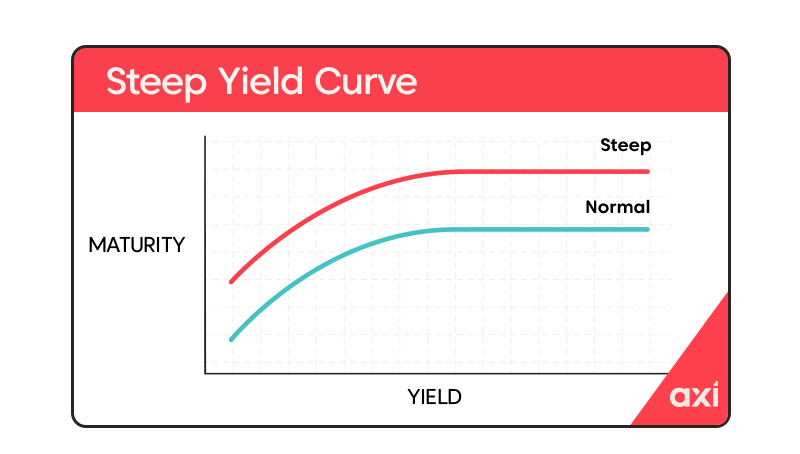
Table of Contents
Causes of Japan's Steepening Bond Curve
Several interconnected factors contribute to the steepening of Japan's bond curve. Understanding these root causes is crucial for assessing the overall economic risk.
Inflationary Pressures
Rising inflation is a primary driver of the steepening yield curve. Inflation erodes the purchasing power of future interest payments on long-term government bonds (JGBs), leading investors to demand higher yields as compensation for this risk. The Bank of Japan's (BOJ) recent shift towards a more flexible yield curve control (YCC) policy, while intended to address deflationary pressures, has inadvertently contributed to increased volatility and a steeper curve. Global inflationary pressures, fueled by factors like increased energy costs and supply chain disruptions, further exacerbate this effect.
- Increased energy costs: The global surge in energy prices significantly impacts inflation in Japan, impacting consumer prices and investor expectations.
- Supply chain disruptions: Ongoing supply chain bottlenecks lead to higher production costs and increased prices for consumer goods.
- Rising import prices: A weaker Yen, combined with global inflation, increases the cost of imported goods, fueling domestic inflationary pressures.
Shifting Investor Sentiment
Uncertainty surrounding the BOJ's future monetary policy actions plays a key role. Investors are carefully watching for signs of further adjustments to YCC, impacting their demand for JGBs. Concerns about Japan's high levels of public debt and the long-term fiscal sustainability of the country also weigh heavily on investor sentiment. A global economic slowdown further reduces investor appetite for Japanese government bonds, leading to increased yield spreads.
- Uncertainty surrounding BOJ policy: The ambiguity around future monetary policy changes creates volatility in the bond market.
- Concerns about Japan's debt levels: Japan's substantial public debt raises concerns about its long-term fiscal stability.
- Global risk aversion: Global economic uncertainties drive investors towards safer assets, potentially reducing demand for JGBs.
Government Borrowing
Japan's high public debt necessitates frequent issuance of government bonds. This increased supply of long-term JGBs can put downward pressure on prices and upward pressure on yields, contributing to a steeper yield curve. The aging population and rising social security costs, coupled with ongoing infrastructure spending, further fuel the need for government borrowing.
- Aging population: Japan's rapidly aging population increases the burden on social security and healthcare systems.
- Social security costs: The increasing cost of providing social security benefits contributes to government spending.
- Infrastructure spending: Investments in infrastructure projects require significant government borrowing.
Economic Implications of a Steep Bond Curve
A steepening bond curve has several significant implications for the Japanese economy.
Increased Borrowing Costs
Higher bond yields translate to increased borrowing costs for corporations and the government. This can stifle economic growth by reducing investment and dampening consumer spending. Businesses may postpone expansion plans, and consumers may delay purchases due to higher interest rates on loans.
- Reduced capital expenditures: Higher borrowing costs discourage companies from investing in new equipment and technologies.
- Delayed expansion plans: Businesses may postpone or cancel expansion projects due to higher financing costs.
- Higher interest payments on debt: Existing debt becomes more expensive to service, reducing profitability for businesses.
Currency Fluctuations
The steep bond curve can influence the value of the Japanese Yen. Higher bond yields can attract foreign capital inflows, potentially strengthening the Yen. Conversely, concerns about Japan's economic outlook stemming from the steepening yield curve could lead to capital outflows and a weakening Yen. This creates significant uncertainty in the foreign exchange market.
- Capital flows: Changes in bond yields influence the flow of capital into and out of Japan.
- Investor confidence: Negative sentiment towards Japan's economy can lead to capital flight.
- Speculative trading: The volatility in the bond market can attract speculative trading, further influencing the Yen's value.
Risk to Financial Stability
A sharply rising yield curve poses risks to financial stability. Investors holding long-term JGBs could face significant losses if yields rise unexpectedly. This risk extends to financial institutions with substantial JGB holdings, potentially creating systemic risks and contagion effects within the financial system.
- Pension funds: Pension funds with large JGB holdings are particularly vulnerable to yield curve shifts.
- Insurance companies: Insurance companies also hold significant JGBs, exposing them to potential losses.
- Banking sector exposure: Japanese banks hold a substantial amount of JGBs, potentially impacting their capital adequacy.
Potential Mitigation Strategies
Addressing the challenges posed by Japan's steep bond curve requires a multi-pronged approach.
- Gradual adjustment of monetary policy: The BOJ needs to carefully manage its monetary policy to avoid abrupt shifts that could destabilize the bond market.
- Fiscal reforms: Implementing fiscal reforms to address Japan's high debt levels is crucial for long-term stability. This could involve measures such as tax reforms and spending cuts.
- Strategies for managing risks within the financial system: Strengthening the resilience of the financial system is vital to mitigate potential systemic risks.
- International collaboration: Addressing global inflationary pressures through international cooperation is necessary to stabilize global markets.
Conclusion
Japan's steep bond curve presents significant challenges and risks to the nation's economic outlook. Understanding the underlying causes – from inflationary pressures and shifting investor sentiment to the government's substantial borrowing needs – is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies. The implications, including increased borrowing costs, currency fluctuations, and potential financial instability, necessitate proactive policy responses. By closely monitoring the yield curve and implementing appropriate measures, Japan can strive to mitigate the risks and foster sustainable economic growth. Further research and analysis of Japan's steep bond curve are essential for investors, policymakers, and economists alike. Stay informed about the latest developments concerning Japan's steep bond curve and its economic impact to make informed decisions.

Featured Posts
-
 Week 26 Update 2024 25 High School Confidential
May 17, 2025
Week 26 Update 2024 25 High School Confidential
May 17, 2025 -
 Donald Trumps Scandals Did Allegations Of Sexual Misconduct Impact His Election
May 17, 2025
Donald Trumps Scandals Did Allegations Of Sexual Misconduct Impact His Election
May 17, 2025 -
 Djokovic In Kortlardaki Basarisi Rakipsiz Bir Efsane
May 17, 2025
Djokovic In Kortlardaki Basarisi Rakipsiz Bir Efsane
May 17, 2025 -
 Reddit Down Current Status And Potential Fixes
May 17, 2025
Reddit Down Current Status And Potential Fixes
May 17, 2025 -
 Kosarkaska Reprezentacija Srbije Izvestaj Sa Generalne Probe Pred Evrobasket
May 17, 2025
Kosarkaska Reprezentacija Srbije Izvestaj Sa Generalne Probe Pred Evrobasket
May 17, 2025
