When The Students Leave: The Economic Consequences For College Towns

Table of Contents
Reduced Spending Power & Decreased Revenue Streams
The departure of students significantly reduces the spending power within a college town, leading to decreased revenue streams across multiple sectors. This "summer slump" or post-graduation dip can have profound consequences.
Impact on Local Businesses
The most immediate impact is felt by local businesses heavily reliant on student patronage.
- Reduced foot traffic: Restaurants, bars, shops, and entertainment venues experience a noticeable drop in customers, leading to lower sales. This directly affects businesses specializing in affordable options popular with students, such as inexpensive eateries, bookstores, and printing services.
- Decreased demand: The demand for goods and services specifically tailored to students plummets. This includes everything from late-night pizza deliveries to campus-area convenience stores.
- Financial hardship: Lower sales revenue can force businesses to reduce staff, cut operating hours, or even face closure, impacting the local college town businesses and the wider student spending ecosystem. The resulting economic downturn can be substantial.
Impact on the Housing Market
The student population significantly influences the housing market in college towns. When students leave, this has cascading effects:
- Increased vacancy rates: Student housing units, including apartments and off-campus rentals, experience increased vacancy rates, directly impacting rental income for landlords.
- Decreased property values: In areas heavily reliant on student renters, property values may decrease due to the reduced demand. This impacts property owners and the overall student housing market.
- Reduced demand for services: The demand for property management services, maintenance, and other related services also declines, leading to further economic ripples. The impact on landlord income can be severe during these periods.
Impact on the Service Sector
The service sector, too, feels the pinch when students leave. The reduced demand affects various areas:
- Transportation services: Taxis, ride-sharing services, and even public transportation experience lower ridership, impacting their profitability.
- Healthcare services: Demand for healthcare services specifically catering to the student population (e.g., student health clinics) decreases significantly.
- Academic support services: Tutoring services, academic advising, and other student support services see a considerable drop in demand. The overall service industry impact is a tangible reflection of the reduced student presence.
Strategies for Mitigating Economic Downward Pressure
College towns can proactively implement strategies to lessen the blow of student departures and build more resilient economies.
Diversifying the Local Economy
Reducing reliance on student spending is key. This requires:
- Attracting diverse businesses: Focus on attracting businesses that cater to a wider demographic, not just students. This could include family-friendly restaurants, retail stores targeting a broader age range, and businesses offering services to the broader community. This boosts economic diversification.
- Promoting tourism: Developing and promoting local attractions, historical sites, and events can attract tourists and generate revenue throughout the year. Investing in tourism development can create a more stable economic base.
- Supporting local entrepreneurs: Fostering a supportive environment for local entrepreneurs and small businesses can create jobs and diversify the economic landscape. Providing resources and support for small business support is crucial.
Strengthening Community Partnerships
Collaboration is crucial to navigate the challenges.
- University-community partnerships: Strong partnerships between the university, local government, and businesses are essential to coordinate economic development initiatives.
- Graduate retention: Implementing programs to encourage graduates to stay and work in the town, as well as attracting young professionals, is crucial for maintaining a vibrant workforce and economy.
- Infrastructure development: Investing in infrastructure improvements (e.g., parks, recreational facilities, public transportation) enhances the overall appeal of the town and attracts residents and visitors alike, contributing to infrastructure development.
Adapting Business Models
Businesses need to adapt to the seasonal changes in demand.
- Seasonal adjustments: Businesses can offer alternative services or products during off-peak times to maintain revenue.
- Online sales: Expanding online sales and delivery options allows businesses to reach a wider customer base, mitigating the impact of reduced local foot traffic. This supports online business strategies.
- Cost-saving measures: Implementing cost-saving measures during periods of reduced demand can help businesses weather the leaner times. Strategic seasonal marketing can also help maintain customer engagement.
Long-Term Economic Planning and Sustainability
Long-term planning is essential for creating a resilient economy.
- Strategic planning: Proactive measures are essential to anticipate and mitigate the impact of seasonal fluctuations in the student population. This involves long-term economic planning.
- Sustainable economy: The goal is to build a sustainable economy that is not solely dependent on student spending. This requires diversification and investment in other sectors.
- Workforce development: Investing in education and skills development programs attracts and retains a skilled workforce beyond the student population, thus strengthening the sustainable economy and fostering workforce development.
Conclusion:
The economic consequences of student departures from college towns are far-reaching and impact multiple sectors. Understanding these impacts, implementing proactive strategies for diversification and collaboration, and embracing long-term planning are crucial for building resilient and sustainable communities. By focusing on attracting a wider demographic, improving infrastructure, and adapting business models, college towns can mitigate the negative effects of seasonal changes and ensure their long-term economic health and prosperity. Investing in strategies to lessen the effects of the college town economic impact should be a priority for the sustained success of these unique communities.

Featured Posts
-
 March 13 2025 Nyt Mini Crossword Complete Answers And Clues
May 21, 2025
March 13 2025 Nyt Mini Crossword Complete Answers And Clues
May 21, 2025 -
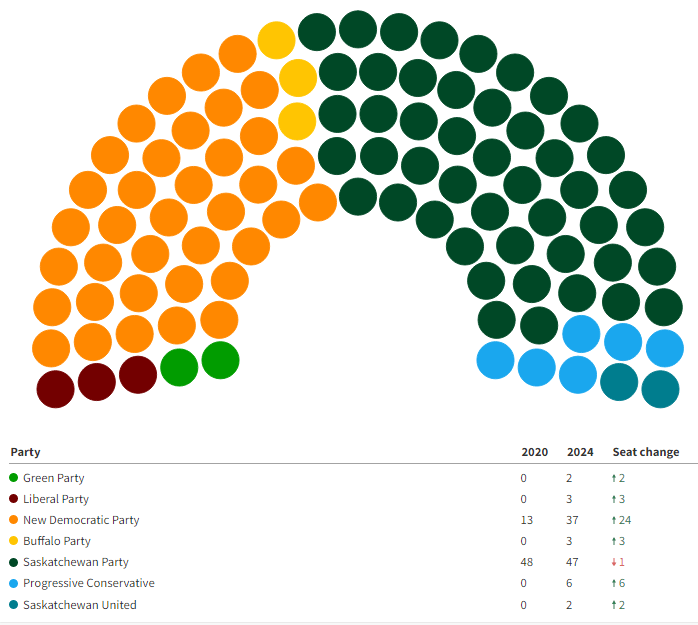 How The Federal Election Results Reshape Saskatchewans Political Future
May 21, 2025
How The Federal Election Results Reshape Saskatchewans Political Future
May 21, 2025 -
 Love Monster Exploring The Power Of Friendship And Self Acceptance
May 21, 2025
Love Monster Exploring The Power Of Friendship And Self Acceptance
May 21, 2025 -
 Tyler Bates Wwe Return When And Where To Watch
May 21, 2025
Tyler Bates Wwe Return When And Where To Watch
May 21, 2025 -
 Prica S Reddita Postaje Film Sa Sydney Sweeney
May 21, 2025
Prica S Reddita Postaje Film Sa Sydney Sweeney
May 21, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Iroiki Prokrisi Gia Tin Kroyz Azoyl Xari Ston Giakoymaki Telikos Champions League
May 21, 2025
Iroiki Prokrisi Gia Tin Kroyz Azoyl Xari Ston Giakoymaki Telikos Champions League
May 21, 2025 -
 Giakoymakis Sti Los Antzeles
May 21, 2025
Giakoymakis Sti Los Antzeles
May 21, 2025 -
 Metagrafi Giakoymaki I Los Antzeles Deixnei Endiaferon
May 21, 2025
Metagrafi Giakoymaki I Los Antzeles Deixnei Endiaferon
May 21, 2025 -
 Aston Villas Fa Cup Hopes Dashed By Rashfords Double For Manchester United
May 21, 2025
Aston Villas Fa Cup Hopes Dashed By Rashfords Double For Manchester United
May 21, 2025 -
 Los Antzeles Endiaferon Gia Ton Giakoymaki
May 21, 2025
Los Antzeles Endiaferon Gia Ton Giakoymaki
May 21, 2025
