Why Some Forecasts Omit Excessive Heat Warnings
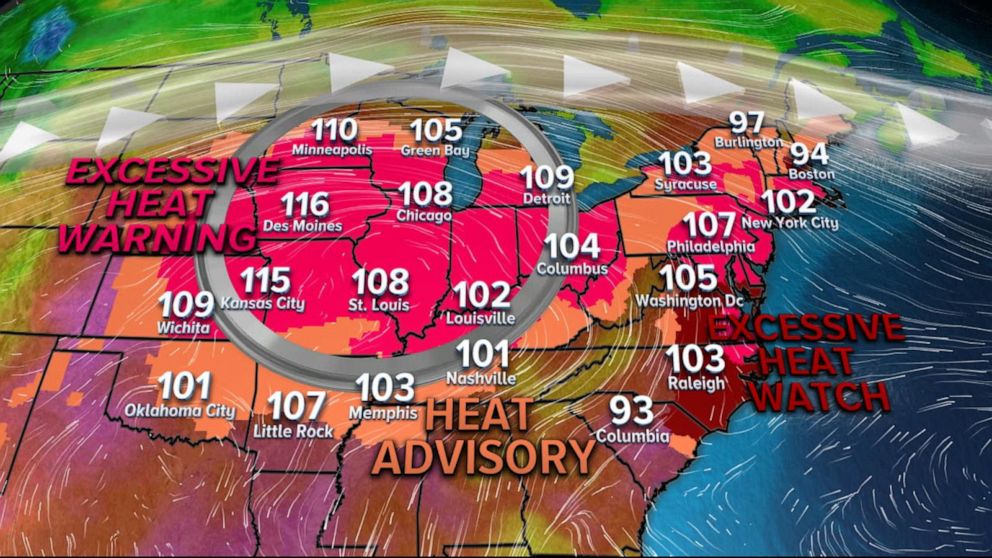
Table of Contents
Data Limitations and Predictive Modeling Challenges
Accurately predicting extreme weather events requires robust data and sophisticated models. However, when it comes to excessive heat warnings, significant challenges exist. Limitations in historical weather data, particularly for extreme heat events, directly affect the accuracy of predictive models. While temperature records exist for many areas, comprehensive data on the intensity and duration of past heat waves, especially in certain regions, remains insufficient.
This lack of data makes it difficult to train models to accurately forecast the precise onset, duration, and intensity of future heatwaves. Further complicating the issue are challenges in incorporating localized microclimates into these models. Urban heat islands, for example, can significantly amplify temperatures compared to surrounding rural areas. Failing to account for these localized effects can lead to inaccurate heat forecasts and insufficient excessive heat warnings.
- Insufficient historical data on extreme heat events in certain regions: Many developing nations lack long-term, reliable weather data.
- Challenges in incorporating localized microclimates into predictive models: Urban heat islands and other microclimatic variations significantly impact local temperatures.
- Limitations of current computational power to process vast amounts of data effectively: Running high-resolution models that account for all variables requires significant computing resources.
- Uncertainty related to climate change impacts on heat wave frequency and severity: Climate change is intensifying heat waves, making accurate predictions even more challenging.
Thresholds and Criteria for Issuing Excessive Heat Warnings
Defining "excessive heat" is not straightforward. The criteria for issuing excessive heat warnings vary considerably among different meteorological agencies globally. This lack of standardization leads to inconsistencies in warning issuance, potentially leaving some communities vulnerable to extreme heat without sufficient warning.
Different agencies utilize varying temperature thresholds, often considering factors like duration and the heat index—a combination of temperature and humidity. The heat index provides a more accurate reflection of how hot it actually feels, accounting for the added stress of humidity on the human body. Furthermore, the definition of "excessive heat" should also consider vulnerable populations, such as the elderly, infants, and individuals with pre-existing health conditions, who are more susceptible to heat-related illnesses. Failing to account for these sensitivities can result in inadequate or untimely excessive heat warnings.
- Variations in temperature thresholds used by different weather agencies: What constitutes an "excessive heat warning" varies greatly depending on the location and agency issuing the warning.
- The role of heat index (combining temperature and humidity) in warning issuance: The heat index offers a more realistic representation of the perceived temperature, but its use isn't consistent across all agencies.
- The importance of considering vulnerable populations in defining thresholds: Thresholds should account for the increased risk faced by sensitive groups.
Resource Constraints and Prioritization of Other Weather Events
Meteorological agencies often face resource limitations, including staffing and technological capabilities. These constraints can impact the prioritization of weather warnings, potentially leading to underemphasis on excessive heat warnings. When severe weather events like hurricanes or tornadoes occur simultaneously with periods of extreme heat, the more immediately life-threatening events may naturally receive greater attention and resource allocation.
This prioritization is understandable, but it can unintentionally diminish the emphasis on the insidious dangers of prolonged extreme heat. Effectively communicating about multiple simultaneous weather hazards also presents a challenge, demanding clear and concise messaging that avoids information overload.
- Limited staffing levels in meteorological agencies: Understaffing can lead to delays in processing data and issuing warnings.
- Allocation of resources towards more immediately life-threatening events: Hurricanes and tornadoes often draw more immediate attention and resources than heat waves.
- The challenge of communicating effectively about multiple simultaneous weather hazards: Getting the right information to the right people at the right time is crucial during multiple weather events.
Communication Challenges and Public Awareness
Effective communication is essential for ensuring public understanding and response to excessive heat warnings. However, factors like information overload and varying media coverage can hinder public awareness. People might overlook or dismiss heat warnings if they are not presented clearly, concisely, and accessibly.
Using diverse communication channels—including social media, traditional media, and community outreach programs—is crucial for reaching a wide audience. Public education campaigns play a vital role in increasing awareness of heat-related risks and promoting preventative measures. Improving public understanding of the dangers of extreme heat and promoting proactive behavioral changes are key to mitigating its impact.
- The need for clear, concise, and accessible communication of heat warnings: Warnings should be easy to understand and avoid technical jargon.
- The importance of using multiple communication channels (e.g., social media, traditional media): Reaching a broad audience requires a multi-pronged approach.
- The role of public education campaigns in increasing awareness of heat-related risks: Educating the public about heatstroke prevention and preparedness is vital.
Conclusion: Understanding the Omission of Excessive Heat Warnings
Several interconnected factors contribute to the omission or underemphasis of excessive heat warnings in some forecasts. These include limitations in historical weather data and predictive modeling capabilities, inconsistencies in the criteria for issuing warnings, resource constraints leading to prioritization of other events, and challenges in effectively communicating the risks to the public.
Accurate and timely excessive heat warnings are crucial for public safety and preparedness. We must advocate for improved weather forecasting resources, better communication strategies, and increased public awareness to protect communities from the dangers of extreme heat. Contact your local meteorological agency to learn more about their excessive heat warning systems and stay informed and prepared during periods of extreme heat. Understanding the limitations and challenges associated with heat wave forecasting is the first step towards improving preparedness and saving lives.

Featured Posts
-
 Ilaiyaraajas Musical Triumph Rajinikanths Acknowledgment
May 30, 2025
Ilaiyaraajas Musical Triumph Rajinikanths Acknowledgment
May 30, 2025 -
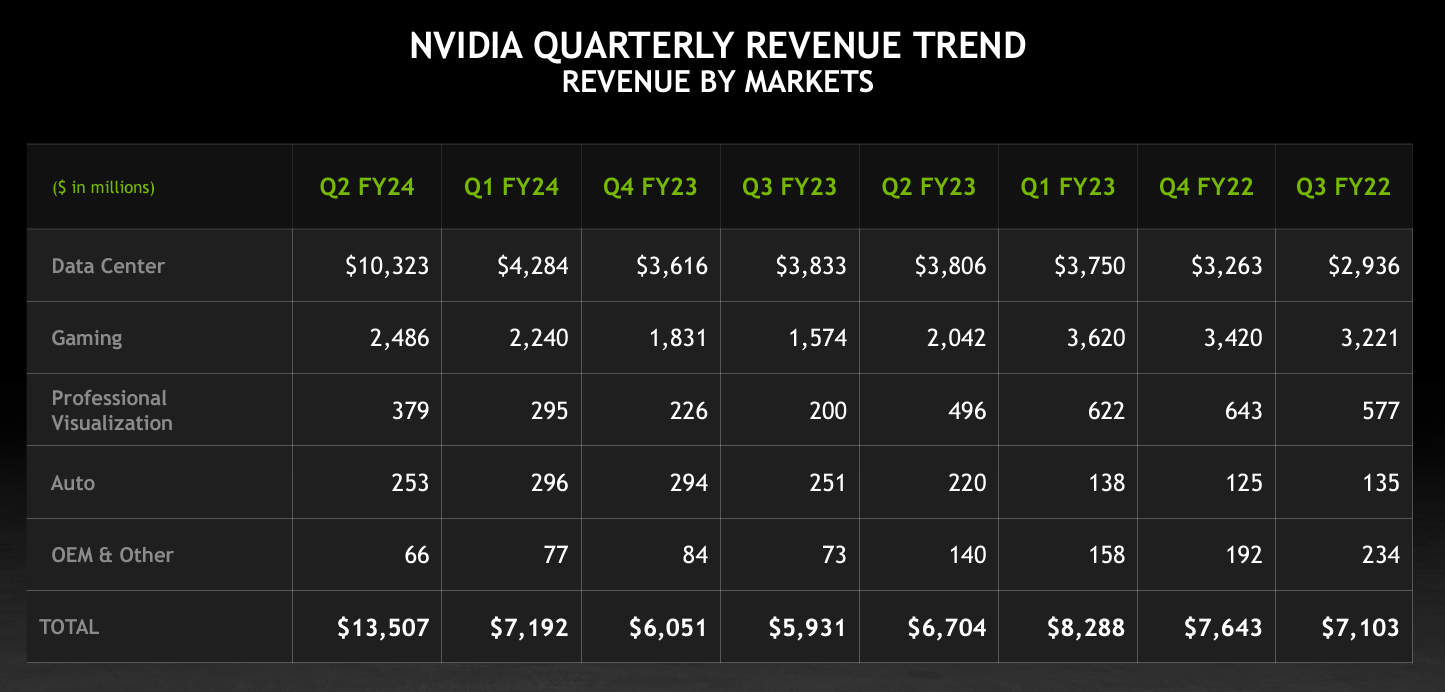 Solid Corporate Earnings A Temporary Trend Analysis And Forecast
May 30, 2025
Solid Corporate Earnings A Temporary Trend Analysis And Forecast
May 30, 2025 -
 Listen Now Jacob Alons Fairy In A Bottle
May 30, 2025
Listen Now Jacob Alons Fairy In A Bottle
May 30, 2025 -
 Torwart Garteig Verlaesst Ingolstadt Augsburg Sichert Sich Seine Dienste
May 30, 2025
Torwart Garteig Verlaesst Ingolstadt Augsburg Sichert Sich Seine Dienste
May 30, 2025 -
 Kasus Suspek Campak Di Pohuwato Meningkat Dinkes Gorontalo Soroti Rendahnya Imunisasi Anak
May 30, 2025
Kasus Suspek Campak Di Pohuwato Meningkat Dinkes Gorontalo Soroti Rendahnya Imunisasi Anak
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Grigor Dimitrov Vliyanieto Na Kontuziyata Vrkhu Karierata Mu
May 31, 2025
Grigor Dimitrov Vliyanieto Na Kontuziyata Vrkhu Karierata Mu
May 31, 2025 -
 Kontuziyata Na Grigor Dimitrov Aktualna Informatsiya I Analiz
May 31, 2025
Kontuziyata Na Grigor Dimitrov Aktualna Informatsiya I Analiz
May 31, 2025 -
 Trumps Uncertainty What Made Him Question Elon Musk
May 31, 2025
Trumps Uncertainty What Made Him Question Elon Musk
May 31, 2025 -
 Uncertainty And The End Trumps Doubts About Elon Before The Break
May 31, 2025
Uncertainty And The End Trumps Doubts About Elon Before The Break
May 31, 2025 -
 Everything Revealed In The Star Trek Strange New Worlds Season 3 Teaser
May 31, 2025
Everything Revealed In The Star Trek Strange New Worlds Season 3 Teaser
May 31, 2025
