WHO Reports New COVID-19 Variant Contributing To Increased Case Numbers
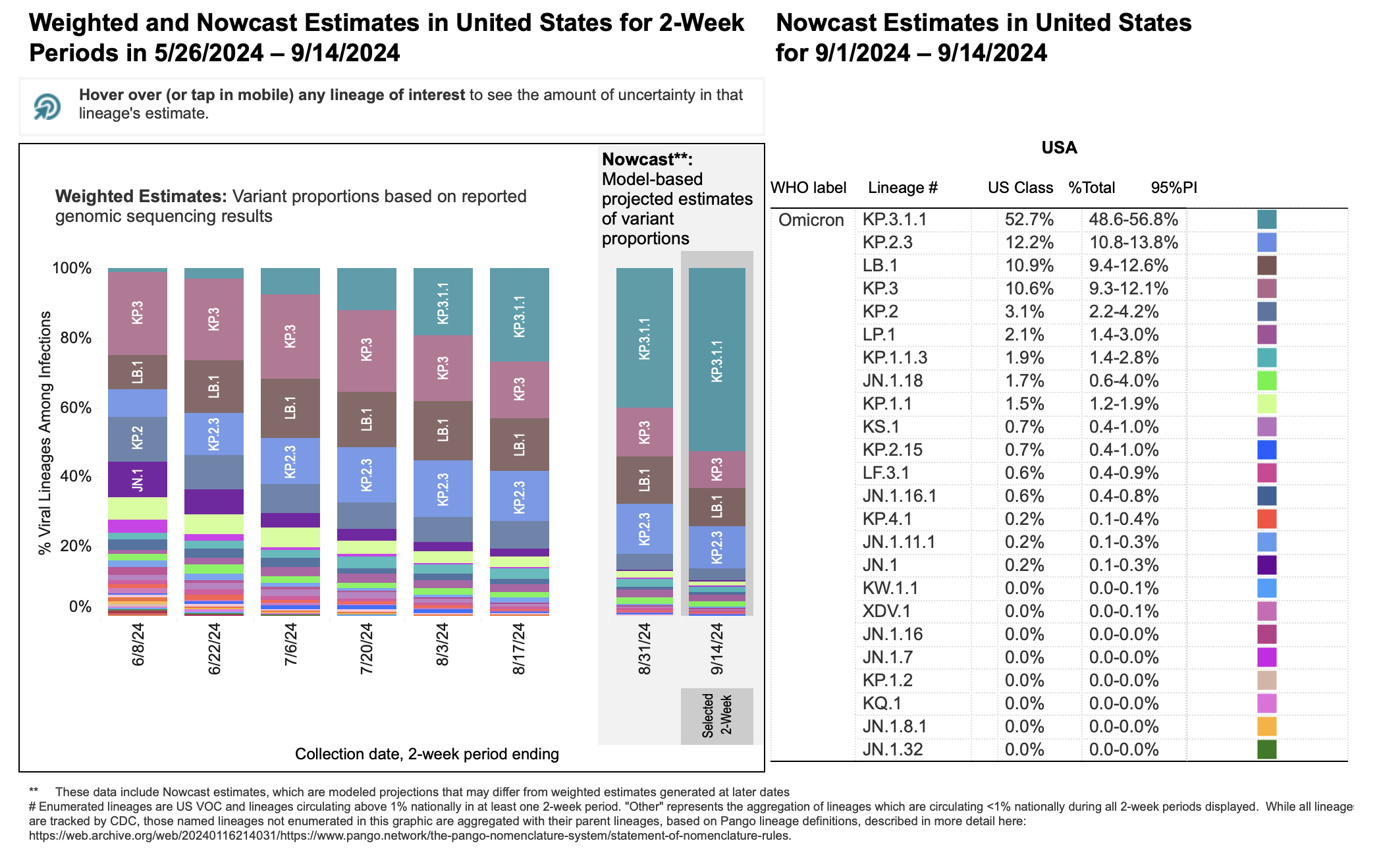
Table of Contents
Characteristics of the New COVID-19 Variant
While awaiting official naming from the WHO, let's refer to this new variant as "Variant X" for clarity. Preliminary data suggests Variant X possesses several key genetic mutations. These viral mutations are of particular concern, as they may affect its transmissibility rate, disease severity, and vaccine efficacy.
- Specific Mutation Details: Initial genomic sequencing indicates mutations in the spike protein, specifically in regions known to influence receptor binding and immune evasion. Further research is underway to fully characterize these changes.
- Impact on Existing Immunity: The mutations in Variant X raise concerns about its ability to evade both natural immunity acquired through previous infection and immunity conferred by existing vaccines. Early evidence suggests a potential reduction in vaccine effectiveness.
- Increased Contagiousness: Several studies show Variant X demonstrates a significantly higher transmissibility rate compared to previous dominant variants, leading to more rapid spread within communities.
Geographic Spread and Case Numbers
Variant X has been identified in several countries across multiple continents, raising concerns about its global spread. The geographic distribution currently appears to be centered around [insert specific regions/countries, cite sources like WHO or CDC], with rapidly increasing prevalence rates in these areas. We are seeing the formation of distinct infection clusters, highlighting the need for robust public health interventions.
- Country-Specific Data: [Insert data on infection rates from reputable sources for specific countries. Include charts and graphs if possible].
- Mapping the Spread: [Insert a map visually depicting the spread of Variant X. Cite the source of the map].
- Comparison to Previous Variants: The speed and extent of Variant X's spread outpace previous variants, emphasizing its heightened contagiousness.
Severity of Illness Caused by the New Variant
While early data suggests Variant X may be more transmissible, the severity of illness remains under investigation. Current hospitalization rates seem [higher/lower/similar] compared to previous variants, and mortality rate data is still being collected and analyzed. [Insert data and sources if available].
- Hospitalization Rates: [Insert data on hospitalization rates for Variant X infections, with a comparison to previous variants].
- Mortality Rates: [Insert data on mortality rates for Variant X infections, with a comparison to previous variants. If data is unavailable, state this clearly].
- Clinical Presentation: While some reports suggest a similar clinical presentation to previous variants, further research is needed to confirm this. Any differences in symptoms will be reported as they become available.
WHO Recommendations and Public Health Response
In response to the emergence of Variant X and the increasing case numbers, the WHO has issued several crucial recommendations to curb its spread. These public health measures focus on a multi-pronged approach to minimize transmission and protect vulnerable populations.
- Specific WHO Recommendations: These include renewed emphasis on virus surveillance, improved testing strategies, maintaining good hygiene practices, and increased vaccination rates. The WHO also strongly recommends the continued use of masks in indoor settings and social distancing in crowded areas.
- Governmental Responses: [Provide examples of governmental responses from different countries. Discuss measures such as travel restrictions, mask mandates, or public health campaigns].
- Importance of Monitoring: Continued monitoring and data collection are vital to understanding the long-term impact of Variant X and to inform future pandemic response strategies.
Impact on Existing Vaccines and Treatments
The effectiveness of existing COVID-19 vaccines and treatments against Variant X is a key area of focus. Studies are ongoing to assess vaccine effectiveness and therapeutic efficacy against this new variant.
- Vaccine Effectiveness: Preliminary data suggests a potential decrease in effectiveness of existing vaccines against Variant X, although more research is needed.
- Antiviral Treatment Effectiveness: The effectiveness of current antiviral treatments against Variant X is also being evaluated.
- Potential Need for Updates: Depending on the findings of these studies, modifications to existing vaccines or the development of new treatments may be necessary to maintain protection against this evolving virus.
Conclusion: Staying Informed About the New COVID-19 Variant
The emergence of Variant X, as reported by the WHO, highlights the continued threat posed by COVID-19 and the importance of staying informed about evolving variants. The increased transmissibility of this variant underscores the need for continued vigilance and adherence to public health guidelines. Following the WHO's recommendations, practicing good hygiene, and staying updated on the latest information are crucial steps in protecting ourselves and our communities. Remain vigilant, follow public health recommendations, and continue to seek updates on the evolving situation regarding the new COVID-19 variant and its impact on case numbers. For the latest information, visit the WHO website: [Insert link to WHO COVID-19 page].

Featured Posts
-
 Indian Wells 2024 Tsitsipas Triumphs Medvedev Advances
May 31, 2025
Indian Wells 2024 Tsitsipas Triumphs Medvedev Advances
May 31, 2025 -
 Glastonbury Festival Veterans One Essential Item To Save You Money
May 31, 2025
Glastonbury Festival Veterans One Essential Item To Save You Money
May 31, 2025 -
 Emerging Covid 19 Variant Who Investigating Global Case Spike
May 31, 2025
Emerging Covid 19 Variant Who Investigating Global Case Spike
May 31, 2025 -
 Friday Night Baseball Tigers Vs Twins Season Matchup
May 31, 2025
Friday Night Baseball Tigers Vs Twins Season Matchup
May 31, 2025 -
 Bispecific Myeloid Cell Engager Sanofis New Weapon In Immunology
May 31, 2025
Bispecific Myeloid Cell Engager Sanofis New Weapon In Immunology
May 31, 2025
